Abstract
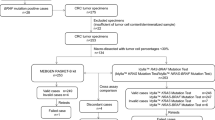
In some situations, there is a need for rapid mutation tests for guiding clinical decisions and starting targeted therapies with minimal delays. In this study we evaluated the turnaround time before and after the implementation of a fully automated multiplex assay for KRAS and NRAS/BRAF mutation tests (Idylla™ platform, Biocartis) in metastatic colorectal cancer. The objective of this project was to compare the turnaround times in 2017–2018 with the fully automated multiplex assay to the 2016 results with previous methods. Centers with a number of tests for metastatic colorectal cancer > 100 yearly and a usual turnaround time ≥ 3 weeks for mutation detection were selected. Results of 505 KRAS tests and 369 NRAS/BRAF tests were transmitted by 10 centers. The mean turnaround time from test prescription to reception of results was reduced from 25.8 days in 2016 to 4.5 days in 2017–2018. In conclusion, this pilot project shows that the Idylla™ platform for testing KRAS and NRAS/BRAF mutations allows an optimized turnaround time from test prescription to reception of results.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuipers EJ, Grady WM, Lieberman D, Seufferlein T, Sung JJ, Boelens PG, van de Velde CJ, Watanabe T (2015) Colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers 1:15065
Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E, Lortet-Tieulent J, Rosso S, Coebergh JW, Comber H, Forman D, Bray F (2013) Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer 49:1374–1403
Hocking CM, Price TJ (2014) Panitumumab in the management of patients with KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer. Therap Adv Gastroenterol 7:20–37
Prenen H, Tejpar S, Van Cutsem E (2010) New strategies for treatment of KRAS mutant metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16:2921–2926
Siena S, Sartore-Bianchi A, Di Nicolantonio F, Balfour J, Bardelli A (2009) Biomarkers predicting clinical outcome of epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 101:1308–1324
Er TK, Chen CC, Bujanda L, Herreros-Villanueva M (2014) Current approaches for predicting a lack of response to anti-EGFR therapy in KRAS wild-type patients. Biomed Res Int 2014:591867
Amado RG, Wolf M, Peeters M, Van Cutsem E, Siena S, Freeman DJ, Juan T, Sikorski R, Suggs S, Radinsky R, Patterson SD, Chang DD (2008) Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 26:1626–1634
Karapetis CS, Khambata-Ford S, Jonker DJ, O’Callaghan CJ, Tu D, Tebbutt NC, Simes RJ, Chalchal H, Shapiro JD, Robitaille S, Price TJ, Shepherd L, Au HJ, Langer C, Moore MJ, Zalcberg JR (2008) K-ras mutations and benefit from cetuximab in advanced colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 359:1757–1765
Douillard JY, Oliner KS, Siena S, Tabernero J, Burkes R, Barugel M, Humblet Y, Bodoky G, Cunningham D, Jassem J, Rivera F, Kocakova I, Ruff P, Blasinska-Morawiec M, Smakal M, Canon JL, Rother M, Williams R, Rong A, Wiezorek J, Sidhu R, Patterson SD (2013) Panitumumab-FOLFOX4 treatment and RAS mutations in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 369:1023–1034
Hecht JR, Douillard JY, Schwartzberg L, Grothey A, Kopetz S, Rong A, Oliner KS, Sidhu R (2015) Extended RAS analysis for anti-epidermal growth factor therapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 41:653–659
Sorich MJ, Wiese MD, Rowland A, Kichenadasse G, McKinnon RA, Karapetis CS (2015) Extended RAS mutations and anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody survival benefit in metastatic colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Ann Oncol 26:13–21
Zenonos K, Kyprianou K (2013) RAS signaling pathways, mutations and their role in colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 5:97–101
Malumbres M, Barbacid M (2003) RAS oncogenes: the first 30 years. Nat Rev Cancer 3:459–465
