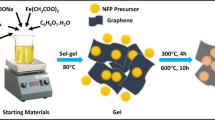
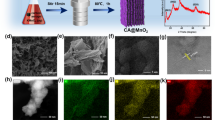
Abstract
Transition metal chalcogenides represent a class of the most promising alternative electrode materials for high-performance lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) owing to their high theoretical capacities. However, they suffer from large volume expansion, particle agglomeration, and low conductivity during charge/discharge processes, leading to unsatisfactory energy storage performance. In order to address these issues, we rationally designed three-dimensional (3D) hybrid composites consisting of ZnSe nanodots uniformly confined within a N-doped porous carbon network (ZnSe ND@N-PC) obtained via a convenient pyrolysis process. When used as anodes for LIBs, the composites exhibited outstanding electrochemical performance, with a high reversible capacity (1,134 mA·h·g−1 at a current density of 600 mA·g−1 after 500 cycles) and excellent rate capability (696 and 474 mA·h·g−1 at current densities of 6.4 and 12.8 A·g−1, respectively). The significantly improved lithium storage performance can be attributed to the 3D architecture of the hybrid composites, which not only mitigated the internal mechanical stress induced by the volume change and formed a 3D conductive network during cycling, but also provided a large reactive area and reduced the lithium diffusion distance. The strategy reported here may open a new avenue for the design of other multifunctional composites towards high-performance energy storage devices.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tarascon, J. M.; Armand, M. Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 2001, 414, 359–367.
Goodenough, J. B.; Park, K. S. The Li-ion rechargeable battery: A perspective. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 135, 1167–1176.
Ji, L. W.; Lin, Z.; Alcoutlabi, M.; Zhang, X. W. Recent developments in nanostructured anode materials for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 2682–2699.
Li, H.; Wang, Z. X.; Chen, L. Q.; Huang, X. J. Research on advanced materials for Li-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4593–4607.
Mahmood, N.; Tang, T. Y.; Hou, Y. L. Nanostructured anode materials for lithium ion batteries: Progress, challenge and perspective. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1600374.
Lim, J.; Li, Y. Y.; Alsem, D. H.; So, H.; Lee, S. C.; Bai, P.; Cogswell, D. A.; Liu, X. Z.; Jin, N.; Yu, Y. S. et al. Origin and hysteresis of lithium compositional spatiodynamics within battery primary particles. Science 2016, 353, 566–571.
Kim, C.; Yang, K. S.; Kojima, M.; Yoshida, K.; Kim, Y. J.; Kim, Y. A.; Endo, M. Fabrication of electrospinning-derived carbon nanofiber webs for the anode material of lithium-ion secondary batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 2393–2397.
Cao, K. Z.; Jiao, L. F.; Liu, Y. C.; Liu, H. Q.; Wang, Y. J.; Yuan, H. T. Ultra-high capacity lithium-ion batteries with hierarchical CoO nanowire clusters as binder free electrodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 1082–1089.
Zhang, H. W.; Zhou, L.; Noonan, O.; Martin, D. J.; Whittaker, A. K.; Yu, C. Z. Tailoring the void size of iron oxide@carbon yolk–shell structure for optimized lithium storage. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4337–4342.
Li, H.; Su, Y.; Sun, W. W.; Wang, Y. Carbon nanotubes rooted in porous ternary metal sulfide@N/S-doped carbon dodecahedron: Bimetal-organic-frameworks derivation and electrochemical application for high-capacity and long-life lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 8345–8353.
Zhang, G. H.; Hou, S. C.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, W.; Yan, F. L.; Li, C. C.; Duan, H. G. High-performance and ultra-stable lithium-ion batteries based on MOF-derived ZnO@ZnO quantum dots/C core–shell nanorod arrays on a carbon cloth anode. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2400–2405.
Shi, Y. F.; Hua, C. X.; Li, B.; Fang, X. P.; Yao, C. H.; Zhang, Y. C.; Hu, Y. S.; Wang, Z. X.; Chen, L. Q.; Zhao, D. Y. et al. Highly ordered mesoporous crystalline MoSe2 material with efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity and enhanced lithium storage performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1832–1838.
