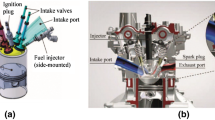
Abstract
This paper reviews the particle emissions formed during the combustion process in spark ignition and diesel engine. Proposed legislation in Europe and California will impose a particle number requirement for GDI (gasoline direct injection) vehicles and will introduce the Euro 6 and LEV-III emission standards. More careful optimization for reducing particulate emission on engine hardware, fuel system, and control strategy to reduce particulate emissions will be required during cold start and warm-up phases. Because The diesel combustion inherently produces significant amounts of PM as a result of incomplete combustion around individual fuel droplets in the combustion zone, much attention has been paid to reducing particle emissions through electronic engine control, high pressure injection systems, combustion chamber design, and exhaust after-treatment technologies. In this paper, recent research and development trends to reduce the particle emissions from internal combustion engines are summarized, with a focus on PMP activity in EU, CARB and SAE papers and including both state-of-the-art light-duty vehicles and heavy-duty engines.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostinelli, D., Carter, N., Fang, G. and Hamori, F. (2011). Optimization of a mono-fuel liquid phase LPG MPI fuel system. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-0382.
Andersson, J., Wedekind, B., Hall, D., Stradling, R. and Barnes, C. (2001). DERT/SMMT/CONCAWE particle research programme: Light-duty results. SAE Paper No. 2001-01-3577.
Andersson, J., Clarke, D. and Watson, J. A. (2004). UK Particulate Measurement Programme (PMP): A near US 2007 approach to heavy duty diesel particulate measurements — Comparison with the standard European method. SAE Paper No. 2004-01-1990.
Andersson, J., Giechaskiel, B., Munoz-Bueno, R., Sandbach, E. and Dilara, P. (2007). Particle Measurement Programme (PMP) Light-duty Inter-laboratory Correlation Exercise (ILCE-LD) Final Report.
Andersson, J. and Clarke, D. (2008). UN-GRPE PMP Phase 3 Inter-laboratory Correlation Exercise: Updated Framework and Laboratory Guide for Heavy Duty (HD) Engine Testing.
Andersson, J., Mamakos, A., Giechaskiel, B., Carriero, M. and Martini, G. (2010). Particle Measurement Programme (PMP) Heavy-duty Inter-laboratory Correlation Exercise (ILCE-HD) Final Report.
Andrew, P., Timothy, C., Ahmadinejad, M., David, B., Paul, R. and Swallow, D. (2009). Modeling the emissions control performance of a catalyzed diesel particulate filter (CDPF) system for light duty diesel applications. SAE Paper No. 2009-01-1266
Arcoumanis, C., Bae, C., Crookes, R. and Kinoshita, E. (2008). The potential of di-methyl ether (DME) as an alternative fuel for compression-ignition engines: A review. Fuel, 87, 1014–1030.
Austin, G., Naber, J., Johnson, J. and Hutton, C. (2010). Effects of biodiesel blends on particulate mater oxidation in a catalyzed particulate filter during active regeneration. SAE Paper No. 2010-01-0557.
Ayala, A., Zhang, S., Collins, J., Zhan, T., Dwyer, H., Huai, T., Herner, J. and Chau, W. (2008). California’s Informal Participation in the Particle Measurement Programme (PMP) Light-duty Inter-laboratory Correlation Exercise (ILCE-LD) Final Research Report.
Basshuysen, R. (2009). Gasoline Engine with Direct Injection. Vieweg+Teubner. Germany.
Benajes, J., Novella, R., Arthozoul, S. and Kolodziej, C. (2010). Particle size distribution measurements from early to late injection timing low temperature combustion in a heavy duty diesel engine. SAE Paper No. 2010-01-1121.
Brück, R., Hirth, P. and Rice, M. (2009). NOx aftertreatment for passenger cars and heavy duty truck applications for EU 6 and EUVI/US2010 legislation. SAE Paper No. 2009-01-0904.
Bukowiecki, N., Kittelson, D., Watts, W., Burtscher, H., Weingartner, E. and Baltensperger, U. (2002). Real-time characterization of ultrafine and accumulation mode particles in ambient combustion aerosols. J. Aerosol Sci., 33, 1139–1154.
Burtscher, H. (2005). Physical characterization of particulate emissions from diesel engines: A review. J. Aerosol Sci., 36, 896–932.
CARB (2010). Proposed Amendments to California’s Lowemission Vehicle Regulations-particulate Matter Mass, Ultrafine Solid Particle Number and Black Carbon Emissions.
Cho, J., Yoon, Y., Lee, J. and Kim, H. (2011). Hyundai’s new generation 1.8L gasoline engine. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-0417.
