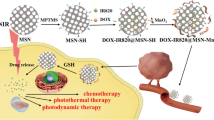
Abstract
Multimodal combinatorial therapy merges different modes of therapies in one platform, which can overcome several clinical challenges such as premature drug loss during blood circulation and significantly improve treatment efficiency. Here we report a combinatorial therapy nanoplatform that enables dual photothermal therapy and pH-stimulus-responsive chemotherapy. By super-assembly of mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN) with metal-phenolic networks (MPN), anti-cancer drugs can be loaded in the MSN matrix, while the outer MPN coating allows dual photothermal and pH-responsive properties. Upon near-infrared light irradiation, the MSN@MPN nanoplatform exhibits excellent photothermal effect, and demonstrates outstanding pH-triggered drug release property. In vitro cell experiments suggest the MSN@MPN system exhibits superior biocompatibility and can effectively kill tumor cells after loading anti-cancer drugs. Consequently, the MSN@MPN system shows promising prospects in clinical application for tumor therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, Y. L.; Ai, K. L.; Liu, J. H.; Deng, M.; He, Y. Y.; Lu, L. H. Dopamine-melanin colloidal nanospheres: An efficient near-infrared photothermal therapeutic agent for in vivo cancer therapy. Adv. Mater.2013, 25, 1353–1359.
Fan, J. X.; Zheng, D. W.; Mei, W. W.; Chen, S.; Chen, S. Y.; Cheng, S. X.; Zhang, X. Z. A metal-polyphenol network coated nano-theranostic system for metastatic tumor treatments. Small2017, 13, 1702714.
Jiang, Y. J.; Liu, S. J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. C.; He, H.; Dai, J. T.; Jiang, T.; Ji, W. H.; Geng, D. Y.; Elzatahry, A. A. et al. Magnetic mesoporous nanospheres anchored with LyP-1 as an efficient pancreatic cancer probe. Biomaterials2017, 115, 9–18.
Yang, J. P.; Shen, D. K.; Zhou, L.; Li, W.; Li, X. M.; Yao, C.; Wang, R.; El-Toni, A. M.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, D. Y. Spatially confined fabrication of core-shell gold nanocages@mesoporous silica for near-infrared controlled photothermal drug release. Chem. Mater.2013, 25, 3030–3037.
Chen, W. S.; Ouyang, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, M.; Zeng, K.; Sheng, J. P.; Liu, Z. J.; Han, Y. J.; Wang, L. Q.; Li, J. et al. Black phosphorus nanosheet-based drug delivery system for synergistic photodynamic/photothermal/chemotherapy of cancer. Adv. Mater.2017, 29, 1603864.
Liu, Y.; Yin, J. J.; Nie, Z. H. Harnessing the collective properties of nanoparticle ensembles for cancer theranostics. Nano Res.2014, 7, 1719–1730.
Chen, G. J.; Jaskula-Sztul, R.; Esquibel, C. R.; Lou, I.; Zheng, Q. F.; Dammalapati, A.; Harrison, A.; Eliceiri, K. W.; Tang, W. P.; Chen, H. et al. Neuroendocrine tumor-targeted upconversion nanoparticle-based micelles for simultaneous NIR-controlled combination chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy, and fluorescence imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater.2017, 27, 1604671.
Lin, L. S.; Song, J. B.; Yang, H. H.; Chen, X. Y. Yolk-shell nanostructures: Design, synthesis, and biomedical applications. Adv. Mater.2018, 30, 1704639.
Zeng, J. Y.; Zhang, M. K.; Peng, M. Y.; Gong, D.; Zhang, X. Z. Porphyrinic metal-organic frameworks coated gold nanorods as a versatile nanoplatform for combined photodynamic/photothermal/chemotherapy of tumor. Adv. Funct. Mater.2018, 28, 1705451.
Poulose, A. C.; Veeranarayanan, S.; Mohamed, M. S.; Nagaoka, Y.; Aburto, R. R.; Mitcham, T.; Ajayan, P. M.; Bouchard, R. R.; Sakamoto, Y.; Yoshida, Y. et al. Multi-stimuli responsive Cu2S nano-crystals as trimodal imaging and synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy agents. Nanoscale2015, 7, 8378–8388.
