Abstract
Background
Systematic surveys of undergraduate medical education have cautiously supported the outcomes of Problem Based Learning (PBL) compared with traditional learning. This article provides a critical overview of PBL, its limitations in the developing country scenario and our proposed model of PBL triggered by Real cases, to address these limitations.
Aim
Our hypothesis was to see whether the proposed CBL model would work in Indian set up in comparison with traditional teaching
Methods
We followed a modified Barrow’s Model. A tutor selected a real case and created a problem scenario which was progressively disclosed to students, and learning issues were raised.
In session 2 students presented self studied learning issues. The process was evaluated throughout with feedback from students and faculty.
Results
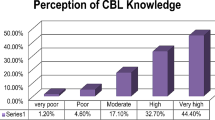
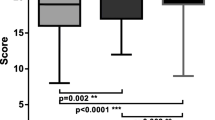
We were successful in establishing CBL. Study group (n=57) students scored better in SAQ((short Answer question) and EMQ((extended matching question)) assessment, (Mean study 21.15+/− 4.0565, control 18.5357+/−3.8632, n=56, p value 0.01.) Students appreciated it as good learning activity
Statistical design
SAQ and EMQ, are compared in study vs. control groups by unpaired ‘t’ test & also by equivalent non-parametric Mann-Whitney test
Conclusion
The training of doctors is too important an activity for bold experiments to be conducted without discovery what really happens. We had success in establishing Case based learning with faculty of almost all departments participating in the project as Resources. Although size of sample is small, CBL is found to be an effective modality of imparting medical education with effective integration of all departments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Colliver JA (2000) Effectiveness of problem-based learning curricula: research and theory. Acad Med 75(3):259–226
Sundblad G, Sigrell B, Knutson John L, Lindkvist C (2002) Stsudents’ evolution of a learning method: a comparison between problem-based learning and more traditional methods in a specialist university training programme in psychotherapy; Med Teach 24(3):268–271
Vernon D, Blake R (1993) Does problem-based learning work? A meta-analysis of evaluative research. Acad Med 68(7):550–563
Kiguli-Malwadde E, Muyinda Z, Kiguli S (2007) Problem-based learning: a place in the sun for radiology. Med Educ 41(5):507–508
Ronco R, Munoz G, Prado P (2007) Problem-based learning in tiny tots and mothers-to-be. Med Educ 41(5):512
Barrows HS (1986) A taxonomy of problem-based learning methods. Med Educ. 20(6):481–486
Schmidt HG (1993) Foundation of problem based learning: some explanatory notes. Med Educ 27(5):422–432
Wyller VB, Wyller TB (2002) Relations between background, process and outcome in the first semester of a new, problem-based medical curriculum. Med Teach 24(5):502–506
Mennin SP, Kalishman S, Friedman M, Pathak D, Snyder J (1996) A survey of graduates from the University of New Mexico’s conventional and community-oriented, problem-based tracks. Acad Med 71(10):1079–1089
Mennin SP, Friedman M, Skipper B, Kalishman S, Snyder J (1993) Performances on the NBME I, II, and III by medical students in the problem-based learning and conventional tracks at the University of New Mexico. Acad Med 68(8):616–624
Neville AJ, Norman GR (2007) PBL in the undergraduate MD program at McMaster University: three iterations in three decades. Acad Med 82(4):370–374
Norman G, Schmidt HG (1992) The psychological basis of problem-based learning: a review of the evidence. Acad Med 67(9):557–565
Albanese M, Mitchell S (1993) Problem-based learning: A review of literature on its outcomes and implementation issues. Acad Med 68:52–81
Nandi PL, Chan JN, Chan CP, et al. (2000) Undergraduate medical education: Comparison of problem-based learning and conventional teaching. Hong Kong Med J 6(3):301–306
Newman M. (2003) A pilot systematic review and meta analysis on the effectiveness of PBL. On behalf of the Campbell collaboration Systematic Review group on the effectiveness of PBL. Newcastle upon Tyne, U.K. Learning and Teaching Support Network-01, Univ of Newcastle upon Tyne
Laurence B, Guttmacher. A guide to PBL case construction, the university of Rochester http://www.urmc.rochester.edu/smd/ca/PBLCaseConstructionGuide.pdf
Queen’s University MD Program Problem-Based Learning Handbook This handbook, with updates and links to other sites on the web, can be found at http://meds.queensu.ca/medicine/pbl/pblhome.htm
Indrayan A and Sarmukaddam S. Medical Biostatistics published, Ed 1. Marcell Dekker, New York, 2001: Pg 114 for grouped data median formula used for column, Refer to page 297 for 95% CI of median
Novak JD (1990) Concept mapping: A useful tool for science education, Journal of Research in Science Teaching 27(10): 937–950
Novak JD (2003) The promise of new ideas and new technology for improving teaching and learning. Cell Biol Educ 2(2):122–132
Spinello E, Fischbach R (2004) Problem-based learning in public health instructions: a pilot study of an online simulation as a problem based approach. Educ Health (Abingdon) 17(3):354–364
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jamkar, A.V., Burdick, W., Morahan, P. et al. Proposed model of case based learning for training undergraduate medical student in surgery. Indian J Surg 69, 176–183 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-007-0016-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-007-0016-2