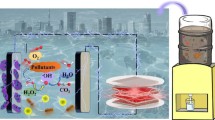
Abstract
Environmental deterioration, especially water pollution, is widely dispersed and could affect the quality of people’s life at large. Though the sewage treatment plants are constructed to meet the demands of cities, distributed treatment units are still in request for the supplementary of centralized purification beyond the range of plants. Electrochemical degradation can reduce organic pollution to some degree, but it has to be powered. Triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) is a newly-invented technology for low-frequency mechanical energy harvesting. Here, by integrating a rotary TENG (R-TENG) as electric power source with an electrochemical cell containing a modified graphite felt cathode for hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) along with hydroxyl radical (•OH) generation by Fenton reaction and a platinum sheet anode for active chlorine generation, a self-powered electrochemical system (SPECS) was constructed. Under the driven of mechanical energy or wind flow, such SPECS can efficiently degrade dyes after power management in neutral condition without any O2 aeration. This work not only provides a guideline for optimizing self-powered electrochemical reaction, but also displays a strategy based on the conversion from distributed mechanical energy to chemical energy for environmental remediation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fan, F. R.; Tian, Z. Q.; Wang, Z. L. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy2012, 1, 328–334.
Wang, Z. L. Nanogenerators, self-powered systems, blue energy, piezotronics and piezo-phototronics-A recall on the original thoughts for coining these fields. Nano Energy2018, 54, 477–483.
Wang, Z. L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as new energy technology and self-powered sensors-Principles, problems and perspectives. Faraday Discuss.2014, 176, 447–458.
Wu, C. S.; Wang, A. C.; Ding, W. B.; Guo, H. Y.; Wang, Z. L. Triboelectric nanogenerator: A foundation of the energy for the new era. Adv. Energy Mater.2019, 9, 1802906.
Wang, Z. L. On Maxwell’s displacement current for energy and sensors: The origin of nanogenerators. Mater. Today2017, 20, 74–82.
Shao, J. J.; Willatzen, M.; Jiang, T.; Tang, W.; Chen, X. Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z. L. Quantifying the power output and structural figure-of-merits of triboelectric nanogenerators in a charging system starting from the Maxwell’s displacement current. Nano Energy2019, 59, 380–389.
Liu, W. L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Liu, G. L.; Chen, J.; Pu, X. J.; Xi, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, H. Y.; Hu, C. G. et al. Integrated charge excitation triboelectric nanogenerator. Nat. Commun.2019, 10, 1426.
Liang, X.; Jiang, T.; Liu, G. X.; Xiao, T. X.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Xi, F. B.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z. L. Triboelectric nanogenerator networks integrated with power management module for water wave energy harvesting. Adv. Funct. Mater.2019, 29, 1807241.
Zhang, C.; Wang, Z. L. Tribotronics-A new field by coupling triboelectricity and semiconductor. Nano Today2016, 11, 521–536.
Yin, W. L.; Xie, Y. D.; Long, J.; Zhao, P. F.; Chen, J. K.; Luo, J. K.; Wang, X. Z.; Dong, S. R. A self-power-transmission and non-contact-reception keyboard based on a novel resonant triboelectric nanogenerator (R-TENG). Nano Energy2018, 50, 16–24.
Zhou, C. J.; Yang, Y. Q.; Sun, N.; Wen, Z.; Cheng, P.; Xie, X. K.; Shao, H. Y.; Shen, Q. Q.; Chen, X. P.; Liu, Y. N. et al. Flexible self-charging power units for portable electronics based on folded carbon paper. Nano Res.2018, 11, 4313–4322.
Liu, Z. R.; Nie, J. H.; Miao, B.; Li, J. D.; Cui, Y. B.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X. D.; Zhao, G. R.; Deng, Y. B.; Wu, Y. H. et al. Self-powered intracellular drug delivery by a biomechanical energy-driven triboelectric nanogenerator. Adv. Mater.2019, 31, 1807795.
Gao, S. Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Tian, M.; Zhu, Y. Z.; Wei, X. J.; Jiang, T. An advanced electro-Fenton degradation system with triboelectric nanogenerator as electric supply and biomass-derived carbon materials as cathode catalyst. Nano Energy2018, 45, 21–27.
Cui, S. W.; Zheng, Y. B.; Liang, J.; Wang, D. A. Triboelectrification based on double-layered polyaniline nanofibers for self-powered cathodic protection driven by wind. Nano Res.2018, 11, 1873–1882.
