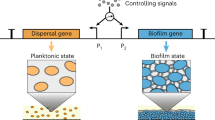
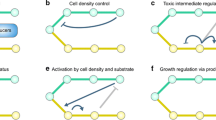
Abstract
Microbial engineering requires accurate information about cellular metabolic networks and a set of molecular tools that can be predictably applied to the efficient redesign of such networks. Recent advances in the field of metabolic engineering and synthetic biology, particularly the development of molecular tools for synthetic regulation in the static and dynamic control of gene expression, have increased our ability to efficiently balance the expression of genes in various biological systems. It would accelerate the creation of synthetic pathways and genetic programs capable of adapting to environmental changes in real time to perform the programmed cellular behavior. In this paper, we review current developments in the field of synthetic regulatory tools for static and dynamic control of microbial gene expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nandagopal, N. and M. B. Elowitz (2011) Synthetic biology: Integrated gene circuits. Science 333: 1244–1248.
Mitchell, W. (2011) Natural products from synthetic biology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 15: 505–515.
Feng, Z. -H., Y. -S. Wang, and Y. -G. Zheng (2011) A new microtiter plate-based screening method for microorganisms producing Alpha-amylase inhibitors. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 16: 894–900.
Meng, H., Y. Wang, Q. Hua, S. Zhang, and X. Wang (2011) In silico analysis and experimental improvement of taxadiene heterologous biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 16: 205–215.
Keasling, J. D. (2008) Synthetic biology for synthetic chemistry. ACS. Chem. Biol. 3: 64–76.
Meng, H., Z. Lu, Y. Wang, X. Wang, and S. Zhang (2011) In silico improvement of heterologous biosynthesis of erythromycin precursor 6-deoxyerythronolide B in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 16: 445–456.
Won, W., C. Park, S. Lee, K. Lee, and J. Lee (2011) Parameter estimation and dynamic control analysis of central carbon metabolism in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 16: 216–228.
Ajikumar, P. K., W. H. Xiao, K. E. Tyo, Y. Wang, F. Simeon, E. Leonard, O. Mucha, T. H. Phon, B. Pfeifer, and G. Stephanopoulos (2010) Isoprenoid pathway optimization for Taxol precursor overproduction in Escherichia coli. Science 330: 70–74.
Anderson, J. C., C. A. Voigt, and A. P. Arkin (2007) Environmental signal integration by a modular AND gate. Mol. Syst. Biol. 3: 133.
Lee, S., E. Jeon, H. Yun, and J. Lee (2011) Improvement of fatty acid biosynthesis by engineered recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 16: 706–713.
Braatsch, S., S. Helmark, H. Kranz, B. Koebmann, and P. R. Jensen (2008) Escherichia coli strains with promoter libraries constructed by Red/ET recombination pave the way for transcriptional fine-tuning. Biotechniques 45: 335–337.
Miksch, G., F. Bettenworth, K. Friehs, E. Flaschel, A. Saalbach, T. Twellmann, and T. W. Nattkemper (2005) Libraries of synthetic stationary-phase and stress promoters as a tool for fine-tuning of expression of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. J. Biotechnol. 120: 25–37.
De Mey, M., J. Maertens, G. J. Lequeux, W. K. Soetaert, and E. J. Vandamme (2007) Construction and model-based analysis of a promoter library for E. coli: An indispensable tool for metabolic engineering. BMC. Biotechnol. 7: 34.
Rud, I., P. R. Jensen, K. Naterstad, and L. Axelsson (2006) A synthetic promoter library for constitutive gene expression in Lactobacillus plantarum. Microbiol. 152: 1011–1019.
Jensen, P. R. and K. Hammer (1998) The sequence of spacers between the consensus sequences modulates the strength of prokaryotic promoters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64: 82–87.
Solem, C. and P. R. Jensen (2002) Modulation of gene expression made easy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68: 2397–2403.
Nevoigt, E., J. Kohnke, C. R. Fischer, H. Alper, U. Stahl, and G. Stephanopoulos (2006) Engineering of promoter replacement cassettes for fine-tuning of gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72: 5266–5273.
Alper, H., C. Fischer, E. Nevoigt, and G. Stephanopoulos (2005) Tuning genetic control through promoter engineering. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 102: 12678–12683.
Qin, X., J. Qian, G. Yao, Y. Zhuang, S. Zhang, and J. Chu (2011) GAP promoter library for fine-tuning of gene expression in Pichia pastoris. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77: 3600–3608.
Blazeck, J., L. Liu, H. Redden, and H. Alper (2011) Tuning gene expression in Yarrowia lipolytica using a hybrid promoter approach. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 22: 7905–7014.
Davis, J. H., A. J. Rubin, and R. T. Sauer (2011) Design, construction and characterization of a set of insulated bacterial promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 39: 1131–1141.
Kelly, J. R., A. J. Rubin, J. H. Davis, C. M. Ajo-Franklin, J. Cumbers, M. J. Czar, K. de Mora, A. L. Glieberman, D. D. Monie, and D. Endy (2009) Measuring the activity of BioBrick promoters using an in vivo reference standard. J. Biol. Eng. 3: 4.
