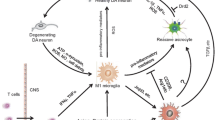
Abstract
Glial cells outnumber neurons in the brain and play important roles in the neuroinflammation that accompanies brain damage in neurodegenerative diseases. In Parkinson’s disease (PD), dopaminergic neuronal loss is accompanied by inflammatory changes in microglia, astrocytes, innate immune cells, and infiltrating peripheral immune cells. Neuroinflammation is probably a fundamental immune response to protect neurons from harm and compensate for neuronal damage, but at the same time, its neurotoxic effects exacerbate neuron damage. Furthermore, neuroinflammatory response is regulated by immune cells, such as microglia, astrocytes, and peripheral immune cells, and by cytokines and chemokines. Accordingly, it is crucial that we understand how such immune cells in the brain regulate neuroinflammatory responses in PD pathology. This review describes the roles played by glia-mediated neuroinflammation in PD, both good and bad, and the therapeutic strategies used to treat PD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal S, Yadav A, Chaturvedi RK (2017) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) as therapeutic target in neurodegenerative disorders. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 483:1166–1177
Agostinho P, Cunha RA, Oliveira C (2010) Neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 16:2766–2778
Aid S, Bosetti F (2011) Targeting cyclooxygenases-1 and -2 in neuroinflammation: therapeutic implications. Biochimie 93:46–51
Aloisi F (2001) Immune function of microglia. Glia 36:165–179
Anderson MA, Burda JE, Ren Y, Ao Y, O’shea TM, Kawaguchi R, Coppola G, Khakh BS, Deming TJ, Sofroniew MV (2016) Astrocyte scar formation aids central nervous system axon regeneration. Nature 532:195–200
Appel SH, Beers DR, Henkel JS (2010) T cell-microglial dialogue in Parkinson’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: are we listening? Trends Immunol 31:7–17
Attwell D, Buchan AM, Charpak S, Lauritzen M, Macvicar BA, Newman EA (2010) Glial and neuronal control of brain blood flow. Nature 468:232–243
Barcia C, Ros CM, Annese V, Gomez A, Ros-Bernal F, Aguado-Yera D, Martinez-Pagan ME, De Pablos V, Fernandez-Villalba E, Herrero MT (2011) IFN-gamma signaling, with the synergistic contribution of TNF-alpha, mediates cell specific microglial and astroglial activation in experimental models of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Dis 2:e142
Bayraktar OA, Fuentealba LC, Alvarez-Buylla A, Rowitch DH (2014) Astrocyte development and heterogeneity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7:a020362
Becerra-Calixto A, Cardona-Gomez GP (2017) The role of astrocytes in neuroprotection after brain stroke: potential in cell therapy. Front Mol Neurosci 10:88
Benarroch EE (2013) Microglia: multiple roles in surveillance, circuit shaping, and response to injury. Neurology 81:1079–1088
Bernardinelli Y, Randall J, Janett E, Nikonenko I, Konig S, Jones EV, Flores CE, Murai KK, Bochet CG, Holtmaat A, Muller D (2014) Activity-dependent structural plasticity of perisynaptic astrocytic domains promotes excitatory synapse stability. Curr Biol 24:1679–1688
Boato F, Hechler D, Rosenberger K, Ludecke D, Peters EM, Nitsch R, Hendrix S (2011) Interleukin-1 beta and neurotrophin-3 synergistically promote neurite growth in vitro. J Neuroinflamm 8:183
Boka G, Anglade P, Wallach D, Javoy-Agid F, Agid Y, Hirsch EC (1994) Immunocytochemical analysis of tumor necrosis factor and its receptors in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 172:151–154
Bortolanza M, Cavalcanti-Kiwiatkoski R, Padovan-Neto FE, Da-Silva CA, Mitkovski M, Raisman-Vozari R, Del-Bel E (2015) Glial activation is associated with l-DOPA induced dyskinesia and blocked by a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 73:377–387
