Abstract
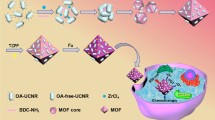
Rattle structure is a topic of great interest in design and application of nanomaterials due to the unique core@void@shell architecture and the integration of functions. Herein, we developed a novel “ship-in-a-bottle” method to fabricate upconverting (UC) luminescent nanorattles by incorporating lanthanide-doped fluorides into hollow mesoporous silica. The size of nanorattles and the filling amount of fluorides can be well controlled. In addition, the modification of silica shell (with phenylene and amine groups) and the variation of efficient UC fluorides (NaYF4:Yb,Er, NaLuF4:Yb,Er, NaGdF4:Yb,Er and LiYF4:Yb,Er) were readily achieved. The resulting nanorattles exhibited a high capacity and pH-dependent release of the anti-cancer drug doxorubicin (DOX). Furthermore, we employed these nanorattles in proof-of-concept UC-monitoring drug release by utilizing the energy transfer process from UC fluorides to DOX, thus revealing the great potential of the nanorattles as efficient cancer theranostic agent.

Similar content being viewed by others

References
Wang, F.; Banerjee, D.; Liu, Y. S.; Chen, X. Y.; Liu, X. G. Upconversion nanoparticles in biological labeling, imaging, and therapy. Analyst 2010, 135, 1839–1854.
Luo, W. Q.; Liu, Y. S.; Chen, X. Y. Lanthanide-doped semiconductor nanocrystals: Electronic structures and optical properties. Sci. China Mater. 2015, 58, 819–850.
Yang, D. M.; Ma, P. A.; Hou, Z. Y.; Cheng, Z. Y.; Li, C. X.; Lin, J. Current advances in lanthanide ion (ln3+)-based upconversion nanomaterials for drug delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1416–1448.
Gai, S. L.; Li, C. X.; Yang, P. P.; Lin, J. Recent progress in rare earth micro/nanocrystals: Soft chemical synthesis, luminescent properties, and biomedical applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 2343–2389.
Dai, Y. L.; Xiao, H. H.; Liu, J. H.; Yuan, Q. H.; Ma, P. A.; Yang, D. M.; Li, C. X.; Cheng, Z. Y.; Hou, Z. Y.; Yang, P. P. et al. In vivo multimodality imaging and cancer therapy by near-infrared light-triggered trans-platinum pro-drugconjugated upconverison nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 18920–18929.
Liu, J. N.; Bu, W. B.; Shi, J. L. Silica coated upconversion nanoparticles: A versatile platform for the development of efficient theranostics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1797–1805.
Zhao, L. Z.; Peng, J. J.; Huang, Q.; Li, C. Y.; Chen, M.; Sun, Y.; Lin, Q. N.; Zhu, L. Y.; Li, F. Y. Near-infrared photoregulated drug release in living tumor tissue via yolk–shell upconversion nanocages. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 363–371.
Liu, J. A.; Bu, W. B.; Pan, L. M.; Shi, J. L. Nir-triggered anticancer drug delivery by upconverting nanoparticles with integrated azobenzene-modified mesoporous silica. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4375–4379.
Yang, Y. M.; Velmurugan, B.; Liu, X. G.; Xing, B. G. Nir photoresponsive crosslinked upconverting nanocarriers toward selective intracellular drug release. Small 2013, 9, 2937–2944.
Li, X. M.; Zhou, L.; Wei, Y.; El-Toni, A. M.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, D. Y. Anisotropic encapsulation-induced synthesis of asymmetric single-hole mesoporous nanocages. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5903–5906.
Chen, H. Y.; Qi, B.; Moore, T.; Wang, F. L.; Colvin, D. C.; Sanjeewa, L. D.; Gore, J. C.; Hwu, S. J.; Mefford, O. T.; Alexis, F. et al. Multifunctional yolk-in-shell nanoparticles for pH-triggered drug release and imaging. Small 2014, 10, 3364–3370.
Fan, W. P.; Shen, B.; Bu, W. B.; Chen, F.; He, Q. J.; Zhao, K. L.; Zhang, S. J.; Zhou, L. P.; Peng, W. J.; Xiao, Q. F. et al. A smart upconversion-based mesoporous silica nanotheranostic system for synergetic chemo-/radio-/photodynamic therapy and simultaneous mr/ucl imaging. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 8992–9002.
Lu, S.; Tu, D. T.; Hu, P.; Xu, J.; Li, R. F.; Wang, M.; Chen, Z.; Huang, M. D.; Chen, X. Y. Multifunctional nano-bioprobes based on rattle-structured upconverting luminescent nanoparticles. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 7915–7919.
Qian, H. S.; Guo, H. C.; Ho, P. C. L.; Mahendran, R.; Zhang, Y. Mesoporous-silica-coated up-conversion fluorescent nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy. Small 2009, 5, 2285–2290.
Idris, N. M.; Gnanasammandhan, M. K.; Zhang, J.; Ho, P. C.; Mahendran, R.; Zhang, Y. In vivo photodynamic therapy using upconversion nanoparticles as remote-controlled nanotransducers. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1580–1585.
Hou, Z. Y.; Li, X. J.; Li, C. X.; Dai, Y. L.; Ma, P. A.; Zhang, X.; Kang, X. J.; Cheng, Z. Y.; Lin, J. Electrospun upconversion composite fibers as dual drugs delivery system with individual release properties. Langmuir 2013, 29, 9473–9482.