Fearon ER (2011) Molecular genetics of colorectal cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 6:479–507
Rajagopalan H, Bardelli A, Lengauer C, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Velculescu VE (2002) Tumorigenesis: RAF/RAS oncogenes and mismatch-repair status. Nature 418:934
Oikonomou E, Koustas E, Goulielmaki M, Pintzas A (2014) BRAF vs RAS oncogenes: are mutations of the same pathway equal? Differential signalling and therapeutic implications. Oncotarget 5:11752–11777
Van Cutsem E, Cervantes A, Nordlinger B, Arnold D, Group EGW (2014) Metastatic colorectal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 25(Suppl 3):iii1–i9
Ciardiello F, Tejpar S, Normanno N, Mercadante D, Teague T, Wohlschlegel B, Van Cutsem E (2011) Uptake of KRAS mutation testing in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer in Europe, Latin America and Asia. Target Oncol 6:133–145
Institut National du Cancer. Accès aux tests moléculaires EGFR, RAS et BRAF. Résultats d’une enquête dans 5 régions françaises. Janvier 2016
de Biase D, de Luca C, Gragnano G, Visani M, Bellevicine C, Malapelle U, Tallini G, Troncone G (2016) Fully automated PCR detection of KRAS mutations on pancreatic endoscopic ultrasound fine-needle aspirates. J Clin Pathol
Solassol J, Vendrell J, Markl B, Haas C, Bellosillo B, Montagut C, Smith M, O’Sullivan B, D’Haene N, Le Mercier M, Grauslund M, Melchior LC, Burt E, Cotter F, Stieber D, Schmitt FL, Motta V, Lauricella C, Colling R, Soilleux E, Fassan M, Mescoli C, Collin C, Pages JC, Sillekens P (2016) Multi-Center Evaluation of the Fully Automated PCR-Based Idylla KRAS Mutation Assay for Rapid KRAS Mutation Status Determination on Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue of Human Colorectal Cancer. PLoS One 11:e0163444
Johnston L, Power M, Sloan P, Long A, Silmon A, Chaffey B, Lisgo AJ, Little L, Vercauteren E, Steiniche T, Meyer T, Simpson J (2018) Clinical performance evaluation of the Idylla NRAS-BRAF mutation test on retrospectively collected formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded colorectal cancer tissue. J Clin Pathol 71:336–343
Scott RJ, Fox SB, Desai J, Grieu F, Amanuel B, Garrett K, Harraway J, Cheetham G, Pattle N, Haddad A, Byron K, Rudzki B, Waring P, Iacopetta B (2014) KRAS mutation testing of metastatic colorectal cancer in Australia: where are we at? Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 10:261–265
INCa (Bonnes pratiques pour la recherche à visée théranostique demutations somatiques dans les tumeurs solides. Août 2010) https://www.e-cancer.fr/content/download/63175/568709/file/OUTTHERANOS10.pdf
INCa. Plan Cancer 2014–2019 https://www.e-cancer.fr/Expertises-et-publications/Catalogue-des-publications/Plan-Cancer-2014-2019
Funding
Amgen France.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Stéphane ROSSAT: No conflict of interest.
Hervé PERRIER : Amgen, Roche, Servier, Sanofi
Marine LEFEVRE: No conflict of interest
Christophe LOUVET: MSD, Roche, Halozyme, Servier, AstraZeneca
Nathalie LE BERRE: No conflict of interest
Jérôme CHAMOIS : Astellas, Ipsen, Janssen, Sanofi Aventis
Maryline DOREL: No conflict of interest
Daniel VAQUE: Amgen, Roche, Janssen
Angélique GUILLAUDEAU: No conflict of interest
Dominique GENET: Novartis, Pfizer, Roche
Evelyne MAILLET: No conflict of interest
Simon TRIBY: Amgen employee
Jean-Christophe SABOURIN: Amgen, Merck Serono, Pfizer, Bayer, BMS, MSD, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rossat, S., Perrier, H., Lefevre, M. et al. Drastic Reduction of Turnaround Time After Implementation of a Fully Automated Assay for RAS-BRAF Mutations in Colorectal Cancer: A Pilot Prospective Study in Real-life Conditions. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 26, 2469–2473 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-020-00818-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-020-00818-y