Breidert T, Callebert J, Heneka MT, Landreth G, Launay JM, Hirsch EC (2002) Protective action of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonist pioglitazone in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 82:615–624
Brenneman DE, Schultzberg M, Bartfai T, Gozes I (1992) Cytokine regulation of neuronal survival. J Neurochem 58:454–460
Brochard V, Combadiere B, Prigent A, Laouar Y, Perrin A, Beray-Berthat V, Bonduelle O, Alvarez-Fischer D, Callebert J, Launay JM, Duyckaerts C, Flavell RA, Hirsch EC, Hunot S (2009) Infiltration of CD4+ lymphocytes into the brain contributes to neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson disease. J Clin Invest 119:182–192
Calabrese V, Santoro A, Monti D, Crupi R, Di Paola R, Latteri S, Cuzzocrea S, Zappia M, Giordano J, Calabrese EJ, Franceschi C (2018) Aging and Parkinson’s Disease: inflammaging, neuroinflammation and biological remodeling as key factors in pathogenesis. Free Radic Biol Med 115:80–91
Chen PC, Vargas MR, Pani AK, Smeyne RJ, Johnson DA, Kan YW, Johnson JA (2009) Nrf2-mediated neuroprotection in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: critical role for the astrocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:2933–2938
Chen H, Lin W, Zhang Y, Lin L, Chen J, Zeng Y, Zheng M, Zhuang Z, Du H, Chen R, Liu N (2016) IL-10 promotes neurite outgrowth and synapse formation in cultured cortical neurons after the oxygen-glucose deprivation via JAK1/STAT3 pathway. Sci Rep 6:30459
Chen Z, Chen S, Liu J (2018) The role of T cells in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 169:1–23
Cheray M, Joseph B (2018) Epigenetics control microglia plasticity. Front Cell Neurosci 12:243
Cherry JD, Olschowka JA, O’banion MK (2014) Neuroinflammation and M2 microglia: the good, the bad, and the inflamed. J Neuroinflamm 11:98
Chhor V, Le Charpentier T, Lebon S, Ore MV, Celador IL, Josserand J, Degos V, Jacotot E, Hagberg H, Savman K, Mallard C, Gressens P, Fleiss B (2013) Characterization of phenotype markers and neuronotoxic potential of polarised primary microglia in vitro. Brain Behav Immun 32:70–85
Choi SY, Son TG, Park HR, Jang YJ, Oh SB, Jin B, Lee J (2012) Naphthazarin has a protective effect on the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine-induced Parkinson’s disease model. J Neurosci Res 90:1842–1849
Collins LM, Toulouse A, Connor TJ, Nolan YM (2012) Contributions of central and systemic inflammation to the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Neuropharmacology 62:2154–2168
Curran CS, Bertics PJ (2012) Eosinophils in glioblastoma biology. J Neuroinflamm 9:11
Dehmer T, Heneka MT, Sastre M, Dichgans J, Schulz JB (2004) Protection by pioglitazone in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease correlates with I kappa B alpha induction and block of NF kappa B and iNOS activation. J Neurochem 88:494–501
Doorn KJ, Moors T, Drukarch B, Van De Berg W, Lucassen PJ, Van Dam AM (2014) Microglial phenotypes and toll-like receptor 2 in the substantia nigra and hippocampus of incidental Lewy body disease cases and Parkinson’s disease patients. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2:90
Eikelenboom P, Van Exel E, Hoozemans JJ, Veerhuis R, Rozemuller AJ, Van Gool WA (2010) Neuroinflammation—an early event in both the history and pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurodegener Dis 7:38–41
Episcopo FL, Tirolo C, Testa N, Caniglia S, Morale MC, Marchetti B (2013) Reactive astrocytes are key players in nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurorepair in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: focus on endogenous neurorestoration. Curr Aging Sci 6:45–55
Fawcett JW, Asher RA (1999) The glial scar and central nervous system repair. Brain Res Bull 49:377–391
Franco R, Fernandez-Suarez D (2015) Alternatively activated microglia and macrophages in the central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 131:65–86
