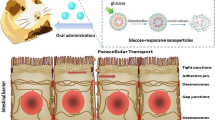
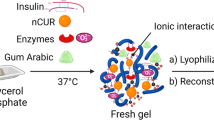
Abstract
Glucose-responsive closed-loop insulin delivery systems represent a promising treatment strategy for diabetes, but current systems generally cannot achieve long-term effects. In this study, we designed an erythrocyte-biomimetic glucose-responsive system (EGRS) by coupling glucose-responsive nanoparticles (GRNs) to red blood cells; these nanoparticles exhibited the dual functions of glucose-responsiveness and persistent presence in circulation. GRNs are generated by encapsulating with insulin through ion crosslinking, followed by coloading with glucose oxidase (GOx) and catalase (CAT), a process that endows the nanoparticles with glucose-responsiveness. Simultaneously, the GRNs are coupled with red blood cells to camouflage them from the immune system, therefore, these erythrocyte-coupled GRNs can circulate in the blood for a long time. Under conditions of hyperglycemia, GOx acts on blood glucose to produce gluconic acid, which causes the rupture of GRNs and efficient release of insulin. Conversely, insulin is only released at the basic rate during hypoglycemia. Thus, EGRS can efficiently and continuously respond to hyperglycemia to maintain blood glucose levels within the normal range.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberti, K. G. M. M.; Zimmet, P. Z. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet. Med. 1998, 15, 539–553.
Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A. A.; Ogurtsova, K. et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843.
Laakso, M. Hyperglycemia and cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 1999, 48, 937–942.
Garyu, J. W.; Meffre, E.; Cotsapas, C.; Herold, K. C. Progress and challenges for treating Type 1 diabetes. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 71, 1–9.
Wang, J. Q.; Wang, Z. J.; Yu, J. C.; Kahkoska, A. R.; Buse, J. B.; Gu, Z. Glucose-responsive insulin and delivery systems: Innovation and translation. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1902004.
Yu, J. C.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Yan, J. J.; Kahkoska, A. R.; Gu, Z. Advances in bioresponsive closed-loop drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 544, 350–357.
Bratlie, K. M.; York, R. L.; Invernale, M. A.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D. G. Materials for diabetes therapeutics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 1, 267–284.
Wilson, R.; Turner, A. P. F. Glucose oxidase: An ideal enzyme. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1992, 7, 165–185.
Huggett, A. S. G.; Nixon, D. A. Use of glucose oxidase, peroxidase, and O-dianisidine in determination of blood and urinary glucose. Lancet 1957, 270, 368–370.
Bankar, S. B.; Bule, M. V.; Singhal, R. S.; Ananthanarayan, L. Glucose oxidase—an overview. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 489–501.
Luo, F. Q.; Chen, G. J.; Xu, W.; Zhou, D. J.; Li, J. X.; Huang, Y. C.; Lin, R.; Gu, Z.; Du, J. Z. Microneedle-array patch with pH-sensitive formulation for glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 2689–2696.
Qi, W.; Yan, X. H.; Fei, J. B.; Wang, A. H.; Cui, Y.; Li, J. B. Triggered release of insulin from glucose-sensitive enzyme multilayer shells. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2799–2806.
Yu, J. C.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Wang, J. Q.; Wen, D.; Kahkoska, A. R.; Buse, J. B.; Gu, Z. Glucose-responsive oral insulin delivery for postprandial glycemic regulation. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 1539–1545.
Fu, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, L. Y.; Zhu, B. Y.; Qu, M. K.; Yang, L. Q.; Sun, X.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Z. R.; Lin, Q. et al. Erythrocyte-membrane-camouflaged nanoplatform for intravenous glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Ad. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802250.
Biagiotti, S.; Paoletti, M. F.; Fraternale, A.; Rossi, L.; Magnani, M. Drug delivery by red blood cells. IUBMB Life 2011, 63, 621–631.
Bush, L. M.; Healy, C. P.; Javdan, S. B.; Emmons, J. C.; Deans, T. L. Biological cells as therapeutic delivery vehicles. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 42, 106–118.
Suk, J. S.; Xu, Q. G.; Kim, N.; Hanes, J.; Ensign, L. M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 28–51.
Chambers, E.; Mitragotri, S. Prolonged circulation of large polymeric nanoparticles by non-covalent adsorption on erythrocytes. J. Control. Release 2004, 100, 111–119.
Xia, D. L.; He, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K. Y.; Zuo, H. Q.; Gu, H. Y.; Xu, P. P.; Hu, Y. Ultrafast glucose-responsive, high loading capacity erythrocyte to self-regulate the release of insulin. Acta Biomater. 2018, 69, 301–312.
