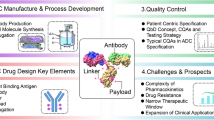
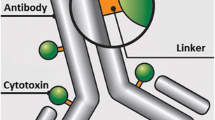
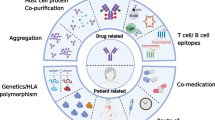
Abstract
Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) are promising cancer therapeutics with minimal toxicity as compared to small cytotoxic molecules alone and have shown the evidence to overcome resistance against tumor and prevent relapse of cancer. The ADC has a potential to change the paradigm of cancer chemotherapeutic treatment. At present, 13 ADCs have been approved by USFDA for the treatment of various types of solid tumor and haematological malignancies. This review covers the three structural components of an ADC—antibody, linker, and cytotoxic payload—along with their respective structure, chemistry, mechanism of action, and influence on the activity of ADCs. It covers comprehensive insight on structural role of linker towards efficacy, stability & toxicity of ADCs, different types of linkers & various conjugation techniques. A brief overview of various analytical techniques used for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of ADC is summarized. The current challenges of ADCs, such as heterogeneity, bystander effect, protein aggregation, inefficient internalization or poor penetration into tumor cells, narrow therapeutic index, emergence of resistance, etc., are outlined along with recent advances and future opportunities for the development of more promising next-generation ADCs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdollahpour-Alitappeh M, Lotfinia M, Gharibi T, Mardaneh J, Farhadihosseinabadi B, Larki P, Faghfourian B, Sepehr KS, Abbaszadeh-Goudarzi K, Abbaszadeh-Goudarzi G, Johari B, Zali MR, Bagheri N (2019) Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) for cancer therapy: strategies, challenges, and successes. J Cell Physiol 234:5628–5642. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27419
Ackerman S, Pearson C, Gregorio J, Gonzalez J, Kenkel J, Hartmann F, Luo A, Ho P, LeBlanc H, Blum L, Kimmey S, Luo A, Nguyen M, Paik J, Sheu L, Ackerman B, Lee A, Li H, Melrose J, Laura R, Ramani V, Henning K, Jackson D, Safina B, Yonehiro G, Devens B, Carmi Y, Chapin S, Bendall S, Kowanetz M, Dornan D, Engleman E, Alonso M (2021) Immune-stimulating antibody conjugates elicit robust myeloid activation and durable antitumor immunity. Nat Cancer 2:18–33. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-020-00136-x
Adair JR, Howard PW, Hartley JA, Williams DG, Chester KA (2012) Antibody–drug conjugates—a perfect synergy. Expert Opin Biol Ther 12:1191–1206. https://doi.org/10.1517/14712598.2012.693473
Adumeau P, Sharma SK, Brent C, Zeglis B (2016) Site-specifically labeled immunoconjugates for molecular imaging—part 1: cysteine residues and glycans. Mol Imaging Biol 18:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-015-0919-4
Agarwal P, Bertozzi CR (2015) Site-specific antibody–drug conjugates: the nexus of bioorthogonal chemistry, protein engineering, and drug development. Bioconjug Chem 26:176–192. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc5004982
Albin N, Massaad L, Toussaint C, Mathieu M-C, Morizet J, Parise O, Gouyette A, Chabot GG (1993) Main drug-metabolizing enzyme systems in human breast tumors and peritumoral tissues. Cancer Res 53:3541–3546
Alley SC, Anderson KE (2013) Analytical and bioanalytical technologies for characterizing antibody-drug conjugates. Curr Opin Chem Biol 17:406–411
Aretin M-B (2022) Antibody–drug conjugates—the magic bullet? Memo-magazine. Eur Med Oncol 15:125–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12254-021-00780-8
Bardia A, Mayer I, Vahdat L, Tolaney S, Isakoff S, Diamond J, O’Shaughnessy J, Moroose R, Santin A, Abramson V, Shah N, Rugo H, Goldenberg D, Sweidan A, Iannone R, Washkowitz S, Sharkey R, Wegener W, Kalinsky K (2019) Sacituzumab govitecan-hziy in refractory metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med 380:741–751. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1814213
Bargh JD, Isidro-Llobet A, Parker JS, Spring DR (2019) Cleavable linkers in antibody–drug conjugates. Chem Soc Rev 48:4361–4374. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CS00676H
Barok M, Joensuu H, Isola J (2014) Trastuzumab emtansine: mechanisms of action and drug resistance. Breast cancer Res 16:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr3621
Beck A, D’atri V, Ehkirch A, Fekete S, Hernandez-Alba O, Gahoual R, Leize-Wagner E, Francois Y, Guillarme D, Cianférani S (2019) Cutting-edge multi-level analytical and structural characterization of antibody-drug conjugates: present and future. Expert Rev Proteomics 16:337–362. https://doi.org/10.1080/14789450.2019.1578215
Beerli RR, Grawunder U (2017) In: Grawunder U, Barth S (eds) Enzyme-based strategies to Generate Site-Specifically conjugated antibody drug conjugates BT - Next generation antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) and immunotoxins. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 85–106
Beusker PF. “Magic bullets” to “Trojan-Horses”: the evolution of next-generation antibody-drug conjugates. https://www.byonids.com/who-we-are/blogs/2022-03-28. Accessed 5 Aug 2022
BiopharmPEG 9 types of drug conjugates overview : ADC, RDC, ISAC, SMDC, AOC… https://www.biochempeg.com/article/266.html. Accessed 30 Aug 2022
Bobály B, Fleury-Souverain S, Beck A, Veuthey J-L, Guillarme D, Fekete S (2018) Current possibilities of liquid chromatography for the characterization of antibody-drug conjugates. J Pharm Biomed Anal 147:493–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2017.06.022
Buecheler JW, Winzer M, Tonillo J, Weber C, Gieseler H (2018) Impact of payload hydrophobicity on the stability of antibody–drug conjugates. Mol Pharm 15:2656–2664. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00177