Gan L, Vargas MR, Johnson DA, Johnson JA (2012) Astrocyte-specific overexpression of Nrf2 delays motor pathology and synuclein aggregation throughout the CNS in the alpha-synuclein mutant (A53T) mouse model. J Neurosci 32:17775–17787
Gelders G, Baekelandt V, Van Der Perren A (2018) Linking neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. J Immunol Res 2018:4784268
Glass CK, Saijo K, Winner B, Marchetto MC, Gage FH (2010) Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell 140:918–934
Gorshkov K, Aguisanda F, Thorne N, Zheng W (2018) Astrocytes as targets for drug discovery. Drug Discov Today 23:673–680
Graeber MB (2010) Changing face of microglia. Science 330:783–788
Gu XL, Long CX, Sun L, Xie C, Lin X, Cai H (2010) Astrocytic expression of Parkinson’s disease-related A53T alpha-synuclein causes neurodegeneration in mice. Mol Brain 3:12
Harms AS, Barnum CJ, Ruhn KA, Varghese S, Trevino I, Blesch A, Tansey MG (2011) Delayed dominant-negative TNF gene therapy halts progressive loss of nigral dopaminergic neurons in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Mol Ther 19:46–52
Harry GJ, Kraft AD (2008) Neuroinflammation and microglia: considerations and approaches for neurotoxicity assessment. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 4:1265–1277
Hashida K, Kitao Y, Sudo H, Awa Y, Maeda S, Mori K, Takahashi R, Iinuma M, Hori O (2012) ATF6alpha promotes astroglial activation and neuronal survival in a chronic mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 7:e47950
Hirsch EC, Hunot S (2009) Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: a target for neuroprotection? Lancet Neurol 8:382–397
Hoenen C, Gustin A, Birck C, Kirchmeyer M, Beaume N, Felten P, Grandbarbe L, Heuschling P, Heurtaux T (2016) Alpha-synuclein proteins promote pro-inflammatory cascades in microglia: stronger effects of the A53T mutant. PLoS ONE 11:e0162717
Huhner L, Rilka J, Gilsbach R, Zhou X, Machado V, Spittau B (2017) Interleukin-4 protects dopaminergic neurons in vitro but is dispensable for MPTP-induced neurodegeneration in vivo. Front Mol Neurosci 10:62
Iannaccone S, Cerami C, Alessio M, Garibotto V, Panzacchi A, Olivieri S, Gelsomino G, Moresco RM, Perani D (2013) In vivo microglia activation in very early dementia with Lewy bodies, comparison with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 19:47–52
Imamura K, Hishikawa N, Sawada M, Nagatsu T, Yoshida M, Hashizume Y (2003) Distribution of major histocompatibility complex class II-positive microglia and cytokine profile of Parkinson’s disease brains. Acta Neuropathol 106:518–526
Jakel RJ, Townsend JA, Kraft AD, Johnson JA (2007) Nrf2-mediated protection against 6-hydroxydopamine. Brain Res 1144:192–201
Janda E, Boi L, Carta AR (2018) Microglial phagocytosis and its regulation: a therapeutic target in Parkinson’s disease? Front Mol Neurosci 11:144
Joers V, Tansey MG, Mulas G, Carta AR (2017) Microglial phenotypes in Parkinson’s disease and animal models of the disease. Prog Neurobiol 155:57–75
Kim C, Ho DH, Suk JE, You S, Michael S, Kang J, Joong Lee S, Masliah E, Hwang D, Lee HJ, Lee SJ (2013a) Neuron-released oligomeric alpha-synuclein is an endogenous agonist of TLR2 for paracrine activation of microglia. Nat Commun 4:1562
Kim JH, Choi DJ, Jeong HK, Kim J, Kim DW, Choi SY, Park SM, Suh YH, Jou I, Joe EH (2013b) DJ-1 facilitates the interaction between STAT1 and its phosphatase, SHP-1, in brain microglia and astrocytes: a novel anti-inflammatory function of DJ-1. Neurobiol Dis 60:1–10
Kim ME, Lee JY, Lee KM, Park HR, Lee E, Lee Y, Lee JS, Lee J (2016) Neuroprotective effect of bee venom is mediated by reduced astrocyte activation in a subchronic MPTP-induced model of Parkinson's disease. Arch Pharm Res 39:1160–1170
Klegeris A, Pelech S, Giasson BI, Maguire J, Zhang H, Mcgeer EG, Mcgeer PL (2008) Alpha-synuclein activates stress signaling protein kinases in THP-1 cells and microglia. Neurobiol Aging 29:739–752
