Abstract
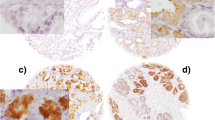
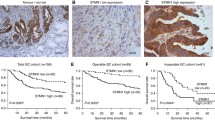
The abnormal expression of Tau protein in breast cancer tissue affects paclitaxel sensitivity. The abnormal expression also exists in gastric carcinoma. Therefore, we speculate that the expression levels of Tau protein is closely related to paclitaxel sensitivity in gastric cancer, thus affecting the efficacy of paclitaxel. In this study, we used immunohistochemical methods to detect Tau protein expression levels in 47 cases of gastric cancer specimens. We also used Western blot to detect the level of Tau protein expression in gastric cancer cell lines and to check the efficacy of paclitaxel in vitro application. Findings indicate that Tau protein expression rate can reach as high as (+ +–+ + +) 63.83 % in gastric cancer. Paclitaxel induces inhibition and apoptosis with low expression of Tau protein in gastric cancer cell lines (P < 0.05). The level of Tau protein expression is significantly correlated with paclitaxel efficacy. If confirmed by further studies, the Tau protein can be another useful marker of gastric cancer, thereby leading to the application of paclitaxel in cancer treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zheng LZ, Chen Q (2005) Gastric cancer chemotherapy status. Gastroenterology 10:178–181
Koizumi W (2005) Available options in chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer: the current developments in Japan. Expert Opin Pharmacother 6:225–231
Scartozzi M, Galizia E, Verdecchia L et al (2007) Chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer: across the years for a standard of care. Expert Opin Pharmaeother 8:797–808
Gu Y, Oyama F, Ihara Y et al (1996) Tau is widely expressed in rat tissues. J Neurochem 67:1235–1244
Shen ZL, Qu MH, He HJ et al (2008) HeLa, HEK293, SH-SY5Y, Tau protein in cells. Res Prog Biochem Biophys 35:1364–1370
Muszyńska-Roslan K, Krawczuk-Rybak M, Protas PT et al (2006) Level of Tau protein in children treated for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Neurol 34:367–371
Van CE, Moiseyenko VM, Tjulandin S et al (2006) Phase Ul study of docetaxel and eisplatin plus fluorouracil compared with eisphtin and fluorouracil as first-line therapy for advanced gastric cancer: a report of the V325 study group. J Clin Oncol 24:4991–4997
Yan S (2006) Antitumor handbook. Beijing: Peking University Medical Press 11:178
Wang F, Han R (2002) Development of research for drug-resistance mechanism of taxol. Ai Zheng 21:439–442
Li Z, Wang LM, Geng MY (2006) Tau protein and nerve cell death. Chin Clinical Rehabilitation 10:124–126
Rossi G, Dalpra L, Crosti F et al (2008) A new function of microtubule-associated protein tau: involvement in chromosome stability. Cell Cycle 7:1788–1794
Pentheroudakis G, Kalogeras KT, Wirtz RM et al (2009) Gene expression of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor and microtubule-associated protein Tau in high-risk early breast cancer: a quest for molecular predictors of treatment benefit in the context of a Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat 116:131–143
Pusztai L, Jeong JH, Gong Y et al (2009) Evaluation of microtubule-associated protein-Tau expression as a prognostic and predictive marker in the NSABP-B 28 randomized clinical trial. J Clin Oncol 10:4287–4292
Andre F, Hatzis C, Anderson K et al (2007) Microtubule-associated protein-tau is a bifunctional predictor of endocrine sensitivity and chemotherapy resistance in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13:2061–2067
Wagner P, Wang B, Clark E et al (2005) Microtubule Associated Protein (MAP)-Tau: a novel mediator of paclitaxel sensitivity in vitro and in vivo. Cell Cycle 4:1149–1152
Rouzier R, Rajan R, Wagner P et al (2005) Microtubule-associated protein tau: a marker of paclitaxel sensitivity in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:8315–8320
Chambonniere ML, Mosnier-Damet M, Mosnier JF et al (2001) Expression of microtubule-associated protein tau by gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Hum Pathol 32:1166–1173
Mimori K, Sadanaga N, Yoshikawa Y et al (2006) Reduced tau expression in gastric cancer can identify candidates for successful Paclitaxel treatment. Br J Cancer 94:1894–1897
Feng R, Bao YZ, Peng CW et al (2010) Tau gene expression and sensitivity of gastric cancer in paclitaxel treatment. Theory Pract Surg 15:432–437
Qiu LX, Qian XP, Liu B (2009) Research progress on Taxane drug efficacy forecast molecular. Modern Oncol 17:1583–1584
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Qiong Wang and Nanyao Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Wang, N., Shao, G. et al. Relationship Between Gastric Cancer Tau Protein Expression and Paclitaxel Sensitivity. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 19, 429–435 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-012-9598-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-012-9598-5