Cahuzac H, Devel L (2020) Analytical methods for the detection and quantification of ADCs in biological matrices. Pharmaceuticals 13:462. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13120462
Carter PJ, Senter PD (2008) Antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Cancer J 14:154–169. https://doi.org/10.1097/ppo.0b013e318172d704
Chatal J-F, Kraeber-Bodéré F, Bodet-milin C, Rousseau C (2016) Therapeutic immunoconjugates. Which cytotoxic payload: chemotherapeutic drug (ADC) or Radionuclide (ARC) ? Curr Cancer Ther Rev 12:54–65. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573394712666160805121312
Chau CH, Steeg PS, Figg WD (2019) Antibody drug conjugates for cancer. Lancet 394:793–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31774-X
Chen T-H, Yang Y, Zhang Z, Fu C, Zhang Q, Williams JD, Wirth MJ (2019) Native reversed-phase liquid chromatography: a technique for LCMS of intact antibody–drug conjugates. Anal Chem 91:2805–2812. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04699
Criscitiello C, Morganti S, Curigliano G (2021) Antibody–drug conjugates in solid tumors: a look into novel targets. J Hematol Oncol 14:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-021-01035-z
Dahl J, Marx K, Jabbour E (2016) Inotuzumab ozogamicin in the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Expert Rev Hematol 9:329–334. https://doi.org/10.1586/17474086.2016.1143771
de Graaf M, Boven E, Scheeren HW, Haisma HJ, Pinedo HM (2002) Beta-glucuronidase-mediated drug release. Curr Pharm Des 8:1391–1403
Dean AQ, Luo S, Twomey JD, Zhang B (2021) In: MAbs (ed) Targeting cancer with antibody-drug conjugates: promises and challenges. Taylor & Francis, p 1951427
Debiopharm Debiopharm and Ubix (2022) Therapeutics launch research to develop a new anti-cancer modality—antibody degraducer® conjugates. https://www.debiopharm.com/drug-development/press-releases/debiopharm-and-ubix-therapeutics-launch-research-to-develop-a-new-anti-cancer-modality-antibody-degraducer-conjugates/
Dennler P, Chiotellis, Aristeidis, Fischer E, Brégeon D, Belmant C, Gauthier L, Lhospice F, Romagne F, Schibli R (2014) Transglutaminase-based chemo-enzymatic conjugation approach yields homogeneous antibody–drug conjugates. Bioconjug Chem 25:569–578. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc400574z
Dennler P, Fischer E, Schibli R (2015) Antibody conjugates: from heterogeneous populations to defined reagents. Antibodies 4:197–224. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib4030197
Deonarain MP, Yahioglu G, Stamati I, Marklew J (2015) Emerging formats for next-generation antibody drug conjugates. Expert Opin Drug Discov 10:463–481. https://doi.org/10.1517/17460441.2015.1025049
DiJoseph JF, Popplewell A, Tickle S, Ladyman H, Lawson A, Kunz A, Khandke K, Armellino DC, Boghaert ER, Hamann PR, Zinkewich-Peotti K, Stephens S, Weir N, Damle NK (2005) Antibody-targeted chemotherapy of B-cell lymphoma using calicheamicin conjugated to murine or humanized antibody against CD22. Cancer Immunol Immunother 54:11–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-004-0572-2
Dornan D, Bennett F, Chen Y, Dennis M, Eaton D, Elkins K, French D, Go M, Jack A, Junutula J, Koeppen H, Lau J, McBride J, Rawstron A, Shi X, Yu N, Yu S, Yue P, Zheng B, Ebens A, Polson A (2009) Therapeutic potential of an anti-CD79b antibody–drug conjugate, anti–CD79b-vc-MMAE, for the treatment of non-hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 114:2721–2729. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-02-205500
Doronina SO, Toki BE, Torgov MY, Mendelsohn BA, Cerveny CG, Chace DF, DeBlanc RL, Gearing RP, Bovee TD, Siegall CB, Francisco JA, Wahl AF, Meyer DL, Senter PD (2003) Erratum: development of potent monoclonal antibody auristatin conjugates for cancer therapy. Nat Biotechnol 21:941. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0803-941a
Dorywalska M, Strop P, Melton-Witt J, Hasa-Moreno A, Farias S, Galindo Casas M, Delaria K, Lui V, Poulsen K, Sutton J, Bolton G, Zhou D, Moine L, Dushin R, Tran T, Liu S, Rickert M, Foletti D, Shelton D, Rajpal A (2015) Site-dependent degradation of a non-cleavable auristatin-based linker-payload in Rodent plasma and its effect on ADC efficacy. PLoS ONE 10:e0132282. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132282
Dott J, Abila B, Wuerthner JU (2018) Current trends in the clinical development of antibody-drug conjugates in oncology. Pharma Med 32:259–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40290-018-0238-6
Dovgan I, Koniev O, Kolodych S, Wagner A (2019) Antibody–Oligonucleotide Conjugates as Therapeutic, Imaging, and detection agents. Bioconjug Chem 30:2483–2501. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.9b00306
Drenkard D, Becke F, Langstein J, Spruss T, Kunz-Schughart L, Tan T, Lim Y, Schwarz H (2007) CD137 is expressed on blood vessel walls at sites of inflammation and enhances monocyte migratory activity. FASEB J 21:456–463. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.05-4739com
Dugal-Tessier J, Barnscher S, Kanai A, Mendelsohn B (2017) Synthesis and evaluation of Dolastatin 10 Analogues containing heteroatoms on the amino acid side chains. J Nat Prod 80:2484–2491. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00359
Dugal-Tessier J, Thirumalairajan S, Jain N (2021) Antibody-oligonucleotide conjugates: a twist to antibody-drug conjugates. J Clin Med 10:838. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040838
Falck G, Müller KM (2018) Enzyme-based labeling strategies for antibody–drug conjugates and antibody mimetics. Antibodies 7:4. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib7010004
Fang Q, Kanugula S, Pegg AE (2005) Function of domains of human O6-Alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase. Biochemistry 44:15396–15405. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi051460d
