Abstract
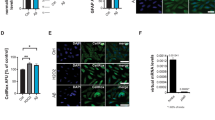
Hippocampal astrocytes play a pivotal role in hippocampal functions. However, trophic factor deprivation during brain injury or neurodegenerative diseases leads to abnormal functions. C-phycocyanin (C-Pc) is an antioxidant compound derived from Spirulina. C-Pc has been studied as a neuroprotectant against brain damage and diseases, however, its effects on hippocampal astrocytes cultured under trophic factor deprivation are unclear. Presently, serum deprivation lowered the metabolic activities, decreasing NADPH diaphorase activity, and decreased production of superoxide dismutase in astrocytes. These effects were reversed after C-Pc treatment. The upregulated NADPH diaphorase activity in activated astrocytes resulted in the increased production of nitric oxide, which protected the hippocampal astrocytes from the harsh trophic factor-deprived environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belay, A., Y. Ota, K. Miyakawa, and H. Shimamatsu (1993) Current knowledge on potential health benefits of Spirulina. J. Appl. Phycol. 5:235–241.
De Oliveira, M. A. C. L., M. P. C. Monteiro, P. G. Robbs, and S. G. F. Leite (1999) Growth and chemical composition of Spirulina maxima and Spirulina platensis biomass at different temperatures. Aquac. Int. 7:261–275.
Romay, C. H., J. Armesto, D. Remirez, R. Gonzalez, N. Ledon, and I. Garcia (1998) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of C-phycocyanin from blue-green algae. Inflamm. Res. 47:36–41.
Romay, C. H., R. Gonzalez, N. Ledon, D. Remirez, and V. Rimbau (2003) C-phycocyanin: a biliprotein with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 4:207–216.
Khan, M., S. Varadharaj, L. P. Ganesan, J. C. Shobha, M. U. Naidu, N. L. Parinandi, S. Tridandapani, V. K. Kutala, and P. Kuppusamy (2006) C-phycocyanin protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury of heart through involvement of p38 MAPK and ERK signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 290: H2136–H2145.
Min, S. K., J. S. Park, L. Luo, Y. S. Kwon, H. C. Lee, H. J. Shim, I. D. Kim, J. K. Lee, and H. S. Shin (2015) Assessment of C-phycocyanin effect on astrocytes-mediated neuroprotection against oxidative brain injury using 2D and 3D astrocyte tissue model. Sci. Rep. 5: 14418.
Khan, Z., P. Bhadouria, and P. S. Bisen (2005) Nutritional and therapeutic potential of Spirulina. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 6:373–379.
Bliss, T. V. and G. L. Collingridge (1993) A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 361:31–39.
Volterra, A. and J. Meldolesi (2005) Astrocytes, from brain glue to communication elements: the revolution continues. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 6:626–640.
Blackburn, D., S. Sargsyan, P. N. Monk, and P. J. Shaw (2009) Astrocyte function and role in motor neuron disease: a future therapeutic target?. Glia. 57:1251–1264.
Becerra-Calixto, A. and G. P. Cardona-Gómez (2017) The role of astrocytes in neuroprotection after brain stroke: potential in cell therapy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 10: 88.
Zhu, H., M. F. Chen, W. J. Yu, W. J. Wang, F. Li, W. C. Liu, Y. Wo, R. Xia, and W. L. Ding (2012) Time-dependent changes in BDNF expression of pentylenetetrazole-induced hippocampal astrocytes in vitro. Brain Res. 1439:1–6.
Payne, C. M., C. Bernstein, and H. Bernstein (1995) Apoptosis overview emphasizing the role of oxidative stress, DNA damage and signal-transduction pathways. Leuk Lymphoma. 19:43–93.
Mosser, D. D., A. W. Caron, L. Bourget, C. Denis-Larose, and B. Massie (1997) Role of the human heat shock protein hsp70 in protection against stress-induced apoptosis. Mol. Cell Biol. 17:5317–5327.
Simm, A., G. Bertsch, H. Frank, U. Zimmermann, and J. Hoppe (1997) Cell death of AKR-2B fibroblasts after serum removal: a process between apoptosis and necrosis. J. Cell Sci. 110:819–828.
Batistatou, A. and L. A. Greene (1993) Internucleosomal DNA cleavage and neuronal cell survival/death. J. Cell Biol. 122:523–532.
Pentón-Rol, G., J. Marín-Prida, G. Pardo-Andreu, G. Martínez-Sánchez, E. F. Acosta-Medina, A. Valdivia-Acosta, N. Lagumersindez-Denis, E. Rodríguez-Jiménez, A. Llópiz-Arzuaga, P. A. López-Saura, G. Guillén-Nieto, and E. Pentón-Arias (2011) C-Phycocyanin is neuroprotective against global cerebralischemia/reperfusion injury in gerbils. Brain Res. Bull. 86:42–52.
Messina, S., G. Molinaro, V. Bruno, G. Battaglia, P. Spinsanti, A. Di Pardo, F. Nicoletti, L. Frati, and A. Porcellini (2008) Enhanced expression of Harvey ras induced by serum deprivation in cultured astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 106:551–559.
Atabay, C., C. M. Cagnoli, E. Kharlamov, M. D. Ikonomovic, and H. Manev (1996) Removal of serum from primary cultures of cerebellar granule neurons induces oxidative stress and DNA fragmentation: protection with antioxidants and glutamate receptor antagonists. J. Neurosci. Res. 43:465–475.
Pandey, S., C. Lopez, and A. Jammu (2003) Oxidative stress and activation of proteasome protease during serum deprivation-induced apoptosis in rat hepatoma cells; inhibition of cell death by melatonin. Apoptosis. 8:497–508.
Hope, B. T., G. J. Michael, K. M. Knigge, and S. R. Vincent (1991) Neuronal NADPH diaphorase is a nitric oxide synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 88:2811–2814.
Dawson, T. M., D. S. Bredt, M. Fotuhi, P. M. Hwang, and S. H. Snyder (1991) Nitric oxide synthase and neuronal NADPH diaphorase are identical in brain and peripheral tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 88:7797–7801.
Ciani, E., S. Guidi, G. Della Valle, G. Perini, R. Bartesaghi, and A. Contestabile (2002) Nitric oxide protects neuroblastoma cells from apoptosis induced by serum deprivation through cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB) activation. J. Biol. Chem. 277:49896–49902.
Kim, Y. M., H. T. Chung, S. S. Kim, J. A. Han, Y. M. Yoo, K. M. Kim, G. H. Lee, H. Y. Yun, A. Green, J. Li, R. L. Simmons, and T. R. Billiar (1999) Nitric oxide protects PC12 cells from serum deprivation-induced apoptosis by cGMP-dependent inhibition of caspase signaling. J. Neurosci. 19:6740–6747.
Brown, G. C., J. P. Bolaños, S. J. Heales, and J. B. Clark (1995) Nitric oxide produced by activated astrocytes rapidly and reversibly inhibits cellular respiration. Neurosci. Lett. 193:201–204.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (NRF-2016 R1D1A1B03931923) and INHA UNIVERSITY research grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, S.J., Choi, J.I., Min, S.K. et al. Evaluation of the Effect of C-phycocyanin on Cultured Rat Primary Hippocampal Astrocytes Undergoing Trophic Factor Deprivation. Biotechnol Bioproc E 24, 870–875 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0102-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0102-x