Seo, S. W., J. Yang, and G. Y. Jung (2009) Quantitative correlation between mRNA secondary structure around the region downstream of the initiation codon and translational efficiency in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 104: 611–616.
Park, Y. S., S. W. Seo, S. Hwang, H. S. Chu, J. H. Ahn, T. W. Kim, D. M. Kim, and G. Y. Jung (2007) Design of 5′-untranslated region variants for tunable expression in Escherichia coli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 356: 136–141.
de Smit, M. H. and J. van Duin (2003) Translational standby sites: How ribosomes may deal with the rapid folding kinetics of mRNA. J. Mol. Biol. 331: 737–743.
de Smit, M. H. and J. van Duin (1994) Control of translation by mRNA secondary structure in Escherichia coli. A quantitative analysis of literature data. J. Mol. Biol. 244: 144–150.
de Smit, M. H. and J. van Duin (1994) Translational initiation on structured messengers. Another role for the Shine-Dalgarno interaction. J. Mol. Biol. 235: 173–184.
de Smit, M. H. and J. van Duin (1990) Secondary structure of the ribosome binding site determines translational efficiency: A quantitative analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 87: 7668–7672.
Pfleger, B. F., D. J. Pitera, C. D. Smolke, and J. D. Keasling (2006) Combinatorial engineering of intergenic regions in operons tunes expression of multiple genes. Nat. Biotechnol. 24: 1027–1032.
Ochi, K. (2007) From microbial differentiation to ribosome engineering. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 71: 1373–1386.
Ochi, K., S. Okamoto, Y. Tozawa, T. Inaoka, T. Hosaka, J. Xu, and K. Kurosawa (2004) Ribosome engineering and secondary metabolite production. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 56: 155–184.
Chin, J. W. (2006) Programming and engineering biological networks. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 16: 551–556.
Rackham, O. and J. W. Chin (2005) A network of orthogonal ribosome x mRNA pairs. Nat. Chem. Biol. 1: 159–166.
Xia, X. X., Z. G. Qian, C. S. Ki, Y. H. Park, D. L. Kaplan, and S. Y. Lee (2010) Native-sized recombinant spider silk protein produced in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli results in a strong fiber. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 107: 14059–14063.
Salis, H. M., E. A. Mirsky, and C. A. Voigt (2009) Automated design of synthetic ribosome binding sites to control protein expression. Nat. Biotechnol. 27: 946–950.
Lim, H. N., Y. Lee, and R. Hussein (2011) Fundamental relationship between operon organization and gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 108: 10626–10631.
Dueber, J. E., G. C. Wu, G. R. Malmirchegini, T. S. Moon, C. J. Petzold, A. V. Ullal, K. L. Prather, and J. D. Keasling (2009) Synthetic protein scaffolds provide modular control over metabolic flux. Nat. Biotechnol. 27: 753–759.
Tsuji, S. Y., D. E. Cane, and C. Khosla (2001) Selective proteinprotein interactions direct channeling of intermediates between polyketide synthase modules. Biochem. 40: 2326–2331.
Roughan, P. G. (1997) Stromal concentrations of coenzyme A and its esters are insufficient to account for rates of chloroplast fatty acid synthesis: Evidence for substrate channelling within the chloroplast fatty acid synthase. Biochem. J. 327: 267–273.
Clancy, K. and C. A. Voigt (2010) Programming cells: Towards an automated ‘Genetic Compiler’ Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 21: 572–581.
Yoon, S. H., S. H. Lee, A. Das, H. K. Ryu, H. J. Jang, J. Y. Kim, D. K. Oh, J. D. Keasling, and S. W. Kim (2009) Combinatorial expression of bacterial whole mevalonate pathway for the production of beta-carotene in E. coli. J. Biotechnol. 140: 218–226.
Ro, D. K., E. M. Paradise, M. Ouellet, K. J. Fisher, K. L. Newman, J. M. Ndungu, K. A. Ho, R. A. Eachus, T. S. Ham, J. Kirby, M. C. Chang, S. T. Withers, Y. Shiba, R. Sarpong, and J. D. Keasling (2006) Production of the antimalarial drug precursor artemisinic acid in engineered yeast. Nature 440: 940–943.
Tamsir, A., J. J. Tabor, and C. A. Voigt (2011) Robust multicellular computing using genetically encoded NOR gates and chemical ‘wires’. Nature 469: 212–215.
Cheung, J. and W. A. Hendrickson (2010) Sensor domains of two-component regulatory systems. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 13: 116–123.
Clarke, E. J. and C. A. Voigt (2011) Characterization of combinatorial patterns generated by multiple two-component sensors in E. coli that respond to many stimuli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 108: 666–675.
Hong, H. J., M. I. Hutchings, and M. J. Buttner (2008) Vancomycin resistance VanS/VanR two-component systems. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 631: 200–213.
Prohinar, P., S. A. Forst, D. Reed, I. Mandic-Mulec, and J. Weiss (2002) OmpR-dependent and OmpR-independent responses of Escherichia coli to sublethal attack by the neutrophil bactericidal/permeability increasing protein. Mol. Microbiol. 43: 1493–1504.