Fatima SW, Khare SK (2022) Benefits and challenges of antibody drug conjugates as novel form of chemotherapy. J Control Release 341:555–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.12.013
Feng Y, Zhu Z, Chen W, Prabakaran P, Lin K, Dimitrov DS (2014) Conjugates of small molecule drugs with antibodies and other proteins. Biomedicines 2:1–13
Fierer JO, Veggiani G, Howarth M (2014) SpyLigase peptide–peptide ligation polymerizes affibodies to enhance magnetic cancer cell capture. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111:E1176–E1181. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1315776111
Firer MA, Gellerman G (2012) Targeted drug delivery for cancer therapy: the other side of antibodies. J Hematol Oncol 5:70. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-8722-5-70
Fu C, Yu L, Miao Y, Liu X, Yu Z, Wei M (2022a) Peptide–drug conjugates (PDCs): A novel trend of research and development on targeted therapy, hype or hope? Acta Pharm Sin B In Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2022.07.020
Fu Z, Li S, Han S, Shi C, Zhang Y (2022b) Antibody drug conjugate: the “biological missile” for targeted cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-00947-7
Fujii T, Matsuda Y, Seki T, Shikida N, Iwai Y, Ooba Y, Takahashi K, Isokawa M, Kawaguchi S, Hatada N (2023) AJICAP second generation: improved chemical site-specific conjugation technology for antibody-drug conjugate production
Garbaccio RM (2014) Chemistry of antibody–small molecule drug conjugates. In: Chemical linkers in antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). Elsevier
Garcia-Alonso S, Ocana A, Pandiella A (2018) Resistance to antibody–drug conjugates. Cancer Res 78:2159–2165. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-3671
Gauzy-Lazo L, Sassoon I, Brun M-P (2020) Advances in antibody–drug conjugate design: current clinical landscape and future innovations. SLAS Discov Adv Sci Drug Discov 25:843–868. https://doi.org/10.1177/2472555220912955
Gaya AM, Rustin GJS (2005) Vascular disrupting agents: a new class of drug in cancer therapy. Clin Oncol 17:277–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clon.2004.11.011
Gerber H-P, Koehn F, Abraham R (2013) The antibody-drug conjugate: an enabling modality for natural product-based cancer therapeutics. Nat Prod Rep 30:625–639. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3np20113a
Gerlach M, Stoschek T, Leonhardt H, Hackenberger CPR, Schumacher D, Helma J (2019) Tubulin tyrosine ligase-mediated modification of proteins. Methods Mol Biol 2012:327–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9546-2_17
Gianolio DA, Rouleau C, Bauta WE, Lovett D, Cantrell WR, Recio A, Wolstenholme-Hogg P, Busch M, Pan P, Stefano JE, Kramer HM, Goebel J, Krumbholz RD, Roth S, Schmid SM, Teicher BA (2012) Targeting HER2-positive cancer with dolastatin 15 derivatives conjugated to trastuzumab, novel antibody–drug conjugates. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 70:439–449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-012-1925-8
Goldenberg D, Sharkey R (2019) Antibody-drug conjugates targeting TROP-2 and incorporating SN-38: a case study of anti-TROP-2 sacituzumab govitecan. MAbs 11:987–995. https://doi.org/10.1080/19420862.2019.1632115
Goldmacher VS, Kovtun YV (2011) Antibody–drug conjugates: using monoclonal antibodies for delivery of cytotoxic payloads to cancer cells. Ther Deliv 2:397–416. https://doi.org/10.4155/tde.10.98
Goli N, Bolla PK, Talla V (2018) Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs): potent biopharmaceuticals to target solid and hematological cancers- an overview. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 48:106–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2018.08.022
Goundry WRF, Parker JS (2022) Payloads for antibody–drug conjugates. Org Process Res Dev 26:2121–2123
Govindan SV, Sharkey RM, Goldenberg DM (2016) Prospects and progress of antibody-drug conjugates in solid tumor therapies. Expert Opin Biol Ther 16:883–893. https://doi.org/10.1517/14712598.2016.1173203
Govindan SV, Cardillo TM, Goldenberg DM (2019) Topoisomerase inhibitors as antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) payloads. In: Thurston DE, Jackson P (ed) Cytotoxic payloads for antibody–drug conjugates, p 166–186
Goyon A, D’Atri V, Colas O, Fekete S, Beck A, Guillarme D (2017) Characterization of 30 therapeutic antibodies and related products by size exclusion chromatography: feasibility assessment for future mass spectrometry hyphenation. J Chromatogr B 1065:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.09.027
Griebenow N, Dilmaç AM, Greven S, Bräse S (2016) Site-specific conjugation of peptides and proteins via rebridging of Disulfide Bonds using the thiol–yne coupling reaction. Bioconjug Chem 27:911–917. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00682
Grünewald J, Brock A, Geierstanger BH (2019). In: Nuijens T, Schmidt M (eds) Site-specific antibody labeling using Phosphopantetheinyl transferase-catalyzed ligation BT—enzyme-mediated ligation methods. Springer, New York, pp 237–278
Hageman MJ, Morozowich W (2007). In: Stella VJ, Borchardt RT, Hageman MJ, Oliyai R, Maag H, Tilley JW (eds) Case study: irinotecan (CPT-11), a water-soluble prodrug of SN-38 BT—prodrugs: challenges and rewards part 1. Springer, New York, pp 1269–1279
Haque M, Forte N, Baker JR (2021) Site-selective lysine conjugation methods and applications towards antibody–drug conjugates. Chem Commun 57:10689–10702. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CC03976H
Harris L, Tavares D, Rui L, Maloney E, Wilhelm A, Costoplus J, Archer K, Bogalhas M, Harvey L, Wu R, Chen X, Xu X, Connaughton S, Wang L, Whiteman K, Ab O, Hong E, Widdison W, Shizuka M, Miller M, Pinkas J, Keating T, Chari R, Fishkin N (2015) SeriMabs: N-terminal serine modification enables modular, site-specific payload incorporation into antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). Cancer Res 75:647. https://doi.org/10.1158/1538-7445.AM2015-647