Yeh, M. H.; Guo, H. Y.; Lin, L.; Wen, Z.; Li, Z. L.; Hu, C. G.; Wang, Z. L. Rolling friction enhanced free-standing triboelectric nanogenerators and their applications in self-powered electrochemical recovery systems. Adv. Funct. Mater.2016, 26, 1054–1062.
Chen, S. W.; Wang, N.; Ma, L.; Li, T.; Willander, M.; Jie, Y.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z. L. Triboelectric nanogenerator for sustainable wastewater treatment via a self-powered electrochemical process. Adv. Energy Mater.2016, 6, 1501778.
Tang, W.; Han, Y.; Han, C. B.; Gao, C. Z.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z. L. Selfpowered water splitting using flowing kinetic energy. Adv. Mater.2015, 27, 272–276.
Su, Y. J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H. L.; Xie, Y. N.; Wu, Z. M.; Jiang, Y. D.; Fukata, N.; Bando, Y.; Wang, Z. L. Enhanced photodegradation of methyl orange with TiO2 nanoparticles using a triboelectric nanogenerator. Nanotechnology2013, 24, 295401.
Yu, X.; Han, X.; Zhao, Z. H.; Zhang, J.; Guo, W. B.; Pan, C. F.; Li, A. X.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z. L. Hierarchical TiO2 nanowire/graphite fiber photoelectrocatalysis setup powered by a wind-driven nanogenerator: A highly efficient photoelectrocatalytic device entirely based on renewable energy. Nano Energy2015, 11, 19–27.
Wei, A. M.; Xie, X. K.; Wen, Z.; Zheng, H. C.; Lan, H. W.; Shao, H. Y.; Sun, X. H.; Zhong, J.; Lee, S. T. Triboelectric nanogenerator driven self-powered photoelectrochemical water splitting based on hematite photoanodes. ACS Nano2018, 12, 8625–8632.
Feng, Y. W.; Ling, L. L.; Nie, J. H.; Han, K.; Chen, X. Y.; Bian, Z. F.; Li, H. X.; Wang, Z. L. Self-powered electrostatic filter with enhanced photocatalytic degradation of formaldehyde based on built-in triboelectric nanogenerators. ACS Nano2017, 11, 12411–12418.
Liu, W. X.; Wu, J. Y.; He, W.; Xu, F. L. A review on perfluoroalkyl acids studies: Environmental behaviors, toxic effects, and ecological and health risks. Ecosyst. Health Sustain.2019, 5, 1–19.
Deng, W. J.; Li, N.; Ying, G. G. Antibiotic distribution, risk assessment, and microbial diversity in river water and sediment in Hong Kong. Environ. Geochem. Health2018, 40, 2191–2203.
Dominguez, C. M.; Oturan, N.; Romero, A.; Santos, A.; Oturan, M. A. Optimization of electro-Fenton process for effective degradation of organochlorine pesticide lindane. Catal. Today2018, 313, 196–202.
Zhou, M. H.; Yu, Q. H.; Lei, L. C.; Barton, G. Electro-Fenton method for the removal of methyl red in an efficient electrochemical system. Sep. Purif. Technol.2007, 57, 380–387.
An, S. F.; Zhang, G. H.; Wang, T. W.; Zhang, W. N.; Li, K. Y.; Song, C. S.; Miller, J. T.; Miao, S.; Wang, J. H.; Guo, X. W. High-density ultra-small clusters and single-atom fe sites embedded in graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) for highly efficient catalytic advanced oxidation processes. ACS Nano2018, 12, 9441–9450.
Zhang, Z. H.; Meng, H. S.; Wang, Y. J.; Shi, L. M.; Wang, X.; Chai, S. N. Fabrication of graphene@graphite-based gas diffusion electrode for improving H2O2 generation in electro-Fenton process. Electrochim. Acta2018, 260, 112–120.
Schwarz, H. A.; Dodson, R. W. Equilibrium between hydroxyl radicals and thallium (II) and the oxidation potential of hydroxyl(aq). J. Phys. Chem.1984, 88, 3643–3647.
Rositano, J.; Nicholson, B. C.; Pieronne, P. Destruction of cyanobacterial toxins by ozone. Ozone: Sci. Eng.1998, 20, 223–238.
Szpyrkowicz, L.; Kaul, S. N.; Neti, R. N.; Satyanarayan, S. Influence of anode material on electrochemical oxidation for the treatment of tannery wastewater. Water Res.2005, 39, 1601–1613.