Fang, S.; Lin, J.; Li, C. X.; Huang, P.; Hou, W. X.; Zhang, C. L.; Liu, J. J.; Huang, S. S.; Luo, Y. X.; Fan, W. P. et al. Dual-stimuli responsive nanotheranostics for multimodal imaging guided trimodal synergistic therapy. Small2017, 13, 1602580.
Gulzar, A.; Xu, J. T.; Xu, L. G.; Yang, P. P.; He, F.; Yang, D.; An, G. H.; Ansari, M. B. Redox-responsive UCNPs-DPA conjugated NGO-PEG-BPEI-DOX for imaging-guided PTT and chemotherapy for cancer treatment. Dalton Trans.2018, 47, 3921–3930.
Ping, Y.; Guo, J. L.; Ejima, H.; Chen, X.; Richardson, J. J.; Sun, H. L.; Caruso, F. pH-responsive capsules engineered from metal-phenolic networks for anticancer drug delivery. Small2015, 11, 2032–2036.
Hu, C. L.; Huang, P.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, Z. B.; Wang, X. L. A facile strategy to prepare an enzyme-responsive mussel mimetic coating for drug delivery based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Langmuir2017, 33, 5511–5518.
Zhu, X. L.; Huang, H. Q.; Zhang, Y. J.; Zhang, H. J.; Hou, L.; Zhang, Z. Z. Cit/CuS@Fe3O4-based and enzyme-responsive magnetic nano-particles for tumor chemotherapy, photothermal, and photodynamic therapy. J. Biomater. Appl.2017, 31, 1010–1025.
Su, Y.; Ojo, O. F.; Tsengam, I. K. M.; He, J. B.; McPherson, G. L.; John, V. T.; Valla, J. A. Thermoresponsive coatings on hollow particles with mesoporous shells serve as stimuli-responsive gates to species encapsulation and release. Langmuir2018, 34, 14608–14616.
Bathfield, M.; Reboul, J.; Cacciaguerra, T.; Lacroix-Desmazes, P.; Gérardin, C. Thermosensitive and drug-loaded ordered mesoporous silica: A direct and effective synthesis using PEO-b-PNIPAM block copolymers. Chem. Mater.2016, 28, 3374–3384.
Park, K.; Park, S. S.; Yun, Y. H.; Ha, C. S. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles functionalized with a redox-responsive biopolymer. J. Porous Mater.2017, 24, 1215–1225.
Li, C. X.; Zhang, Y. F.; Li, Z. M.; Mei, E. C.; Lin, J.; Li, F.; Chen, C. G.; Qing, X. L.; Hou, L. Y.; Xiong, L. L. et al. Light-responsive biodegradable nanorattles for cancer theranostics. Adv. Mater.2018, 30, 1706150.
Giri, S.; Trewyn, B. G.; Stellmaker, M. P.; Lin, V. S. Y. Stimuli-responsive controlled-release delivery system based on mesoporous silica nanorods capped with magnetic nanoparticles. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed.2005, 44, 5038–5044.
Li, S.; Wu, W.; Xiu, K. M.; Xu, F. J.; Li, Z. M.; Li, J. S. Doxorubicin loaded pH-responsive micelles capable of rapid intracellular drug release for potential tumor therapy. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol.2014, 10, 1480–1489.
Chen, T. C.; Wu, W.; Xiao, H.; Chen, Y. X.; Chen, M.; Li, J. S. Intelligent drug delivery system based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles coated with an ultra-pH-sensitive gatekeeper and poly(ethylene glycol). ACS Macro Lett.2016, 5, 55–58.
Wang, Z. T.; Huang, P.; Jacobson, O.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. J.; Lin, L. S.; Lin, J.; Lu, N.; Zhang, H. M.; Tian, R. et al. Biomineralization-inspired synthesis of copper sulfide-ferritin nanocages as cancer theranostics. ACS Nano2016, 10, 3453–3460.
Lin, J.; Wang, M.; Hu, H.; Yang, X. Y.; Wen, B.; Wang, Z. T.; Jacobson, O.; Song, J. B.; Zhang, G. F.; Niu, G. et al. Multimodal-imaging-guided cancer phototherapy by versatile biomimetic theranostics with UV and γ-irradiation protection. Adv. Mater.2016, 28, 3273–3279.
