Abstract
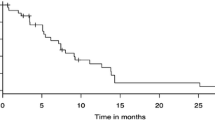
The present study was undertaken to evaluate the efficacy of radiotherapy in palliation of dysphagia in patients with squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of esophagus and to see the quality of life (QoL) following radiotherapy. This was a prospective clinical study done between September 2006 and May 2008. All consecutive patients with SCC of the esophagus, who are not candidates for definitive treatment, were included in the study. Dysphagia and QoL were assessed using modified Takita's grading and modified questionnaire based on EORTC QLQ 30 respectively. External beam radiotherapy (EBRT) was delivered to all patients using linear accelerator 6 Mv photons. Patients who had good response with EBRT were further subjected to intraluminal brachytherapy (ILBT) at 700 cGy using Iridium-192. The cumulative dose each patient received was 65 Gy. Patients were followed up at 6 weeks from completion of treatment to look for any difference in dysphagia grade and QoL following therapy. Thirty-three patients were included in the study. The mean age among males and females was 60.9 and 49.8 years, respectively. Nineteen patients (57.6 %) received EBRT followed by ILBT; the remaining patients received only EBRT. Seven were lost during follow-up, and seven (21.2 %) died during the study period of 6 weeks. Nineteen (57.6 %) were followed up. On follow-up endoscopy, evidence of residual stricture was observed in 57.9 %, and growth in 36.8 %. Of the patients, 27.8 % had biopsy-confirmed residual disease. The median dysphagia score decreased from 4 to 3 after treatment (p = 0.002) in 17 (89.5 %) patients. The mean QoL score improved from 107.5 to 114.1 at 6-week follow-up. Following radiotherapy, 26.3 % had persistent chest pain, increased cough with expectoration in 15.8 %, and hyperpigmentation of skin in 10.5 %. Radiotherapy gives significant relief of dysphagia and improves QoL in 90 % of patients with SCC of esophagus. However, following radiotherapy, a number of patients will have persistent stricture, ulceration, and residual disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108
Cherian JV, Sivaraman R, Muthusamy AK, Jayanthi V (2007) Carcinoma of the esophagus in Tamil Nadu (South India): 16-year trends from a tertiary center. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 16:245–249
Vivekanandam S, Reddy KS, Velavan K, Balasundaram V, Ranga Rao S, Subba Rao KS, Nachiappan M (2001) External beam radiotherapy and intraluminal brachytherapy in advanced inoperable esophageal cancer: JIPMER experience. Am J Clin Oncol 24(2):128–130
Javle M, Ailawadhi S, Yang GY, Nwogu CE, Schiff MD, Nava HR (2006) Palliation of malignant dysphagia in esophageal cancer: a literature-based review. J Support Oncol 4(8):365–73, 379
Wong R, Malthaner R (2006) Combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy (without surgery) compared with radiotherapy alone in localized carcinoma of the esophagus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 25(1):CD002092
O'Toole DM, Golden AM (1991) Evaluating cancer patients for rehabilitation potential. West J Med 155:384–387
Peters JH, Meester TR, Stein HJ (1995) Surgical therapy for cancer of the esophagus and cardia. In: Castell DO (ed) The esophagus, 2nd edn. Little Brown, New York, pp 293–335
Blazeby JM, Alderson D, Winstone K et al (1996) Development of an EORTC questionnaire module to be used in quality of life assessment for patients with oesophageal cancer. The EORTC Quality of Life study Group. Eur J Cancer 32A:1912–1917
Maroju NK, Anbalagan P, Kate V, Ananthakrishnan N (2006) Improvement in dysphagia and quality of life with self-expanding metallic stents in malignant esophageal strictures. Indian J Gastroenterol 25:62–65
Kassam Z, Wong RK, Ringash J, Ung Y, Kamra J, DeBoer G et al (2008) A phase I/II study to evaluate the toxicity and efficacy of accelerated fractionation radiotherapy for the palliation of dysphagia from carcinoma of the oesophagus. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 20:53–60
Daly JM, Fry WA, Little AG, Winchester DP, McKee RF, Stewart AK et al (2000) Esophageal cancer: results of an American College of Surgeons Patient Care Evaluation Study. J Am Coll Surg 190:562–572
Hayter CR, Huff-Winters C, Paszat L, Youssef YM, Shelley WE, Schulze K (2000) A prospective trial of short-course radiotherapy plus chemotherapy for palliation of dysphagia from advanced esophageal cancer. Radiother Oncol 56:329–333
Caspers RJ, Welvaart K, Verkes RJ, Hermans J, Leer JW (1988) The effect of radiotherapy on dysphagia and survival in patients with esophageal cancer. Radiother Oncol 12:15–23
Sule-Suso J, Brunt AM, Lindup R et al (1991) Hyperfractionated accelerated radiotherapy for carcinoma of the oesophagus. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 3:209–213
Harvey JA, Bessell JR, Beller E, Thomas J, Gotley DC, Burmeister BH et al (2004) Chemoradiation therapy is effective for the palliative treatment of malignant dysphagia. Dis Esophagus 17:260–265
Cho SH, Shim HJ, Lee SR, Ahn JS, Yang DH, Kim YK et al (2008) Concurrent chemoradiotherapy with S-1 and cisplatin in advanced esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus 21:697–703
Homs MY, Steyerberg EW, Eijkenboom WM, Tilanus HW, Stalpers LJ, Bartelsman JF et al (2004) Single-dose brachytherapy versus metal stent placement for the palliation of dysphagia from oesophageal cancer: multicentre randomised trial. Lancet 364:1497–504
Datta NR, Kumar S, Nangia S, Hukku S, Ayyagari S (1998) A non-randomized comparison of two radiotherapy protocols in inoperable squamous cell carcinoma of the oesophagus. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 10:306–312
Homs MY, Eijkenboom WM, Coen VL, Haringsma J, van Blankenstein M et al (2003) High dose rate brachytherapy for the palliation of malignant dysphagia. Radiother Oncol 66:327–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, N.R.V., Karthigeyan, M., Vikram, K. et al. Palliative Radiotherapy in Esophageal Cancer. Indian J Surg 77, 34–38 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-013-0817-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-013-0817-4