Hartley JA (2021) Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) delivering pyrrolobenzodiazepine (PBD) dimers for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther 21:931–943. https://doi.org/10.1080/14712598.2020.1776255
Havaei S, Aucoin M, Jahanian-Najafabadi A (2021) Pseudomonas Exotoxin-Based immunotoxins: over three decades of efforts on Targeting Cancer cells with the Toxin. Front Oncol 11:781800–781817. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.781800
Hoppenz P, Els-Heindl S, Beck-Sickinger AG (2020) Peptide-drug conjugates and their targets in Advanced Cancer Therapies. Front Chem 8:571. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00571
Huang RYC, Chen G (2016) Characterization of antibody-drug conjugates by mass spectrometry: advances and future trends. Drug Discov Today 21:850–855
Huisin’t Veld RV, Ma S, Kines R, Savinainen A, Rich CC, Ossendorp F, Jager M (2022) A novel virus-like drug conjugate (VDC) in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of primary tumors and distant metastasis. J Clin Oncol 40:e14544–e14544. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.e14544
Hussain AF, Grimm A, Sheng W, Zhang C, Al-Rawe M, Bräutigam K, Abu Mraheil M, Zeppernick F, Meinhold-Heerlein I (2021) Toward homogenous antibody drug conjugates using enzyme-based conjugation approaches. Pharmaceuticals 14:343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040343
Jain N, Smith SW, Ghone S, Tomczuk B (2015) Current ADC linker chemistry. Pharm Res 32:3526–3540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-015-1657-7
Jeffrey SC, De Brabander J, Miyamoto J, Senter PD (2010) Expanded utility of the β-Glucuronide linker: ADCs that deliver phenolic cytotoxic agents. ACS Med Chem Lett 1:277–280. https://doi.org/10.1021/ml100039h
Jin Y, Edalatian Zakeri S, Bahal R, Wiemer AJ (2022) New Technologies Bloom together for bettering Cancer Drug Conjugates. Pharmacol Rev 74:680–711. https://doi.org/10.1124/pharmrev.121.000499
Johnston MC, Scott CJ (2018) Antibody conjugated nanoparticles as a novel form of antibody drug conjugate chemotherapy. Drug Discov Today Technol 30:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ddtec.2018.10.003
Jones J, Pack L, Hunter JH, Valliere-Douglass JF (2020). In: MAbs (ed) Native size-exclusion chromatography-mass spectrometry: suitability for antibody–drug conjugate drug-to-antibody ratio quantitation across a range of chemotypes and drug-loading levels. Taylor & Francis, p 1682895
Joubert N, Beck A, Dumontet C, Denevault-Sabourin C (2020) Antibody–drug conjugates: the last decade. Pharmaceuticals 13:245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13090245
Jovčevska I, Muyldermans S (2020) The therapeutic potential of nanobodies. BioDrugs 34:11–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40259-019-00392-z
Juan A, Cimas FJ, Bravo I, Pandiella A, Ocaña A, Alonso-Moreno C (2020) Antibody conjugation of nanoparticles as therapeutics for breast cancer treatment. Int J Mol Sci 21:6018. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176018
Junutula J, Raab H, Clark S, Bhakta S, Leipold D, Weir S, Chen Y, Simpson M, Tsai S, Dennis M, Lu Y, Meng Y, Ng C, Yang J, Lee C, Duenas E, Gorrell J, Katta V, Kim A, McDorman K, Flagella K, Venook R, Ross S, Spencer S, Lee W, Lowman H, Vandlen R, Sliwkowski M, Scheller R, Polakis P, Mallet W (2008) Site-specific conjugation of a cytotoxic drug to an antibody improves the therapeutic index. Nat Biotechnol 26:925–932. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1480
Kalinovsky DV, Kibardin AV, Kholodenko IV, Svirshchevskaya EV, Doronin II, Konovalova MV, Grechikhina MV, Rozov FN, Larin SS, Deyev SM (2022) Therapeutic efficacy of antibody-drug conjugates targeting GD2-positive tumors. J Immunother cancer 10:e004646. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2022-004646
Källsten M (2020) Development and evaluation of analytical techniques for antibodies and antibody-drug conjugates: From verification of conjugation to stability testing. Digital Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Science and Technology 1901, Acta Universitatis Upsaliensis
Kang MS, Kong TWS, Khoo JYX, Loh T-P (2021) Recent developments in chemical conjugation strategies targeting native amino acids in proteins and their applications in antibody–drug conjugates. Chem Sci 12:13613–13647. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC02973H
Kern JC, Cancilla M, Dooney D, Kwasnjuk K, Zhang R, Beaumont M, Figueroa I, Hsieh S, Liang L, Tomazela D (2016) Discovery of pyrophosphate diesters as tunable, soluble, and bioorthogonal linkers for site-specific antibody–drug conjugates. J Am Chem Soc 138:1430–1445. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b12547
Khongorzul P, Ling CJ, Khan FU, Ihsan AU, Zhang J (2020) Antibody-drug conjugates: a comprehensive review. Mol Cancer Res 18:3–19. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.mcr-19-0582
Kim D-H, Seo J-M, Shin K-J, Yang S-G (2021) Design and clinical developments of aptamer-drug conjugates for targeted cancer therapy. Biomater Res 25:42. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40824-021-00244-4
Ko MJ, Song D, Kim J, Kim JY, Eom J, Sung B, Son Y-G, Kim YM, Lee SH, You W-K, Jung J (2021) N-terminal selective conjugation method widens the therapeutic window of antibody–drug conjugates by improving tolerability and stability. MAbs 13:1914885. https://doi.org/10.1080/19420862.2021.1914885
Kostova V, Désos P, Starck J-B, Kotschy A (2021) The chemistry behind ADCs. Pharmaceuticals 14:442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050442
Kovtun YV, Goldmacher VS (2007) Cell killing by antibody–drug conjugates. Cancer Lett 255:232–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2007.04.010
