Abstract
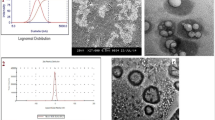
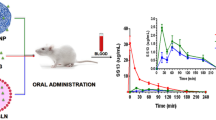
The objective of this study is to investigate the pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of free breviscapine (BVP) and coated BVP-loaded poly (D, L-lactic acid) nanoparticles (BVP-PLA-NPs) in rats after i.v. administration. Coated BVP-PLA-NPs were prepared by the spontaneous emulsification solvent diffusion method and characterized. The BVP content in the NPs, the biological samples and in vitro release was measured by the high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The mean sizes of coated BVP-PLA-NPs were 177 and 319 nm with a narrow distribution and smooth sphere shapes, entrapment efficiency of 86.9% and 93.1%, respectively. Drug release profiles in phosphate buffer and plasma exhibited a biphasic release phenomenon. After i.v. administration of free BVP and NPs suspensions in rats, area under plasma concentration-time curve and elimination t 1/2 were increased 9.3-fold and 10.9-fold for 177 nm of NPs, and 4.4-fold and 17.1-fold for 319 nm of NPs compared with that of free BVP, respectively. NPs were mainly distributed in liver, spleen, heart and brain. In addition, NPs could penetrate blood brain barrier (BBB) and the particle size had some effect on pharmacokinetics and biodistribution. Coated BVP-PLA-NPs could effectively avoid the capture by the reticuloendothelial system and prolong the half-life of BVP. Moreover, these NPs could penetrate BBB and enhance the accumulation of BVP in brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Roman, R., Naik, A., Kalia, Y. N., Guy, R. H., and Fessi, H., Enhancement of topical delivery from biodegradable nanoparticles. Pharm. Res., 21, 1818–1825 (2004).
Cui, J. M. and Wu, S., The advance on the research of breviscapine (in chinese). Natural Product Res. Develop., 15, 225–229 (2003).
Dunn, S. E., Coombes, A. G. A., Garnett, M. C., Davis, S. S., Davies, M. C., and Illum, L., In vitro cell interaction and in vivo biodistribution of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanospheres surface modified by poloxamer and poloxamine copolymers. J. Control. Release, 44, 65–76 (1997).
Elizabeth, C. and Samir, M., Prolonged circulation of large polymeric nanoparticles by non-covalent adsorption on erythrocytes. J. Control. Release, 100, 111–119 (2004).
Ge, Q. H., Zou, Z., Zhi, X. J., Ma, L. L., and Chen, X. H., Pharmacokinetics and absolute bioavailability of breviscapine in beagle dogs (in chinese). Chin. J. Pharm., 34, 618–620 (2003).
Giannavola, C., Bucolo, C., Maltese, A., Paolino, D., Vandelli, M. A., Puglisi, G., Lee, V. H. L., and Fresta, M., Influence of preparation conditions on acyclovir-loaded poly-d,l-lactic acid nanopheres and effect of PEG coating on ocular drug bioavailability. Pharm. Res., 20, 584–590 (2003).
Gulyaev, A., Gelperina, S. E., Skidan, I. N., Antropov, A. S., Kivman, G. Y., and Kreuter, J., Significant transport of doxorubicin into the brain with polysorbate 80 coated nanoparticles. Pharm. Res., 16, 1564–1569 (1999).
Gupta, A. K., Madan, S., Majumdar, D. K., and Maitra, A., Ketorolac entrapped in polymeric micelles: preparation, characterization and ocular anti-inflammatory studies. Int. J. Pharm., 209, 1–14 (2000).
Hitzman, C. J., Elmquist, W. F., Wattenberg, L. W., and Wiedmann, T. S., Development of a respirable, sustained release microcarrier for 5-fluorouracil I: in vitro assessment of liposomes, microspheres, and lipid coated nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Sci., 95, 1114–1126 (2006).
Holland, S. J. and Tighe, B. J., Biodegradable polymers. In: Garderton, D. and Jones, T. (Eds.), Advances in pharmaceutical science, vol. 6. New York, Academic Press. pp. 101–164 (1992).
Illum, L. and Davis, S. S., Effect of the non-ionic surfactant poloxamer 338 on the fate and deposition of polystyrene microspheres following intravenous administration. J. Pharm. Sci., 72, 1086–1089 (1983).