Koprich JB, Reske-Nielsen C, Mithal P, Isacson O (2008) Neuroinflammation mediated by IL-1beta increases susceptibility of dopamine neurons to degeneration in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroinflamm 5:8
Kreft M, Bak LK, Waagepetersen HS, Schousboe A (2012) Aspects of astrocyte energy metabolism, amino acid neurotransmitter homoeostasis and metabolic compartmentation. ASN Neuro 4:20. https://doi.org/10.1042/AN20120007
Kreutzberg GW (1996) Microglia: a sensor for pathological events in the CNS. Trends Neurosci 19:312–318
Lan X, Han X, Li Q, Yang QW, Wang J (2017) Modulators of microglial activation and polarization after intracerebral haemorrhage. Nat Rev Neurol 13:420–433
Lastres-Becker I, Ulusoy A, Innamorato NG, Sahin G, Rabano A, Kirik D, Cuadrado A (2012) alpha-Synuclein expression and Nrf2 deficiency cooperate to aggravate protein aggregation, neuronal death and inflammation in early-stage Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 21:3173–3192
Ledesma MD, Galvan C, Hellias B, Dotti C, Jensen PH (2002) Astrocytic but not neuronal increased expression and redistribution of parkin during unfolded protein stress. J Neurochem 83:1431–1440
Lee HJ, Suk JE, Patrick C, Bae EJ, Cho JH, Rho S, Hwang D, Masliah E, Lee SJ (2010) Direct transfer of alpha-synuclein from neuron to astroglia causes inflammatory responses in synucleinopathies. J Biol Chem 285:9262–9272
Lee E, Park HR, Ji ST, Lee Y, Lee J (2014) Baicalein attenuates astroglial activation in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine-induced Parkinson's disease model by downregulating the activations of nuclear factor-kappaB, ERK, and JNK. J Neurosci Res 92:130–139
Lee KW, Woo JM, Im JY, Park ES, He L, Ichijo H, Junn E, Mouradian MM (2015a) Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 modulates the phenotype of alpha-synuclein transgenic mice. Neurobiol Aging 36:519–526
Lee Y, Chun HJ, Lee KM, Jung YS, Lee J (2015b) Silibinin suppresses astroglial activation in a mouse model of acute Parkinson’s disease by modulating the ERK and JNK signaling pathways. Brain Res 1627:233–242
Lee KM, Lee Y, Chun HJ, Kim AH, Kim JY, Lee JY, Ishigami A, Lee J (2016) Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of morin in a murine model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci Res 94:865–878
Lee Y, Cho JH, Lee S, Lee W, Chang SC, Chung HY, Moon HR, Lee J (2019) Neuroprotective effects of MHY908, a PPAR alpha/gamma dual agonist, in a MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease model. Brain Res 1704:47–58
Li R, Huang YG, Fang D, Le WD (2004) (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial activation and protects against inflammation-mediated dopaminergic neuronal injury. J Neurosci Res 78:723–731
Liddelow SA, Barres BA (2017) Reactive astrocytes: production, function, and therapeutic potential. Immunity 46:957–967
Liddelow SA, Guttenplan KA, Clarke LE, Bennett FC, Bohlen CJ, Schirmer L, Bennett ML, Munch AE, Chung WS, Peterson TC, Wilton DK, Frouin A, Napier BA, Panicker N, Kumar M, Buckwalter MS, Rowitch DH, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Stevens B, Barres BA (2017) Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 541:481–487
Litteljohn D, Mangano E, Shukla N, Hayley S (2009) Interferon-gamma deficiency modifies the motor and co-morbid behavioral pathology and neurochemical changes provoked by the pesticide paraquat. Neuroscience 164:1894–1906
Loane DJ, Byrnes KR (2010) Role of microglia in neurotrauma. Neurotherapeutics 7:366–377
Lucas SM, Rothwell NJ, Gibson RM (2006) The role of inflammation in CNS injury and disease. Br J Pharmacol 147(Suppl 1):S232–240
Maccormac LP, Muqit MM, Faulkes DJ, Wood NW, Latchman DS (2004) Reduction in endogenous parkin levels renders glial cells sensitive to both caspase-dependent and caspase-independent cell death. Eur J Neurosci 20:2038–2048
Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena P, Vecchi A, Locati M (2004) The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol 25:677–686
Martinez FO, Sica A, Mantovani A, Locati M (2008) Macrophage activation and polarization. Front Biosci 13:453–461
Mccoy MK, Ruhn KA, Martinez TN, Mcalpine FE, Blesch A, Tansey MG (2008) Intranigral lentiviral delivery of dominant-negative TNF attenuates neurodegeneration and behavioral deficits in hemiparkinsonian rats. Mol Ther 16:1572–1579
Mcguire SO, Ling ZD, Lipton JW, Sortwell CE, Collier TJ, Carvey PM (2001) Tumor necrosis factor alpha is toxic to embryonic mesencephalic dopamine neurons. Exp Neurol 169:219–230
Mirza B, Hadberg H, Thomsen P, Moos T (2000) The absence of reactive astrocytosis is indicative of a unique inflammatory process in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 95:425–432
Mogi M, Harada M, Kondo T, Riederer P, Inagaki H, Minami M, Nagatsu T (1994) Interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6, epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor-alpha are elevated in the brain from parkinsonian patients. Neurosci Lett 180:147–150
Mullett SJ, Hinkle DA (2009) DJ-1 knock-down in astrocytes impairs astrocyte-mediated neuroprotection against rotenone. Neurobiol Dis 33:28–36
Nakagawa Y, Chiba K (2015) Diversity and plasticity of microglial cells in psychiatric and neurological disorders. Pharmacol Ther 154:21–35
Neal M, Richardson JR (2018) Epigenetic regulation of astrocyte function in neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1864:432–443
Niranjan R (2014) The role of inflammatory and oxidative stress mechanisms in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease: focus on astrocytes. Mol Neurobiol 49:28–38
Niranjan R (2018) Recent advances in the mechanisms of neuroinflammation and their roles in neurodegeneration. Neurochem Int 120:13–20
Ouchi Y, Yoshikawa E, Sekine Y, Futatsubashi M, Kanno T, Ogusu T, Torizuka T (2005) Microglial activation and dopamine terminal loss in early Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 57:168–175
Pekny M, Wilhelmsson U, Pekna M (2014) The dual role of astrocyte activation and reactive gliosis. Neurosci Lett 565:30–38
Pisanu A, Lecca D, Mulas G, Wardas J, Simbula G, Spiga S, Carta AR (2014) Dynamic changes in pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in microglia after PPAR-gamma agonist neuroprotective treatment in the MPTPp mouse model of progressive Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 71:280–291
Prabhakaran K, Chapman GD, Gunasekar PG (2011) alpha-Synuclein overexpression enhances manganese-induced neurotoxicity through the NF-kappaB-mediated pathway. Toxicol Mech Methods 21:435–443
Ransohoff RM (2016) How neuroinflammation contributes to neurodegeneration. Science 353:777–783
Rappold PM, Tieu K (2010) Astrocytes and therapeutics for Parkinson’s disease. Neurotherapeutics 7:413–423
Reynolds AD, Banerjee R, Liu J, Gendelman HE, Mosley RL (2007) Neuroprotective activities of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. J Leukoc Biol 82:1083–1094
Rojo AI, Mcbean G, Cindric M, Egea J, Lopez MG, Rada P, Zarkovic N, Cuadrado A (2014) Redox control of microglial function: molecular mechanisms and functional significance. Antioxid Redox Signal 21:1766–1801
Saijo K, Winner B, Carson CT, Collier JG, Boyer L, Rosenfeld MG, Gage FH, Glass CKA (2009) Nurr1/CoREST pathway in microglia and astrocytes protects dopaminergic neurons from inflammation-induced death. Cell 137:47–59
Sawada M, Imamura K, Nagatsu T (2006) Role of cytokines in inflammatory process in Parkinson’s disease. Springer, Vienna, pp 273–381
Schnegg CI, Kooshki M, Hsu FC, Sui G, Robbins ME (2012) PPARdelta prevents radiation-induced proinflammatory responses in microglia via transrepression of NF-kappaB and inhibition of the PKCalpha/MEK1/2/ERK1/2/AP-1 pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 52:1734–1743