Zhou, L. Y.; Yan, S. C.; Pan, L. J.; Wang, X. R.; Wang, Y. Q.; Shi, Y. A scalable sulfuration of WS2 to improve cyclability and capability of lithium-ion batteries. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 857–865.
Lu, T.; Dong, S. M.; Zhang, C. J.; Zhang, L. X.; Cui, G. L. Fabrication of transition metal selenides and their applications in energy storage. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 332, 75–99.
Xin, S.; Yu, L.; You, Y.; Cong, H. P.; Yin, Y. X.; Du, X. L.; Guo, Y. G.; Yu, S. H.; Cui, Y.; Goodenough, J. B. The electrochemistry with lithium versus sodium of selenium confined to slit micropores in carbon. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 4560−4568.
Xue, M. Z.; Fu, Z. W. Lithium electrochemistry of NiSe2: A new kind of storage energy material. Electrochem. Commun. 2006, 8, 1855–1862.
Li, Z. P.; Xue, H. T.; Wang, J. Q.; Tang, Y. B.; Lee, C. S.; Yang, S. R. Reduced graphene oxide/marcasite-type cobalt selenide nanocrystals as an anode for lithium-ion batteries with excellent cyclic performance. ChemElectroChem 2015, 2, 1682–1686.
Luo, Z. G.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L. R.; Fang, G. Z.; Pan, A. Q.; Liang, S. Q. Two-dimensional hybrid nanosheets of few layered MoSe2 on reduced graphene oxide as anodes for long-cycle-life lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 15302–15308.
Yang, X.; Zhang, Z. A.; Fu, Y.; Li, Q. Porous hollow carbon spheres decorated with molybdenum diselenide nanosheets as anodes for highly reversible lithium and sodium storage. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10198–10203.
Wei, D. H.; Liang, J. W.; Zhu, Y. C.; Hu, L.; Zhang, K. L.; Zhang, J. J.; Yuan, Z. Q.; Qian, Y. T. Layer structured α-FeSe: A potential anode material for lithium storage. Electrochem. Commun. 2014, 38, 124–127.
Zhang, Z. A.; Shi, X. D.; Yang, X. Synthesis of core–shell NiSe/C nanospheres as anodes for lithium and sodium storage. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 208, 238–243.
Hu, H.; Zhang, J. T.; Guan, B. Y.; Lou, X. W. Unusual formation of CoSe@carbon nanoboxes, which have an inhomogeneous shell, for efficient lithium storage. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 9514–9518.
Augustyn, V.; Come, J.; Lowe, M. A.; Kim, J. W.; Taberna, P. L.; Tolbert, S. H.; Abruña, H. D.; Simon, P.; Dunn, B. Highrate electrochemical energy storage through Li+ intercalation pseudocapacitance. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 518–522.
Chen, C. J.; Wen, Y. W.; Hu, X. L.; Ji, X. L.; Yan, M. Y.; Mai, L. Q.; Hu, P.; Shan, B.; Huang, Y. H. Na+ intercalation pseudocapacitance in graphene-coupled titanium oxide enabling ultra-fast sodium storage and long-term cycling. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6929.
Li, S.; Qiu, J. X.; Lai, C.; Ling, M.; Zhao, H. J.; Zhang, S. Q. Surface capacitive contributions: Towards high rate anode materials for sodium ion batteries. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 224–230.
Zhang, L.; Zhao, K. N.; Luo, Y. Z.; Dong, Y. F.; Xu, W. W.; Yan, M. Y.; Ren, W. H.; Zhou, L.; Qu, L. B.; Mai, L. Q. Acetylene black induced heterogeneous growth of macroporous CoV2O6 nanosheet for high-rate pseudocapacitive lithium-ion battery anode. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 7139–7146.
Augustyn, V.; Simon, P.; Dunn, B. Pseudocapacitive oxide materials for high-rate electrochemical energy storage. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1597–1614.