Juliano, R. L., Factors affecting the clearance kinetics and tissue distribution of liposomes, microspheres and emulsions. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 2, 31–54 (1988).
Kreuter, J., Nanoparticulate systems for brain delivery of drug. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 47, 65–81 (2001).
Kreuter, J., Alyautdin, R. N., Kharkevich, D. A., and Ivanov, A. A., Passage of peptides through the blood-brain barrier with colloidal polymeric particles (nanoparticles). Brain Res., 674, 171–174 (1995).
Levy, M. Y. and Benita, S., Drug release from submicronized o/w emulsion: a new in vitro kinetic evaluation model. Int. J. Pharm., 66, 29–37 (1990).
Liu, C., Liu, H. G., Yu, X. L., and Guo, H. C., Advances in studies on Erigeron breviscapus (in chinene). Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 22, 8–11 (2003a).
Liu, M. X., Dong, J., Yang, Y. L., Yang, X. L., and Xu, H. B., Research on system of triptolide-loaded poly (D, L-lactic acid) nanoparticles (in chinese). J. Chinese Pharm. Univ., 35, 117–121 (2004).
Liu, M. X., Dong, J., Yang, Y. L., Yang, X. L., and Xu, H. B., Anti-inflammatory effects of triptolide loaded poly (d,l-lactic acid) nanoparticles on adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol., 97, 219–225 (2005).
Liu, Y. M., Lin, A. H., Chen, H., and Zeng, F. D., Study on pharmacokinetics of scutellarin in rabbits (in chinese). Acta Pharm. Sinica, 38, 775–778 (2003b).
Lu, Q., Qu, L. J., Yu, H., Luo, C. M., Han, C. L., and Liu, A. M., Advances in studies on Erigeron breviscapus (in chinese). Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drug, 36, 141–144 (2005).
Ma, K., Li, Y. L., and Zhang, Y. P., The clinical application of breviscapine (in chinese). Herald of Medicine, 22, 79–80 (2003).
Magenheim, B., Levy, M. Y., and Benita, S., A new in vitro technique for the evaluation of drug release profile from colloidal carriers-ultrafiltration technique at low pressure. Int. J. Pharm., 94, 115–123 (1993).
Manjunath, K. and Venkateswarlu, V., Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and bioavailability of clozapine solid lipid nanoparticles after intravenous and intraduodenal administration. J. Control. Release, 107, 215–228 (2005).
Moghimi, S. M., Pavey K. D., and Hunter A. C., Real-time evidence of surface modification at polystyrene lattices by poloxamine 908 in the presence of serum: in vivo conversion of macrophage-prone nanoparticles to stealth entities by poloxamine 908. FEBS Lett., 547, 177–182 (2003).
Muller, R. H. and Goppert, T. M., Protein adsorption patterns on poloxamer-and poloxamine-stabilized solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN). Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 60, 361–372 (2005).
Owens, D. E. and Peppas, N. A., Opsonization, biodistration and pharmacokinetics of polymeric nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm., 307, 93–102 (2006).
Redhead, H. M., Davis, S. S., and Illum, L., Drug delivery in poly (lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles surface modified with poloxamer 407 and poloxamine 908: in vitro characterization and in vivo evaluation. J. Control. Release, 70, 353–363 (2001).
Schroeder, U., Sommerfeld, P., Ulrich, S., and Sabel, B. A., Nanoparticle technology for delivery of drugs across the blood-brain barrier. J. Pharm. Sci., 87, 1305–1307 (1998).
Soppimath, K. S., Aminabhavi, T. M., Kulkarni, A. R., and Rudzinski, W. E., Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. J. Control. Release, 70, 1–20 (2001).
Vega, E., Egea, M. A., Valls, O., Espina, M., and Garcia, M. L., Flurbiprofen loaded biodegradable nanoparticles for ophtalmic administration. J. Pharm. Sci., 95, 2393–2405 (2006).
Win, K. Y. and Feng, S. S., Effects of particle size and surface coating on cellular uptake of polymeric nanoparticles for oral delivery of anticancer drugs. Biomaterials, 26, 2713–2722 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Li, H., Luo, G. et al. Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of surface modification polymeric nanoparticles. Arch. Pharm. Res. 31, 547–554 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-1191-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-1191-8