Simon C, Gotz M, Dimou L (2011) Progenitors in the adult cerebral cortex: cell cycle properties and regulation by physiological stimuli and injury. Glia 59:869–881
Sofroniew MV (2015) Astrocyte barriers to neurotoxic inflammation. Nat Rev Neurosci 16:249–263
Streit WJ, Mrak RE, Griffin WS (2004) Microglia and neuroinflammation: a pathological perspective. J Neuroinflamm 1:14
Suh HS, Zhao ML, Derico L, Choi N, Lee SC (2013) Insulin-like growth factor 1 and 2 (IGF1, IGF2) expression in human microglia: differential regulation by inflammatory mediators. J Neuroinflamm 10:37
Surmeier DJ, Guzman JN, Sanchez J, Schumacker PT (2012) Physiological phenotype and vulnerability in Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2:a009290
Wang Q, Liu Y, Zhou J (2015a) Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease and its potential as therapeutic target. Transl Neurodegener 4:19
Wang WY, Tan MS, Yu JT, Tan L (2015b) Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines released from microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Transl Med 3:136
Wang YL, Ju B, Zhang YZ, Yin HL, Liu YJ, Wang SS, Zeng ZL, Yang XP, Wang HT, Li JF (2017) Protective effect of curcumin against oxidative stress-induced injury in rats with parkinson’s disease through the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 43:2226–2241
Wilms H, Rosenstiel P, Romero-Ramos M, Arlt A, Schafer H, Seegert D, Kahle PJ, Odoy S, Claasen JH, Holzknecht C, Brandenburg LO, Deuschl G, Schreiber S, Kirik D, Lucius R (2009) Suppression of MAP kinases inhibits microglial activation and attenuates neuronal cell death induced by alpha-synuclein protofibrils. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 22:897–909
Xu X, Zhang A, Zhu Y, He W, Di W, Fang Y, Shi X (2018) MFG-E8 reverses microglial-induced neurotoxic astrocyte (A1) via NF-kappaB and PI3 K-Akt pathways. J Cell Physiol 234:904–914
Yadav S, Gupta SP, Srivastava G, Srivastava PK, Singh MP (2012) Role of secondary mediators in caffeine-mediated neuroprotection in maneb- and paraquat-induced Parkinson's disease phenotype in the mouse. Neurochem Res 37:875–884
Yang TT, Lin C, Hsu CT, Wang TF, Ke FY, Kuo YM (2013) Differential distribution and activation of microglia in the brain of male C57BL/6 J mice. Brain Struct Funct 218:1051–1060
Yang JS, Wu XH, Yu HG, Teng LS (2017) Tangeretin inhibits neurodegeneration and attenuates inflammatory responses and behavioural deficits in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced Parkinson's disease dementia in rats. Inflammopharmacology 25:471–484
Yun SP, Kam TI, Panicker N, Kim S, Oh Y, Park JS, Kwon SH, Park YJ, Karuppagounder SS, Park H, Kim S, Oh N, Kim NA, Lee S, Brahmachari S, Mao X, Lee JH, Kumar M, An D, Kang SU, Lee Y, Lee KC, Na DH, Kim D, Lee SH, Roschke VV, Liddelow SA, Mari Z, Barres BA, Dawson VL, Lee S, Dawson TM, Ko HS (2018) Block of A1 astrocyte conversion by microglia is neuroprotective in models of Parkinson’s disease. Nat Med 24:931–938
Zamanian JL, Xu L, Foo LC, Nouri N, Zhou L, Giffard RG, Barres BA (2012) Genomic analysis of reactive astrogliosis. J Neurosci 32:6391–6410
Zhang QS, Heng Y, Mou Z, Huang JY, Yuan YH, Chen NH (2017) Reassessment of subacute MPTP-treated mice as animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin 38:1317–1328
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (Grant no. 2018R1D1A1B07043493).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no potential conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y., Lee, S., Chang, SC. et al. Significant roles of neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: therapeutic targets for PD prevention. Arch. Pharm. Res. 42, 416–425 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-019-01133-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-019-01133-0