Krüger T, Dierks T, Sewald N (2019) Formylglycine-generating enzymes for site-specific bioconjugation. Biol Chem 400:289–297. https://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2018-0358
Kulkarni PN, Blair AH, Ghose T, Mammen M (1985) Conjugation of methotrexate to IgG antibodies and their F(ab)2 fragments and the effect of conjugated methotrexate on tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Immunol Immunother 19:211–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00199228
Kumar A, Kinneer K, Masterson L, Ezeadi E, Howard P, Wu H, Gao C, Dimasi N (2018) Synthesis of a heterotrifunctional linker for the site-specific preparation of antibody-drug conjugates with two distinct warheads. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 28:3617–3621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.10.043
Lee A (2021) Loncastuximab tesirine: first approval. Drugs 81:1229–1233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-021-01550-w
Lee JM, Lee SH, Hwang J-W, Oh SJ, Kim B, Jung S, Shim S, Lin PW, Lee SB, Cho M-Y, Koh YJ, Kim SY, Ahn S, Lee J, Kim K, Cheong KH, Choi J, Kim K-A (2016) Novel strategy for a bispecific antibody: induction of dual target internalization and degradation. Oncogene 35:4437–4446. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.514
Li X, Fang T, Boons G-J (2014) Preparation of well-defined antibody-drug conjugates through glycan remodeling and strain-promoted azide-alkyne cycloadditions. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201402606
Liu P, Ga L, Aodeng G, Wang Y, Ai J (2022) Aptamer-drug conjugates: New probes for imaging and targeted therapy. Biosens Bioelectron X 10:100126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosx.2022.100126
Liu-Shin L, Fung A, Malhotra A, Ratnaswamy G (2018). In: MAbs (ed) Influence of disulfide bond isoforms on drug conjugation sites in cysteine-linked IgG2 antibody-drug conjugates. Taylor & Francis, pp 583–595
Loganzo F, Sung M, Gerber H-P (2016) Mechanisms of resistance to antibody–drug conjugates. Mol Cancer Ther 15:2825–2834. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0408
Lopus M (2022) Shooting Cancer with magic bullets. Promises and challenges of antibody-drug conjugates. Resonance 27:1127–1130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12045-022-1409-z
Lu J, Jiang F, Lu A, Zhang G (2016) Linkers having a crucial role in antibody–drug conjugates. Int. J. Mol. Sci.17
Lyon R (2018) Drawing lessons from the clinical development of antibody-drug conjugates. Drug Discov Today Technol 30:105–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ddtec.2018.10.001
Mack F, Ritchie M, Sapra P (2014) The next generation of antibody drug conjugates. Semin Oncol 41:637–652. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.seminoncol.2014.08.001
Maderna A, Doroski M, Subramanyam C, Porte A, Leverett C, Vetelino B, Cheng Z, Risley H, Parris K, Pandit J, Varghese A, Shanker S, Song C, Sukuru S, Farley K, Wagenaar M, Shapiro M, Musto S, Lam M, O’Donnell C (2014) Discovery of cytotoxic dolastatin 10 analogues with N-terminal modifications. J Med Chem. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm501649k
Majidi J, Barar J, Baradaran B, Abdolalizadeh J, Omidi Y (2009) Target therapy of cancer: implementation of monoclonal antibodies and nanobodies. Hum Antibodies 18:81–100. https://doi.org/10.3233/HAB-2009-0204
Mallet W, Gadkari R, Pearson C, Dulgeroff L, Luo A, Luo AA, Melrose J, Nolin J, Lee A, Zhou M, Anand P, Sarma G, Henning K, Blum L, Chapin S, Bogaert L, Ackerman S, Kudirka R, Shen Y, Dornan D (2021) 784 BDC-2034: discovery of a CEA-targeting immune-stimulating antibody conjugate (ISAC) for solid tumors. J Immunother Cancer 9:A819–A819. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2021-SITC2021.784
Maruani A (2018) Bispecifics and antibody–drug conjugates: a positive synergy. Drug Discov Today Technol 30:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ddtec.2018.09.003
Matsuda Y, Mendelsohn BA (2021) Recent advances in drug–antibody ratio determination of antibody–drug conjugates. Chem Pharm Bull 69:976–983. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.c21-00258
Mazor R, Onda M, Pastan I (2016) Immunogenicity of therapeutic recombinant immunotoxins. Immunol Rev 270:152–164. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12390
McCombs JR, Owen SC (2015) Antibody drug conjugates: design and selection of linker, payload and conjugation chemistry. AAPS J 17:339–351. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-014-9710-8
Mcdonagh C, Turcott E, Westendorf L, Webster J, Alley S, Kim K, Andreyka J, Stone I, Hamblett K, Francisco J, Carter P (2006) Engineered antibody-drug conjugates with defined sites and stoichiometries of drug attachment. Protein Eng Des Sel 19:299–307. https://doi.org/10.1093/protein/gzl013
Mckertish CM, Kayser V (2021) Advances and limitations of antibody drug conjugates for cancer. Biomedicines 9:872. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9080872
Mendelsohn BA, Barnscher SD, Snyder JT, An Z, Dodd JM, Dugal-Tessier J (2017) Investigation of hydrophilic auristatin derivatives for use in antibody drug conjugates. Bioconjug Chem 28:371–381. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00530
Menon S, Parakh S, Scott A, Gan H (2022) Antibody-drug conjugates: beyond current approvals and potential future strategies. Explor Target anti-tumor Ther 3:252–277. https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2022.00082
Meyer C, Liebscher S, Bordusa F (2016) Selective coupling of click anchors to proteins via trypsiligase. Bioconjug Chem 27:47–53. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00618