Chen, Y. Y.; Liu, S.; Hou, Z. Y.; Ma, P. A.; Yang, D. M.; Li, C. X.; Lin, J. Multifunctional electrospinning composite fibers for orthotopic cancer treatment in vivo. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 1917–1931.
Li, K.; Su, Q. Q.; Yuan, W.; Tian, B.; Shen, B.; Li, Y. H.; Feng, W.; Li, F. Y. Ratiometric monitoring of intracellular drug release by an upconversion drug delivery nanosystem. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 12278–12286.
Liu, J. N.; Bu, J. W.; Bu, W. B.; Zhang, S. J.; Pan, L. M.; Fan, W. P.; Chen, F.; Zhou, L. P.; Peng, W. J.; Zhao, K. L. et al. Real-time in vivo quantitative monitoring of drug release by dual-mode magnetic resonance and upconverted luminescence imaging. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 4551–4555.
Kang, X. J.; Cheng, Z. Y.; Yang, D. M.; Ma, P. A.; Shang, M. M.; Peng, C.; Dai, Y. L.; Lin, J. Design and synthesis of multifunctional drug carriers based on luminescent rattletype mesoporous silica microspheres with a thermosensitive hydrogel as a controlled switch. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1470–1481.
Xiao, M. D.; Zhao, C. M.; Chen, H. J.; Yang, B. C.; Wang, J. F. “Ship-in-a-bottle” growth of noble metal nanostructures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4526–4532.
Priebe, M.; Fromm, K. M. Nanorattles or yolk–shell nanoparticles—What are they, how are they made, and what are they good for? Chem.—Eur. J. 2015, 21, 3854–3874.
Purbia, R.; Paria, S. Yolk/shell nanoparticles: Classifications, synthesis, properties, and applications. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 19789–19873.
Boyer, J. C.; van Veggel, F. C. J. M. Absolute quantum yield measurements of colloidal NaYF4: Er3+, yb3+ upconverting nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1417–1419.
Roberts, J. E. Lanthanum and neodymium salts of trifluoroacetic acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1961, 83, 1087–1088.
Fang, X. L.; Chen, C.; Liu, Z. H.; Liu, P. X.; Zheng, N. F. A cationic surfactant assisted selective etching strategy to hollow mesoporous silica spheres. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 1632–1639.
Jiao, Y. F.; Guo, J.; Shen, S.; Chang, B. S.; Zhang, Y. H.; Jiang, X. G.; Yang, W. L. Synthesis of discrete and dispersible hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles with tailored shell thickness for controlled drug release. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 17636–17643.
Xia, X. H.; Yang, M. X.; Wang, Y. C.; Zheng, Y. Q.; Li, Q. G.; Chen, J. Y.; Xia, Y. N. Quantifying the coverage density of poly(ethylene glycol) chains on the surface of gold nanostructures. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 512–522.
Li, Y. S.; Shi, J. L. Hollow-structured mesoporous materials: Chemical synthesis, functionalization and applications. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3176–3205.
Chen, Y.; Chen, H. R.; Guo, L. M.; He, Q. J.; Chen, F.; Zhou, J.; Feng, J. W.; Shi, J. L. Hollow/rattle-type mesoporous nanostructures by a structural difference-based selective etching strategy. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 529–539.
Zhang, Q.; Ge, J. P.; Goebl, J.; Hu, Y. X.; Lu, Z. D.; Yin, Y. D. Rattle-type silica colloidal particles prepared by a surfaceprotected etching process. Nano Res. 2009, 2, 583–591.
Wu, H. Y.; Chen, C. T.; Hung, I. M.; Liao, C. H.; Vetrivel, S.; Kao, H. M. Direct synthesis of cubic benzene-bridged mesoporous organosilica functionalized with mercaptopropyl groups as an effective adsorbent for mercury and silver ions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 7021–7029.
Wu, H. Y.; Shieh, F. K.; Kao, H. M.; Chen, Y. W.; Deka, J. R.; Liao, S. H.; Wu, K. C. W. Synthesis, bifunctionalization, and remarkable adsorption performance of benzene-bridged periodic mesoporous organosilicas functionalized with high loadings of carboxylic acids. Chem.—Eur. J. 2013, 19, 6358–6367.
Zhang, Q.; Liu, F.; Nguyen, K. T.; Ma, X.; Wang, X. J.; Xing, B. G.; Zhao, Y. L. Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer-targeted and controlled drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 5144–5156.
Wang, C.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Y. M.; Wang, X. J.; Ma, X. X.; Deng, Z. Y.; Li, Y. G.; Liu, Z. Imaging-guided pH-sensitive photodynamic therapy using charge reversible upconversion nanoparticles under near-infrared light. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 3077–3086.
Huang, S.; Peng, S.; Li, Y. B.; Cui, J. B.; Chen, H. L.; Wang, L. Y. Development of NIR-II fluorescence imageguided and pH-responsive nanocapsules for cocktail drug delivery. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 1932–1943.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, S., Tu, D., Li, X. et al. A facile “ship-in-a-bottle” approach to construct nanorattles based on upconverting lanthanide-doped fluorides. Nano Res. 9, 187–197 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0979-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0979-4