Ma, X. J.; Zhou, M. H. A comparative study of azo dye decolorization by electro-Fenton in two common electrolytes. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol.2009, 84, 1544–1549.
Yu, F. K.; Zhou, M. H.; Yu, X. M. Cost-effective electro-Fenton using modified graphite felt that dramatically enhanced on H2O2 electro-generation without external aeration. Electrochim. Acta2015, 163, 182–189.
Sellers, R. M. Spectrophotometric determination of hydrogen peroxide using potassium titanium(IV) oxalate. Analyst1980, 105, 950–954.
Barreto, J. C.; Smith, G. S.; Strobel, N. H. P.; McQuillin, P. A.; Miller, T. A. Terephthalic acid: A dosimeter for the detection of hydroxyl radicals in vitro. Life Sci., 1995, 56, PL89–PL 96.
Wen, S. L.; Niu, Z. Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L. H.; Chen, Y. C. In-situ synthesis of 3D GA on titanium wire as a binder-free electrode for electro-Fenton removing of EDTA-Ni. J. Hazard. Mater.2018, 341, 128–137.
Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. H.; Liu, T. F.; Song, S. Q.; Gui, X. C.; Liu, H.; Tsiakaras, P. Dimethyl phthalate degradation at novel and efficient electro-Fenton cathode. Appl. Catal., B.2014, 156, 1–7.
Agladze, G. R.; Tsurtsumia, G. S.; Jung, B. I.; Kim, J. S.; Gorelishvili, G. Comparative study of hydrogen peroxide electro-generation on gas-diffusion electrodes in undivided and membrane cells. J. Appl. Electrochem.2007, 37, 375–383.
de Araújo, D. M.; Cotillas, S.; Sáez, C.; Cañizares, P.; Martínez-Huitle, C. A.; Rodrigo, M. A. Activation by light irradiation of oxidants electrochemically generated during Rhodamine B elimination. J. Electroanal. Chem.2015, 757, 144–149.
Thiam, A.; Salazar, R.; Brillas, E.; Sirés, I. Electrochemical advanced oxidation of carbofuran in aqueous sulfate and/or chloride media using a flow cell with a RuO2-based anode and an air-diffusion cathode at pre-pilot scale. Chem. Eng. J.2018, 335, 133–144.
Yu, K.; Yang, S. G.; He, H.; Sun, C.; Gu, C. G.; Ju, Y. M. Visible light-driven photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B over NaBiO3: Pathways and mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. A2009, 113, 10024–10032.
Fu, H. B.; Zhang, S. C.; Xu, T. G.; Zhu, Y. F.; Chen, J. M. Photocatalytic degradation of rhb by fluorinated Bi2WO6 and distributions of the intermediate products. Environ. Sci. Technol.2008, 42, 2085–2091.
Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Tian, M.; Zhu, Y. Z.; Wei, X. J.; Jiang, T.; Gao, S. Y. An innovative electro-Fenton degradation system self-powered by triboelectric nanogenerator using biomass-derived carbon materials as cathode catalyst. Nano Energy2017, 42, 314–321.
Qin, H. F.; Cheng, G.; Zi, Y. L.; Gu, G. Q.; Zhang, B.; Shang, W. Y.; Yang, F.; Yang, J. J.; Du, Z. L.; Wang, Z. L. High energy storage efficiency triboelectric nanogenerators with unidirectional switches and passive power management circuits. Adv. Funct. Mater.2018, 28, 1805216.
Li, X. H.; Jin, X. D.; Zhao, N. N.; Angelidaki, I.; Zhang, Y. F. Efficient treatment of aniline containing wastewater in bipolar membrane microbial electrolysis cell-Fenton system. Water Res.2017, 119, 67–72.
Yang, Y.; Zhang, H. L.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.; Hwang, W.; Wang, Z. L. Hybrid energy cell for degradation of methyl orange by self-powered electrocatalytic oxidation. Nano Lett.2013, 13, 803–808.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Technology R&D Program of China (No. 2016YFA0202704), Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission (Nos. Z171100000317001, Z171100002017017, and Y3993113DF), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51432005, 5151101243, 51561145021, and 21761142011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2019_2506_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Self-powered electrochemical system by combining Fenton reaction and active chlorine generation for organic contaminant treatment
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Y., Han, K., Jiang, T. et al. Self-powered electrochemical system by combining Fenton reaction and active chlorine generation for organic contaminant treatment. Nano Res. 12, 2729–2735 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-019-2506-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-019-2506-5