Wang, D. D.; Dong, H. F.; Li, M.; Cao, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, K.; Dai, W. H.; Wang, C. T.; Zhang, X. J. Erythrocyte-cancer hybrid membrane camouflaged hollow copper sulfide nanoparticles for prolonged circulation life and homotypic-targeting photothermal/chemotherapy of melanoma. ACS Nano2018, 12, 5241–5252.
Liu, Y.; Zhen, W. Y.; Jin, L. H.; Zhang, S. T.; Sun, G. Y.; Zhang, T. Q.; Xu, X.; Song, S. Y.; Wang, Y. H.; Liu, J. H. et al. All-in-one theranostic nanoagent with enhanced reactive oxygen species generation and modulating tumor microenvironment ability for effective tumor eradication. ACS Nano2018, 12, 4886–4893.
Meng, Z. Q.; Chao, Y.; Zhou, X. F.; Liang, C.; Liu, J. J.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, L.; Yang, K.; Pan, W.; Zhu, M. F. et al. Near-infrared-triggered in situ gelation system for repeatedly enhanced photothermal brachytherapy with a single dose. ACS Nano2018, 12, 9412–9422.
Shi, D. L.; Cho, H. S.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H.; Gu, H. C.; Lian, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, G. K.; Huth, C.; Wang, L. M. et al. Fluorescent polystyrene-Fe3O4 composite nanospheres for in vivo imaging and hyperthermia. Adv. Mater.2009, 21, 2170–2173.
Yoo, D.; Jeong, H.; Noh, S. H.; Lee, J. H.; Cheon, J. Magnetically triggered dual functional nanoparticles for resistance-free apoptotic hyperthermia. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed.2013, 52, 13047–13051.
Ding, Q.; Liu, D. F.; Guo, D. W.; Yang, F.; Pang, X. Y.; Che, R C.; Zhou, N. Z.; Xie, J.; Sun, J. F.; Huang, Z. H. et al. Shape-controlled fabrication of magnetite silver hybrid nanoparticles with high performance magnetic hyperthermia. Biomaterials2017, 124, 35–46.
Wang, C.; Sun, W. J.; Wright, G.; Wang, A. Z.; Gu, Z. Inflammation-triggered cancer immunotherapy by programmed delivery of CpG and anti-PD1 antibody. Adv. Mater.2016, 28, 8912–8920.
Oberli, M. A.; Reichmuth, A. M.; Dorkin, J. R.; Mitchell, M. J.; Fenton, O. S.; Jaklenec, A.; Anderson, D. G.; Langer, R.; Blankschtein, D. Lipid nanoparticle assisted mRNA delivery for potent cancer immunotherapy. NanoLett.2017, 17, 1326–1335.
Yu, G. T.; Rao, L.; Wu, H.; Yang, L. L.; Bu, L. L.; Deng, W. W.; Wu, L.; Nan, X. L.; Zhang, W. F.; Zhao, X. Z. et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cell membrane-coated magnetic nanoparticles for cancer theranostics by inducing macrophage polarization and synergizing immunogenic cell death. Adv. Funct. Mater.2018, 28, 1801389.
Phuengkham, H.; Song, C.; Um, S. H.; Lim, Y. T. Implantable synthetic immune niche for spatiotemporal modulation of tumor-derived immunosuppression and systemic antitumor immunity: Postoperative immunotherapy. Adv. Mater.2018, 30, 1706719.
Dong, Q.; Wang, X. W.; Hu, X. X.; Xiao, L. Q.; Zhang, L.; Song, L. J.; Xu, M. L.; Zou, Y. X.; Chen, L.; Chen, Z. et al. Simultaneous application of photothermal therapy and an anti-inflammatory prodrug using pyrene-aspirin-loaded gold nanorod graphitic nanocapsules. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed.2018, 57, 177–181.
Chen, S.; Lei, Q.; Qiu, W. X.; Liu, L. H.; Zheng, D. W.; Fan, J. X.; Rong, L.; Sun, Y. X.; Zhang, X. Z. Mitochondria-targeting “Nanoheater” for enhanced photothermal/chemo-therapy. Biomaterials2017, 117, 92–104.
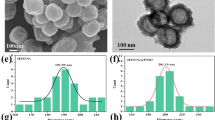
Shen, D. K.; Yang, J. P.; Li, X. M.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, R. Y.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, D. Y. Biphase stratification approach to three-dimensional dendritic biodegradable mesoporous silica nanospheres. Nano Lett.2014, 14, 923–932.
