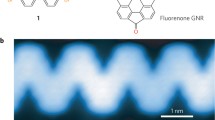
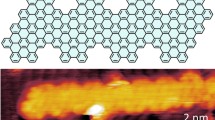
Abstract
Unlike graphene sheets, graphene nanoribbons (GNRs) can exhibit semiconducting band gap characteristics that can be tuned by controlling impurity doping and the GNR widths and edge structures. However, achieving such control is a major challenge in the fabrication of GNRs. Chevron-type GNRs were recently synthesized via surface-assisted polymerization of pristine or N-substituted oligophenylene monomers. In principle, GNR heterojunctions can be fabricated by mixing two different monomers. In this paper, we report the fabrication and characterization of chevron-type GNRs using sulfur-substituted oligophenylene monomers to produce GNRs and related heterostructures for the first time. First-principles calculations show that the GNR gaps can be tailored by applying different sulfur configurations from cyclodehydrogenated isomers via debromination and intramolecular cyclodehydrogenation. This feature should enable a new approach for the creation of multiple GNR heterojunctions by engineering their sulfur configurations. These predictions have been confirmed via scanning tunneling microscopy and scanning tunneling spectroscopy. For example, we have found that the S-containing GNRs contain segments with distinct band gaps, i.e., a sequence of multiple heterojunctions that results in a sequence of quantum dots. This unusual intraribbon heterojunction sequence may be useful in nanoscale optoelectronic applications that use quantum dots.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dutta, S.; Pati, S. K. et al., Novel properties of graphene nanoribbons: A review, J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 8207–8223.
Kim, W. Y.; Kim, K. S. et al., Prediction of very large values of magnetoresistance in a graphene nanoribbon device, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 408–412.
Koch, M.; Ample, F.; Joachim, C.; Grill, L. et al., Voltage-dependent conductance of a single graphene nanoribbon, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 713–717.
Li, X. L.; Wang, X. R.; Zhang, L.; Lee, S. W.; Dai, H. J. et al., Chemically derived, ultrasmooth graphene nanoribbon semiconductors, Science 2008, 319, 1229–1232.
Shifrina, Z. B.; Averina, M. S.; Rusanov, A. L.; Wagner, M.; Mü llen, K. et al., Branched polyphenylenes by repetitive Diels–Alder cycloaddition, Macromolecules 2000, 33, 3525–3529.
Wu, X. J.; Zeng, X. C. et al., Sawtooth-like graphene nanoribbon, Nano Res. 2008, 1, 40–45.
Bets, K. V.; Yakobson, B. I. et al., Spontaneous twist and intrinsic instabilities of pristine graphene nanoribbons, Nano Res. 2009, 2, 161–166.
Huang, H.; Wei, D. C.; Sun, J. T.; Wong, S. L.; Feng, Y. P.; Castro Neto, A. H.; Wee, A. T. S. et al., Spatially resolved electronic structures of atomically precise armchair graphene nanoribbons, Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 983.
Son, Y. W.; Cohen, M. L.; Louie, S. G. et al., Energy gaps in graphene nanoribbons, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 216803.
Yang, L.; Park, C. H.; Son, Y. W.; Cohen, M. L.; Louie, S. G. et al., Quasiparticle energies and band gaps in graphene nanoribbons, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 186801.
Chen, Y. C.; de Oteyza, D. G.; Pedramrazi, Z.; Chen, C.; Fischer, F. R.; Crommie, M. F. et al., Tuning the band gap of graphene nanoribbons synthesized from molecular precursors, ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6123–6128.
Ritter, K. A.; Lyding, J. W. et al., The influence of edge structure on the electronic properties of graphene quantum dots and nanoribbons, Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 235–242.
Bronner, C.; Stremlau, S.; Gille, M.; Brauße, F.; Haase, A.; Hecht, S.; Tegeder, P. et al., Aligning the band gap of graphene nanoribbons by monomer doping, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4422–4425.
Martins, T. B.; Miwa, R. H.; da Silva, A. J. R.; Fazzio, A. et al., Electronic and transport properties of boron-doped graphene nanoribbons, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 196803.
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. F.; Li, G.; Lu, J. C.; Lin, X.; Du, S. X.; Berger, R.; Feng, X. L.; Müllen, K.; Gao, H. J. et al., Direct visualization of atomically precise nitrogen-doped graphene nanoribbons, Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 023101.
Li, Y. F.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, P. W.; Chen, Z. F. et al., Spin gapless semiconductor-metal-half-metal properties in nitrogen-doped zigzag graphene nanoribbons, ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1952–1958.
Cai, J. M.; Ruffieux, P.; Jaafar, R.; Bieri, M.; Braun, T.; Blankenburg, S.; Muoth, M.; Seitsonen, A. P.; Saleh, M.; Feng, X. L. et al. et al., Atomically precise bottom-up fabrication of graphene nanoribbons, Nature 2010, 466, 470–473.
Narita, A.; Feng, X. L.; Müllen, K. et al., Bottom-up synthesis of chemically precise graphene nanoribbons, Chem. Rec. 2015, 15, 295–309.
Narita, A.; Verzhbitskiy, I. A.; Frederickx, W.; Mali, K. S.; Jensen, S. A.; Hansen, M. R.; Bonn, M.; De Feyter, S.; Casiraghi, C.; Feng, X. L. et al. et al., Bottom-up synthesis of liquid-phase-processable graphene nanoribbons with nearinfrared absorption, ACS Nano 2014, 8, 11622–11630.
Liang, L. B.; Meunier, V. et al., Atomically precise graphene nanoribbon heterojunctions for excitonic solar cells, J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 775–783.
Chen, Y. C.; Cao, T.; Chen, C.; Pedramrazi, Z.; Haberer, D.; de Oteyza, D. G.; Fischer, F. R.; Louie, S. G.; Crommie, M. F. et al., Molecular bandgap engineering of bottom-up synthesized graphene nanoribbon heterojunctions, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 156–160.
Perdew, J. P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. et al., Generalized gradient approximation made simple, Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868.
Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. et al., Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set, Comp. Mater. Sci. 1996, 6, 15–50.
Kresse, G.; Hafner, J. et al., Ab initio molecular dynamics for liquid metals, Phys. Rev. B 1993, 47, 558–561.
Tersoff, J.; Hamann, D. R. et al., Theory of the scanning tunneling microscope, Phys. Rev. B 1985, 31, 805–813.
Saleh, M.; Baumgarten, M.; Mavrinskiy, A.; Schäfer, T.; Müllen, K. et al., Triphenylene-based polymers for blue polymeric light emitting diodes, Macromolecules 2010, 43, 137–143.
Acknowledgements
Work at IOP and UCAS was supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFA0202300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61390501, 61471337, 51210003, and 51325204), National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2013CBA01600), the CAS Pioneer Hundred Talents Program, the Transregional Collaborative Research Center TRR 61, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the National Supercomputing Center in Tianjin. A portion of the research was performed in CAS Key Laboratory of Vacuum Physics. Work at the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research were supported by the EC graphene flagship (No. CNECT-ICT-604391) and ERC NANOGRAPH. Work at Vanderbilt University was supported by Department of Energy grant DE-FG02-09ER46554 and by the McMinn Endowment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, YF., Zhang, Y., Li, G. et al. Sulfur-doped graphene nanoribbons with a sequence of distinct band gaps. Nano Res. 10, 3377–3384 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1550-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1550-2