Wang, C.; Ye, Y. Q.; Sun, W. J.; Yu, J. C.; Wang, J. Q.; Lawrence, D. S.; Buse, J. B.; Gu, Z. Red blood cells for glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606617.
Wang, Y. L.; Khan, A.; Liu, Y. X.; Feng, J.; Dai, L.; Wang, G. H.; Alam, N.; Tong, L.; Ni, Y. H. Chitosan oligosaccharide-based dual pH responsive nano-micelles for targeted delivery of hydrophobic drugs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115061.
Motiei, M.; Sedlařík, V.; Lucia, L. A.; Fei, H. J.; Münster, L. Stabilization of chitosan-based polyelectrolyte nanoparticle cargo delivery biomaterials by a multiple ionic cross-linking strategy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 231, 115709.
Yao, H.; Wynendaele, E.; Xu, X. L.; Kosgei, A.; De Spiegeleer, B. Circular dichroism in functional quality evaluation of medicines. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 147, 50–64.
Di, J. W.; Gao, X.; Du, Y. M.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Zheng, A. P. Size, shape, charge and “stealthy” surface: Carrier properties affect the drug circulation time in vivo. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 444–458.
Poon, W.; Zhang, Y. N.; Ouyang, B.; Kingston, B. R.; Wu, J. L. Y.; Wilhelm, S.; Chan, W. C. W. Elimination pathways of nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 5785–5798.
Andrikopoulos, S.; Blair, A. R.; Deluca, N.; Fam, B. C.; Proietto, J. Evaluating the glucose tolerance test in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 295, E1323–E1332.
Paes, T.; Rolim, L. C.; Filho, C. S.; De Sa, J. R.; Dib, S. A. Awareness of hypoglycemia and spectral analysis of heart rate variability in type 1 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complications 2020, 34, 107617.
Chetan, M. R.; Thrower, S. L.; Narendran, P. What is type 1 diabetes? Medicine 2019, 47, 5–9.
Berenson, D. F.; Weiss, A. R.; Wan, Z. L.; Weiss, M. A. Insulin analogs for the treatment of diabetes mellitus: Therapeutic applications of protein engineering. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2011, 1243, E40–E54.
Tékus, V.; Horváth, Á. I.; Csekő, K.; Szabadfi, K.; Kovács-Valasek, A.; Dányádi, B.; Deres, L.; Halmosi, R.; Sághy, É.; Varga, Z. V. et al. Protective effects of the novel amine-oxidase inhibitor multitarget drug SZV 1287 on streptozotocin-induced beta cell damage and diabetic complications in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 134, 111105.
Raghav, A.; Ahmad, J. Glycated serum albumin: A potential disease marker and an intermediate index of diabetes control. Diabetes Metab. Syndr.:Clin. Res. Rev. 2014, 8, 245–251.
Giri, B.; Dey, S.; Das, T.; Sarkar, M.; Banerjee, J.; Dash, S. K. Chronic hyperglycemia mediated physiological alteration and metabolic distortion leads to organ dysfunction, infection, cancer progression and other pathophysiological consequences: An update on glucose toxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 306–328.
Shawahna, R.; Shanti, Y.; Al Zabadi, H.; Sharabati, M.; Alawneh, A.; Shaqu, R.; Taha, I.; Bustami, A. Prevalence and association of clinical characteristics and biochemical factors with complications of diabetes mellitus in Palestinians treated in primary healthcare practice. Diabetes Metab. Syndr.:Clin. Res. Rev. 2018, 12, 693–704.
Jayapandian, C. P.; Chen, Y. J.; Janowczyk, A. R.; Palmer, M. B.; Cassol, C. A.; Sekulic, M.; Hodgin, J. B.; Zee, J.; Hewitt, S. M.; O’Toole, J. et al. Development and evaluation of deep learning-based segmentation of histologic structures in the kidney cortex with multiple histologic stains. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, 86–101.
Mitra, M. S.; DeMarco, S.; Holub, B.; Thiruneelakantapillai, L.; Thackaberry, E. A. Development of peptide therapeutics: A nonclinical safety assessment perspective. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 117, 104766.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Regional Innovation and Development Joint Fund (No. U20A20411), the National Science Fund for Excellent Young Scholars (No. 82022070).
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Ethics Committee of Sichuan University (No. SYXK2013-113).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Xu, Y., Li, Y. et al. Glucose-responsive erythrocyte-bound nanoparticles for continuously modulated insulin release. Nano Res. 15, 5205–5215 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4105-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4105-0