Modi S, Saura C, Yamashita T, Park Y, Kim S, Tamura K, Andre F, Iwata H, Ito Y, Tsurutani J, Sohn J, Denduluri N, Perrin C, Aogi K, Tokunaga E, Im S, Lee K, Hurvitz S, Cortes J, Lee C, Chen S, Zhang L, Shahidi J, Yver A, Krop I (2019) Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in previously treated HER2-Positive breast Cancer. N Engl J Med 382:610–621. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1914510
Müller P, Martin K, Theurich S, Schreiner J, Savic S, Terszowski G, Lardinois D, Heinzelmann-Schwarz VA, Schlaak M, Kvasnicka H-M, Spagnoli G, Dirnhofer S, Speiser DE, von Bergwelt-Baildon M, Zippelius A (2014) Microtubule-depolymerizing agents used in antibody–drug conjugates induce Antitumor Immunity by Stimulation of dendritic cells. Cancer Immunol Res 2:741–755. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-13-0198
Nadkarni DV (2020) Conjugations to endogenous cysteine residues: antibody-drug conjugates. Springer, pp 37–49
Nauseef JT, Bander NH, Tagawa ST (2021) Emerging prostate-specific membrane Antigen-based therapeutics: small molecules, antibodies, and Beyond. Eur Urol Focus 7:254–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2021.02.006
Nessler I, Khera E, Vance S, Kopp A, Qiu Q, Keating TA, Abu-Yousif AO, Sandal T, Legg J, Thompson L, Goodwin N, Thurber GM (2020) Increased tumor penetration of single-domain antibody–drug Conjugates improves in vivo efficacy in prostate Cancer models. Cancer Res 80:1268–1278. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-2295
Neupane R, Bergquist J (2017) Analytical techniques for the characterization of antibody drug conjugates: Challenges and prospects. Eur J Mass Spectrom 23:417–426. https://doi.org/10.1177/1469066717733919
Nicolò E, Giugliano F, Ascione L, Tarantino P, Corti C, Tolaney SM, Cristofanilli M, Curigliano G (2022) Combining antibody-drug conjugates with immunotherapy in solid tumors: current landscape and future perspectives. Cancer Treat Rev 106:102395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2022.102395
Pahl A, Lutz C, Hechler T (2018) Amanitins and their development as a payload for antibody-drug conjugates. Drug Discov Today Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ddtec.2018.08.005
Pander G, Uhl P, Kühl N, Haberkorn U, Anderl J, Mier W (2022) Antibody–drug conjugates: what drives their progress? Drug Discov Today 27:103311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2022.06.011
Panowski S, Bhakta S, Raab H, Polakis P, Junutula JR (2014) Site-specific antibody drug conjugates for cancer therapy. MAbs 6:34–45. https://doi.org/10.4161/mabs.27022
Patel TK, Adhikari N, Amin SA, Biswas S, Jha T, Ghosh B (2021) Small molecule drug conjugates (SMDCs): an emerging strategy for anticancer drug design and discovery. New J Chem 45:5291–5321. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NJ04134C
PEG BioPharma (2020) The history of ADC drugs development. https://www.biochempeg.com/article/125.html. Accessed 11 Aug 2022
Perez HL, Cardarelli PM, Deshpande S, Gangwar S, Schroeder GM, Vite GD, Borzilleri RM (2014) Antibody–drug conjugates: current status and future directions. Drug Discov Today 19:869–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2013.11.004
Pillow T, Adhikari P, Blake R, Chen J, Rosario G, Deshmukh G, Figueroa I, Gascoigne K, Kamath A, Kaufman S, Kleinheinz T, Kozak K, Latifi B, Leipold D, Li C, Li R, Mulvihill M, O’Donohue A, Rowntree R, Dragovich P (2019) Antibody conjugation of a chimeric BET degrader enables. Vivo Activity ChemMedChem. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201900497
Polson A, Calemine-Fenaux J, Chan P, Chang W, Christensen E, Clark S, de Sauvage F, Eaton D, Elkins K, Elliott J, Frantz G, Fuji R, Gray A, Harden K, Ingle G, Kljavin N, Koeppen H, Nelson C, Prabhu S, Raab H, Ross S, Stephan J, Scales S, Spencer S, Vandlen R, Wranik B, Yu S, Zheng B, Ebens A (2009) Antibody-drug conjugates for the treatment of non–Hodgkin’s lymphoma: target and linker-drug selection. Cancer Res 69:2358–2364. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2250
Powles T, Rosenberg JE, Sonpavde GP, Loriot Y, Durán I, Lee J-L, Matsubara N, Vulsteke C, Castellano D, Wu C, Campbell M, Matsangou M, Petrylak DP (2021) Enfortumab Vedotin in previously treated Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma. N Engl J Med 384:1125–1135. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2035807
Qasba PK (2015) Glycans of antibodies as a specific site for drug conjugation using glycosyltransferases. Bioconjug Chem 26:2170–2175. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00173
Ramesh M, Ahlawat P, Srinivas NR (2010) Irinotecan and its active metabolite, SN-38: review of bioanalytical methods and recent update from clinical pharmacology perspectives. Biomed Chromatogr 24:104–123. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.1345
Ricart A, Tolcher A (2007) Technology Insight: cytotoxic drug immunoconjugates for cancer therapy. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 4:245–255. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncponc0774
Robak T, Robak E (2014) Current phase II antibody-drug conjugates for the treatment of lymphoid malignancies. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 23:911–924. https://doi.org/10.1517/13543784.2014.908184
Rosen CB, Francis MB (2017) Targeting the N terminus for site-selective protein modification. Nat Chem Biol 13:697–705. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2416
Sang H, Wan N, Lu G, Tian Y, Wang G, Ye H (2020). In: Tumey LN (ed) Conjugation site analysis of lysine-conjugated ADCs BT—antibody-drug conjugates: methods and protocols. Springer, New York, pp 235–250
Sau S, Alsaab HO, Kashaw SK, Tatiparti K, Iyer AK (2017) Advances in antibody–drug conjugates: a new era of targeted cancer therapy. Drug Discov Today 22:1547–1556