Qi, L. Y.; Zhang, Y. W.; Zuo, Z. C.; Xin, Y. L.; Yang, C. K.; Wu, B.; Zhang, X. X.; Zhou, H. H. In situ quantization of ferroferric oxide embedded in 3D microcarbon for ultrahigh performance sodium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 8822–8829.
Chao, D. L.; Zhu, C. R.; Yang, P. H.; Xia, X. H.; Liu, J. L.; Wang, J.; Fan, X. F.; Savilov, S. V.; Lin, J. Y.; Fan, H. J. et al. Array of nanosheets render ultrafast and high-capacity Na-ion storage by tunable pseudocapacitance. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12122.
Izumi, F.; Ikeda, T. A Rietveld-analysis programm Rietan-98 and its applications to zeolites. Mater. Sci. Forum 2000, 321–324, 198–205.
Cozzoli, P. D.; Manna, L.; Curri, M. L.; Kudera, S.; Giannini, C.; Striccoli, M.; Agnostiano, A. Shape and phase control of colloidal ZnSe nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 1296–1306.
Yang, S. J.; Nam, S.; Kim, T.; Im, J. H.; Jung, H.; Kang, J. H.; Wi, S.; Park, B.; Park, C. R. Preparation and exceptional lithium anodic performance of porous carbon-coated ZnO quantum dots derived from a metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7394–7397.
Qie, L.; Chen, W. M.; Wang, Z. H.; Shao, Q. G.; Li, X.; Yuan, L. X.; Hu, X. L.; Zhang, W. X.; Huang, Y. H. Nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanofiber webs as anodes for lithium ion batteries with a superhigh capacity and rate capability. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2047–2050.
Chen, J. Z.; Yang, L.; Fang, S. H.; Zhang, Z. X.; Deb, A.; Hirano, S. Sn-contained N-rich carbon nanowires for highcapacity and long-life lithium storage. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 127, 390–396.
Pan, H. L.; Yao, B.; Ding, M.; Deng, R.; Yang, T.; Sui, Y. R.; Zhao, T. T.; Gao, L. L. Characterization and properties of Zn–O–Se ternary system thin films deposited by radiofrequency (rf)-magnetron sputtering. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2010, 356, 906–910.
Zhu, J.; Wang, T.; Fan, F. R.; Mei, L.; Lu, B. A. Atomic-scale control of silicon expansion space as ultrastable battery anodes. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8243−8251.
Zhang, L. J.; Su, Z. X.; Jiang, F. L.; Yang, L. L.; Qian, J. J.; Zhou, Y. F.; Li, W. M.; Hong, M. C. Highly graphitized nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanopolyhedra derived from ZIF-8 nanocrystals as efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reactions. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 6590–6602.
Kwon, H. T.; Park, C. M. Electrochemical characteristics of ZnSe and its nanostructured composite for rechargeable Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 251, 319–324.
Xue, M. Z.; Fu, Z. W. Fabrication and electrochemical characterization of zinc selenide thin film by pulsed laser deposition. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 52, 988–995.
Fu, Y.; Zhang, Z. A.; Du, K.; Qu, Y. H.; Li, Q.; Yang, X. Spherical-like ZnSe with facile synthesis as a potential electrode material for lithium ion batteries. Mater. Lett. 2015, 146, 96–98.
Zhang, Z. A.; Fu, Y.; Yang, X.; Qu, Y. H.; Li, Q. Nanostructured ZnSe anchored on graphene nanosheets with superior electrochemical properties for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 168, 285–291.
Xu, Y. H.; Liang, J. W.; Zhang, K. L.; Zhu, Y. C.; Wei, D. H.; Qian, Y. T. Origin of additional capacities in seleniumbased ZnSe@C nanocomposite Li-ion battery electrodes. Electrochem. Commun. 2016, 65, 44–47.
Sun, H. T.; Xin, G. Q.; Hu, T.; Yu, M. P.; Shao, D. L.; Sun, X.; Lian, J. High-rate lithiation-induced reactivation of mesoporous hollow spheres for long-lived lithium-ion batteries. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4526.