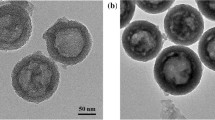
Chen, Y.; Chen, H. R.; Shi, J. L. In vivo bio-safety evaluations and diagnostic/therapeutic applications of chemically designed mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Adv. Mater.2013, 25, 3144–3176.
Luo, Z.; Hu, Y.; Cai, K. Y.; Ding, X. W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M. H.; Ma, X.; Zhang, B. L.; Zeng, Y. F.; Li, P. Z. et al Intracellular redox-activated anticancer drug delivery by functionalized hollow mesoporous silica nanoreservoirs with tumor specificity. Biomaterials2014, 35, 7951–7962.
Schrand, A. M.; Schlager, J. J.; Dai, L. M.; Hussain, S. M. Preparation of cells for assessing ultrastructural localization of nanoparticles with transmission electron microscopy. Nat. Protoc.2010, 5, 744–757.
Rahim, M. A.; Ejima, H.; Cho, K. L.; Kempe, K.; Müllner, M.; Best, J. P.; Caruso, F. Coordination-driven multistep assembly of metal-polyphenol films and capsules. Chem. Mater.2014, 26, 1645–1653.
Ozawa, H.; Haga, M. A. Soft nano-wrapping on graphene oxide by using metal-organic network films composed of tannic acid and Fe ions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.2015, 17, 8609–8613.
Ejima, H.; Richardson, J. J.; Liang, K.; Best, J. P.; van Koeverden, M. P.; Such, G. K.; Cui, J. W.; Caruso, F. One-step assembly of coordination complexes for versatile film and particle engineering. Science2013, 341, 154–157.
Guo, J. L.; Ping, Y.; Ejima, H.; Alt, K.; Meissner, M.; Richardson, J. J.; Yan, Y.; Peter, K.; von Elverfeldt, D.; Hagemeyer, C. E. et al. Engineering multifunctional capsules through the assembly of metal-phenolic networks. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed.2014, 53, 5546–5551.
Chen, W.; Zhong, P.; Meng, F. H.; Cheng, R.; Deng, C.; Feijen, J.; Zhong, Z. Y. Redox and pH-responsive degradable micelles for dually activated intracellular anticancer drug release. J. Control. Release2013, 169, 171–179.
Gerweck, L. E.; Seetharaman, K. Cellular pH gradient in tumor versus normal tissue: Potential exploitation for the treatment of cancer. Cancer Res.1996, 56, 1194–1198.
Fan, J. X.; Zheng, D. W.; Rong, L.; Zhu, J. Y.; Hong, S.; Li, C.; Xu, Z. S.; Cheng, S. X.; Zhang, X. Z. Targeting epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Metal organic network nano-complexes for preventing tumor metastasis. Biomaterials2017, 139, 116–126.
Roper, D. K.; Ahn, W.; Hoepfner, M. Microscale heat transfer transduced by surface plasmon resonant gold nanoparticles. J. Chem. Phys. C2007, 111, 3636–3641.
Li, B.; Wang, Q.; Zou, R. J.; Liu, X. J.; Xu, K. B.; Li, W. Y.; Hu, J. Q. Cu7.2S4 nanocrystals: A novel photothermal agent with a 56.7% photothermal conversion efficiency for photothermal therapy of cancer cells. Nanoscale2014, 6, 3274–3282.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Nos. 2019YFC1604600, 2017YFA0206901, 2017YFA0206900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21705027, 21974029, and 81830052), the Construction project of Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging (No. 18DZ2260400), the Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (Class II Plateau Disciplinary Construction Program of Medical Technology of SUMHS, 2018–2020), the Australia National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) (No. APP1163786), the Scientia Fellowship program at UNSW, the MCTL Visiting Fellowship Program, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging (No. 18DZ2260400), the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai, and the Recruitment Program of Global Experts of China and Shanghai.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2020_2736_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Super-assembled core-shell mesoporous silica-metal-phenolic network nanoparticles for combinatorial photothermal therapy and chemotherapy
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, B., Zhou, S., Zeng, J. et al. Super-assembled core-shell mesoporous silica-metal-phenolic network nanoparticles for combinatorial photothermal therapy and chemotherapy. Nano Res. 13, 1013–1019 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2736-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2736-6