Savinainen A, Kines R, Rich CC (2022) A first in class Virus-Like Drug Conjugate (VDC) shows anti-tumor activity in cancers that commonly metastasize to the Choroid. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 63:2616
Savoy EA, Olatunji FP, Yoon H, Mesbahi N, Knight JR, Berkman CE (2021) Acid-labile linkers. Chem Linkers Antibody-Drug Conjug 81:213. https://doi.org/10.1039/9781839165153
Schettini F, Barbao P, Brasó-Maristany F, Galván P, Martínez D, Paré L, De Placido S, Prat A, Guedan S (2021) Identification of cell surface targets for CAR-T cell therapies and antibody–drug conjugates in breast cancer. ESMO Open 6:100102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100102
Schumacher D, Hackenberger C, Leonhardt H, Helma-Smets J (2016) Current status: site-specific antibody drug conjugates. J Clin Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-016-0265-6
Shah B, Li M, Wypych J, Joubert MK, Zhang Z (2022) Observation of Heavy-Chain C-Terminal Amidation in Human endogenous IgG. J Pharm Sci 111:2445–2450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2022.06.012
Sheyi R, de la Torre BG, Albericio F (2022) Linkers: an assurance for controlled delivery of antibody-drug conjugate. Pharmaceutics 14:396. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020396
Siegmund V, Piater B, Zakeri B, Eichhorn T, Fischer F, Deutsch C, Becker S, Toleikis L, Hock B, Betz UAK, Kolmar H (2016) Spontaneous isopeptide bond formation as a powerful tool for engineering site-specific antibody-drug conjugates. Sci Rep 6:39291. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39291
Singh R, Erickson HK (2009). In: Dimitrov AS (ed) Antibody–cytotoxic agent conjugates: preparation and characterization BT—therapeutic antibodies: methods and protocols. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 445–467
Sochaj AM, Świderska KW, Otlewski J (2015) Current methods for the synthesis of homogeneous antibody–drug conjugates. Biotechnol Adv 33:775–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.05.001
Sun MMC, Beam KS, Cerveny CG, Hamblett KJ, Blackmore RS, Torgov MY, Handley FGM, Ihle NC, Senter PD, Alley SC (2005) Reduction—alkylation strategies for the modification of specific monoclonal antibody disulfides. Bioconjug Chem 16:1282–1290. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc050201y
Sussman D, Westendorf L, Meyer D, Leiske C, Anderson M, Okeley N, Alley S, Lyon R, Sanderson R, Carter P, Benjamin D (2018) Engineered cysteine antibodies: an improved antibody-drug conjugate platform with a novel mechanism of drug-linker stability. Protein Eng Des Sel. https://doi.org/10.1093/protein/gzx067
Tan C (2015). In: Wang J, Shen W-C, Zaro JL (eds) Payloads of antibody-drug conjugates BT—antibody-drug conjugates: the 21st century magic bullets for Cancer. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 11–22
Tang H, Liu Y, Yu Z, Sun M, Lin L, Liu W, Han Q, Wei M, Jin Y (2019) The analysis of key factors related to adcs structural design. Front Pharmacol 10:373. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00373
Tarantino P, Hamilton E, Tolaney SM, Cortes J, Morganti S, Ferraro E, Marra A, Viale G, Trapani D, Cardoso F, Penault-Llorca F, Viale G, Andrè F, Curigliano G (2020) HER2-Low breast Cancer: pathological and clinical Landscape. J Clin Oncol 38:1951–1962. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.19.02488
Tarantino P, Carmagnani Pestana R, Corti C, Modi S, Bardia A, Tolaney SM, Cortes J, Soria J, Curigliano G (2022) Antibody–drug conjugates: Smart chemotherapy delivery across tumor histologies. CA Cancer J Clin 72:165–182. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21705
Tedeschini T, Campara B, Grigoletto A, Bellini M, Salvalaio M, Matsuno Y, Suzuki A, Yoshioka H, Pasut G (2021) Polyethylene glycol-based linkers as hydrophilicity reservoir for antibody-drug conjugates. J Control Release 337:431–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.07.041
Tiberghien AC, Levy J-N, Masterson LA, Patel NV, Adams LR, Corbett S, Williams DG, Hartley JA, Howard PW (2016) Design and synthesis of Tesirine, a clinical antibody–drug conjugate pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer payload. ACS Med Chem Lett 7:983–987. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.6b00062
Tsuchikama K, An Z (2018) Antibody-drug conjugates: recent advances in conjugation and linker chemistries. Protein Cell 9:33–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-016-0323-0
U.S.F.D.A (2022) FDA D.I.S.C.O. Burst edition: FDA approval of Elahere (mirvetuximab soravtansine-gynx) for FRα positive, platinum-resistant epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or peritoneal cancer. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-disco-burst-edition-fda-approval-elahere-mirvetuximab-soravtansine-gynx-fra-positive-platinum. Accessed 31 Jan 2023
van Berkel SS, van Delft FL (2018) Enzymatic strategies for (near) clinical development of antibody-drug conjugates. Drug Discov Today Technol 30:3–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ddtec.2018.09.005
Vankemmelbeke M, Durrant L (2016) Third-generation antibody drug conjugates for cancer therapy–a balancing act. Ther Deliv 7:141–144. https://doi.org/10.4155/tde-2016-0002
Wagh A, Song H, Zeng M, Tao L, Das TK (2018) In: MAbs (ed) Challenges and new frontiers in analytical characterization of antibody-drug conjugates. Taylor & Francis, pp 222–243
Wakanka A, Chen Y, Gokarn Y, Jacobson FS (2011) In: MAbs (ed) Analytical methods for physicochemical characterization of antibody drug conjugates. Taylor & Francis, pp 161–172
Waldum HL, Sandvik AK, Brenna E, Fossmark R, Qvigstad G, Soga J (2008) Classification of tumours. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 27:70. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-9966-27-70