Wu, R. B.; Qian, X. K.; Rui, X. H.; Liu, H.; Yadian, B. L.; Zhou, K.; Wei, J.; Yan, Q. Y.; Feng, X. Q.; Long, Y. et al. Zeolitic imidazolate framework 67-derived high symmetric porous Co3O4 hollow dodecahedra with highly enhanced lithium storage capability. Small 2014, 10, 1932–1938.
Jiao, J. Q.; Qiu, W. D.; Tang, J. G.; Chen, L. P.; Jing, L. Y. Synthesis of well-defined Fe3O4 nanorods/N-doped graphene for lithium-ion batteries. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 1256–1266.
Wu, R. B.; Qian, X. K.; Zhou, K.; Wei, J.; Lou, J.; Ajayan, P. M. Porous spinel ZnxCo3–xO4 hollow polyhedra templated for high-rate lithium-ion batteries. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6297–6303.
Wu, R. B.; Wang, D. P.; Rui, X. H.; Liu, B.; Zhou, K.; Law, A. W. K.; Yan, Q. Y.; Wei, J.; Chen, Z. In-situ formation of hollow hybrids composed of cobalt sulfides embedded within porous carbon polyhedra/carbon nanotubes for highperformance lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3038–3044.
Cong, H. P.; Xin, S.; Yu, S. H. Flexible nitrogen-doped graphene/SnO2 foams promise kinetically stable lithium storage. Nano Energy 2015, 13, 482–490.
Zhou, F.; Xin, S.; Liang, H. W.; Song, L. T.; Yu, S. H. Carbon nanofibers decorated with molybdenum disulfide nanosheets: Synergistic lithium storage and enhanced electrochemical performance. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 11552–11556.
Shan, T. T.; Xin, S.; You, Y.; Cong, H. P.; Yu, S. H.; Manthiram, A. Combining nitrogen-doped graphene sheets and MoS2: A unique film–foam–film structure for enhanced lithium storage. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 12783–12788.
Xin, S.; Chang, Z. W.; Zhang, X. B.; Guo, Y. G. Progress of rechargeable lithium metal batteries based on conversion reactions. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 54–70.
Zou, F.; Hu, X. L.; Qie, L.; Jiang, Y.; Xiong, X. Q.; Qiao, Y.; Huang, Y. H. Facile synthesis of sandwiched Zn2GeO4- graphene oxide nanocomposite as a stable and high-capacity anode for lithium-ion batteries. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 924–930.
Song, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. N.; Fang, F.; Li, Y. S.; Gao, S. P.; Gu, Q. F.; Hu, L. F.; Sun, D. L. Bottom-up approach design, band structure, and lithium storage properties of atomically thin γ-FeOOH nanosheets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 21334–21342.
Wang, Y. G.; Hong, Z. S.; Wei, M. D.; Xia, Y. Y. Layered H2Ti6O13-nanowires: A new promising pseudocapacitive material in non-aqueous electrolyte. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 5185–5193.
Brezesinski, T.; Wang, J.; Tolbert, S. H.; Dunn, B. Ordered mesoporous α-MoO3 with iso-oriented nanocrystalline walls for thin-film pseudocapacitors. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 146–151.
Dawood, F.; Schaak, R. E. ZnO-templated synthesis of wurtzite-type ZnS and ZnSe nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 424–425.
Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H. Y.; Liu, Z. Q.; Zhang, X. Y.; Du, Y. P. Synthesis of high-quality α-MnSe nanostructures with superior lithium storage properties. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 2765–2770.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51672049, 51671058, and 51571063), the Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (No. 15YF1401300), Research Grant for Talent Introduction of Fudan University, China (No. JJH2021103) and Thousand Youth Talents Program of China (Recruitment Program of Global Youth Experts).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Wu, R., Wang, H. et al. Embedding ZnSe nanodots in nitrogen-doped hollow carbon architectures for superior lithium storage. Nano Res. 11, 966–978 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1709-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1709-x