Tabor, J. J., H. M. Salis, Z. B. Simpson, A. A. Chevalier, A. Levskaya, E. M. Marcotte, C. A. Voigt, and A. D. Ellington (2009) A synthetic genetic edge detection program. Cell 137: 1272–1281.
Sinha, J., S. J. Reyes, and J. P. Gallivan (2010) Reprogramming bacteria to seek and destroy an herbicide. Nat. Chem. Biol. 6: 464–470.
Elowitz, M. B. and S. Leibler (2000) A synthetic oscillatory network of transcriptional regulators. Nature 403: 335–338.
Gardner, T. S., C. R. Cantor, and J. J. Collins (2000) Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli. Nature 403: 339–342.
Lee, S. K., H. H. Chou, B. F. Pfleger, J. D. Newman, Y. Yoshikuni, and J. D. Keasling (2007) Directed evolution of AraC for improved compatibility of arabinose- and lactose-inducible promoters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73: 5711–5715.
Cox, R. S., M. G. Surette, and M. B. Elowitz (2007) Programming gene expression with combinatorial promoters. Mol. Syst. Biol. 3: 145.
Lutz, R. and H. Bujard (1997) Independent and tight regulation of transcriptional units in Escherichia coli via the LacR/O, the TetR/O and AraC/I1-I2 regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 25: 1203–1210.
Stock, A. M., V. L. Robinson, and P. N. Goudreau (2000) Twocomponent signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 69: 183–215.
Utsumi, R., R. E. Brissette, A. Rampersaud, S. A. Forst, K. Oosawa, and M. Inouye (1989) Activation of bacterial porin gene expression by a chimeric signal transducer in response to aspartate. Science 245: 1246–1249.
Farmer, W. R. and J. C. Liao (2000) Improving lycopene production in Escherichia coli by engineering metabolic control. Nat. Biotechnol. 18: 533–537.
Nystrom, T. (1995) Glucose starvation stimulon of Escherichia coli: role of integration host factor in starvation survival and growth phase-dependent protein synthesis. J. Bacteriol. 177: 5707–5710.
Bulter, T., S. G. Lee, W. W. Wong, E. Fung, M. R. Connor, and J. C. Liao (2004) Design of artificial cell-cell communication using gene and metabolic networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 101: 2299–2304.
Fung, E., W. W. Wong, J. K. Suen, T. Bulter, S. G. Lee, and J. C. Liao (2005) A synthetic gene-metabolic oscillator. Nature 435: 118–122.
Liang, J. C., R. J. Bloom, and C. D. Smolke (2011) Engineering biological systems with synthetic RNA molecules. Mol. Cell. 43: 915–926.
Mironov, A. S., I. Gusarov, R. Rafikov, L. E. Lopez, K. Shatalin, R. A. Kreneva, D. A. Perumov, and E. Nudler (2002) Sensing small molecules by nascent RNA: A mechanism to control transcription in bacteria. Cell 111: 747–756.
Winkler, W., A. Nahvi, and R. R. Breaker (2002) Thiamine derivatives bind messenger RNAs directly to regulate bacterial gene expression. Nature 419: 952–956.
Winkler, W. C., A. Nahvi, A. Roth, J. A. Collins, and R. R. Breaker (2004) Control of gene expression by a natural metabolite-responsive ribozyme. Nature 428: 281–286.
Batey, R. T., S. D. Gilbert, and R. K. Montange (2004) Structure of a natural guanine-responsive riboswitch complexed with the metabolite hypoxanthine. Nature 432: 411–415.
Suess, B., B. Fink, C. Berens, R. Stentz, and W. Hillen (2004) A theophylline responsive riboswitch based on helix slipping controls gene expression in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 32: 1610–1614.
Winkler, W. C., S. Cohen-Chalamish, and R. R. Breaker (2002) An mRNA structure that controls gene expression by binding FMN. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 99: 15908–15913.
Muranaka, N., K. Abe, and Y. Yokobayashi (2009) Mechanismguided library design and dual genetic selection of synthetic OFF riboswitches. Chembiochem. 10: 2375–2381.
Sharma, V., Y. Nomura, and Y. Yokobayashi (2008) Engineering complex riboswitch regulation by dual genetic selection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130: 16310–16315.
Nomura, Y. and Y. Yokobayashi (2007) Reengineering a natural riboswitch by dual genetic selection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129: 13814–13815.
Kim, D. S., V. Gusti, S. G. Pillai, and R. K. Gaur (2005) An artificial riboswitch for controlling pre-mRNA splicing. RNA 11: 1667–1677.
Culler, S. J., K. G. Hoff, and C. D. Smolke (2010) Reprogramming cellular behavior with RNA controllers responsive to endogenous proteins. Science 330: 1251–1255.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, S.W., Kim, S.C. & Jung, G.Y. Synthetic regulatory tools for microbial engineering. Biotechnol Bioproc E 17, 1–7 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-011-0563-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-011-0563-z