Walsh SJ, Bargh JD, Dannheim FM, Hanby AR, Seki H, Counsell AJ, Ou X, Fowler E, Ashman N, Takada Y, Isidro-Llobet A, Parker JS, Carroll JS, Spring DR (2021) Site-selective modification strategies in antibody–drug conjugates. Chem Soc Rev 50:1305–1353. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CS00310G
Widdison WC, Chari RVJ (2013) In: Phillips GL (ed) Factors involved in the design of cytotoxic payloads for antibody–drug Conjugates BT - antibody-drug conjugates and immunotoxins: from pre-clinical development to therapeutic applications. Springer, New York, pp 93–115
Woitok M, Klose D, Niesen J, Richter W, Abbas M, Stein C, Fendel R, Bialon M, Püttmann C, Fischer R (2016) The efficient elimination of solid tumor cells by EGFR-specific and HER2-specific scFv-SNAP fusion proteins conjugated to benzylguanine-modified auristatin F. Cancer Lett 381:323–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.08.003
Wolf P, Elsässer-Beile U (2009) Pseudomonas exotoxin A: from virulence factor to anti-cancer agent. Int J Med Microbiol 299:161–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2008.08.003
Wu T, Zhu J (2021) Recent development and optimization of pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin immunotoxins in cancer therapeutic applications. Int Immunopharmacol 96:107759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107759
Yamada K, Shikida N, Shimbo K, Ito Y, Khedri Z, Matsuda Y, Mendelsohn BA (2019) AJICAP: affinity peptide mediated regiodivergent functionalization of native antibodies. Angew Chemie 131:5648–5653
Yamazaki CM, Yamaguchi A, Anami Y, Xiong W, Otani Y, Lee J, Ueno NT, Zhang N, An Z, Tsuchikama K (2021) Antibody-drug conjugates with dual payloads for combating breast tumor heterogeneity and drug resistance. Nat Commun 12:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23793-7
Yin J, Liu F, Li X, Walsh CT (2004) Labeling proteins with small molecules by site-specific posttranslational modification. J Am Chem Soc 126:7754–7755. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja047749k
You J, Zhang J, Wang J, Jin M (2021) Cysteine-based coupling: challenges and solutions. Bioconjug Chem 32:1525–1534. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.1c00213
Yuan D, Zhang Y, Lim KH, Leung SKP, Yang X, Liang Y, Lau WCY, Chow KT, Xia J (2022) Site-selective lysine acetylation of human immunoglobulin G for immunoliposomes and bispecific antibody complexes. J Am Chem Soc 144:18494–18503
Zacharias N, Podust VN, Kajihara KK, Leipold D, Del Rosario G, Thayer D, Dong E, Paluch M, Fischer D, Zheng K (2022) A homogeneous high-DAR antibody–drug conjugate platform combining THIOMAB antibodies and XTEN polypeptides. Chem Sci 13:3147–3160. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC05243H
Zhang Y, Park K-Y, Suazo KF, Distefano MD (2018) Recent progress in enzymatic protein labelling techniques and their applications. Chem Soc Rev 47:9106–9136. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CS00537K
Zhang J, Jain A, Milhas S, Williamson DJ, Mysliwy J, Lodge A, Thirlway J, Al Nakeeb M, Miller A, Rabbitts TH (2021) An antibody-drug conjugate with intracellular drug release properties showing specific cytotoxicity against CD7-positive cells. Leuk Res 108:106626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2021.106626
Zhao P, Zhang Y, Li W, Jeanty C, Xiang G, Dong Y (2020) Recent advances of antibody drug conjugates for clinical applications. Acta Pharm Sin B 10:1589–1600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2020.04.012
Zhou L, Xu N, Sun Y, Liu X, Margaret (2014a) Targeted biopharmaceuticals for cancer treatment. Cancer Lett 352:145–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2014.06.020
Zhou Q, Stefano JE, Manning C, Kyazike J, Chen B, Gianolio DA, Park A, Busch M, Bird J, Zheng X, Simonds-Mannes H, Kim J, Gregory RC, Miller RJ, Brondyk WH, Dhal PK, Pan CQ (2014b) Site-specific antibody–drug conjugation through Glycoengineering. Bioconjug Chem 25:510–520. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc400505q
Zhu X, Huo S, Xue C, An B, Qu J (2020) Current LC-MS-based strategies for characterization and quantification of antibody-drug conjugates. J Pharm Anal 10:209–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2020.05.008
Zou S (2023) Directions for next generation antibody-drug conjugates. https://www.eposters.net/poster/directions-for-next-generation-antibody-drug-conjugates#. Accessed 31 Jan 2023
Zuberbühler K, Casi G, Bernardes GJL, Neri D (2012) Fucose-specific conjugation of hydrazide derivatives to a vascular-targeting monoclonal antibody in IgG format. Chem Commun 48:7100–7102. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC32412A
Zugazagoitia J, Guedes C, Ponce S, Ferrer I, Molina-Pinelo S, Paz-Ares L (2016) Current challenges in cancer treatment. Clin Ther 38:1551–1566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2016.03.026
Acknowledgements
Authors, Ritwik Maiti, Bhumika Patel and Nrupesh Patel are thankful to Nirma University, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India for providing resourceful support to carry out literature review for the present work. The efforts of author, Dr. NIrav Dhanesha for this publication were supported by grants from the NHLBI/NIH (R01HL15854601), and by the Career Development Award (20CDA3560123) from American Heart Association.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Institute of Health, NHLBI/NIH (R01HL15854601), and American Heart Association, Career Development Award (20CDA3560123) to Nirav Dhanesha
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Declared None.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Maiti, R., Patel, B., Patel, N. et al. Antibody drug conjugates as targeted cancer therapy: past development, present challenges and future opportunities. Arch. Pharm. Res. 46, 361–388 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-023-01447-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-023-01447-0