Choi, B., Yoon, Y., Kang, H. and Lim, M. (2006). Oxidation characteristics of particulate matter on diesel warm-up catalytic converter. Int. J. Automotive Technology 7,5, 527–534.
Czerwinski, J., Zimmerli, Y., Mayer, A., Heeb, N. and D’Urbano, G. (2011). Diesel emission with DPF+SCR in VERTdePN — testing & potentials. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-1139.
Daniel, S., Achim, K., Peter, S., Jan, F. and Arndt, D. (2011). The influence of DISI engine operating parameters on particle number emissions. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-0143.
Dimou, I., Kar, K. and Cheng, W. (2011). Particulate matter emissions from a direct injection spark ignition engine under cold fast idle conditions for ethanol-gasoline blends. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-1305.
Di-Penta, D., Bencherifm, K. and Le-Morvan, P. (2011). System approach for NOx reduction: Double LNT diesel after-treatment architecture. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-1300.
Dockery, D., Pope, C. and Wu, X. (1993). An association between air pollution and mortality in six US cities. New England J. Med. 329,24, 1753–1759.
Eastwood, P. (2008). Particulate Emissions from Vehicles. John Wiley & Sons Ltd. UK.
Filippo, A. (2011). Particle size and number emissions from modern light-duty diesel vehicles. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-0632.
Furuta, Y., Mizutani, T., Miyairi, Y., Yuki, K. and Kurachi, H. (2009). Study on next generation diesel particulate filter. SAE Paper No. 2009-01-0292.
Giechaskiel, B., Ntziachristos, L., Samaras, Z., Scheer, V., Casati, R. and Vogt, R. (2005). Formation potential of vehicle exhaust nucleation mode particles on-road and in the laboratory. Atmos. Environ. 39,18, 3191–3198.
Giechaskiel, B., Munoz-Bueno, R., Rubino, L., Manfredi, U., Dilara, P., Santi, G. D. and Andersson, J. (2007). Particle size and number emissions before, during and after regeneration events of a Euro 4 DPF equipped light-duty diesel vehicle. SAE Paper No. 2007-01-1944.
Giechaskiel, B., Alessandrini, S., Forni, F., Martinez-Lozano, P., Lesueur, D., Carriero, M. and Martini, G. (2008a). Particle Measurement Programme (PMP): Heavy-Duty (HD) Inter-laboratory Exercise: Exploratory work at JRC (Oct’ 07–Feb’ 08). EU Report 23426.
Giechaskiel, B., Martinez-Lozano, P., Alessandrini, S., Forni, F., Montigny, F., Fumagalli, I., Carriero, M. and Martini, G. (2008b). Particle Measurement Programme (PMP) Heavy Duty (HD) Inter-laboratory Exercise: Validation Exercise Tests at JRC (Feb 08). EU Report 23496.
Gong, C., Huang, K., Deng, B. and Liu, X. (2011). Catalyst light-off behavior of a spark-ignition LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) engine during cold start. Energy, 36, 53–59.
Hassaneen, A., Samuel, S., Morrey, D. and Gonzalez-Oropeza, R. (2009). Influence of physical and chemical parameters on characteristics of nano-scale particulate in spark ignition engine. SAE Paper No. 2009-01-2651.
Heywood, J. and Welling, O. (2009). Trends in performance characteristics of modern automobile SI and diesel engines. SAE Paper No. 2009-01-1892.
Hwang, I., Choi, K., Kim, J., Myung, C. and Park, S. (2011). Experimental evaluation of combustion phenomena and nano-particle emission from the side mounted directed injection engine with gasoline and liquid phase LPG fuel. J. Autombile Engineering, DOI 10.1177/0954407011413058.
Iorio, S., Lazzaro, M., Sementa, P., Vaglieco, B. and Catapano, F. (2011). Use of renewable oxygenated fuels in order to reduce particle emissions from a GDI high performance engine. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-0628.
Johnson, T. (2009). Review of diesel emissions and control. Int. J. Engine Res., 10, 275–285.
Johnson, T. (2010). Review of diesel emissions and control. SAE Paper No. 2010-01-0301.
Johnson, T. (2011). Diesel emissions in review. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-0304.
Joshi, A., Chatterjee, S. and Walker, A. (2011). An evaluation of particle size distributions and particle number-based reductions from various PM emission control technologies. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-0600.
Kannapin, O. and Guske, T. (2010). Reducing Particulate Emissions New Challenge for Spark-ignition Engines with Direct Injection. MTZ. Berlin.
Kapus, P. and Jansen, H. (2010). Reduction of Particulate Number Emissions Through Calibration Methods. MTZ. Berlin.
Kayes, D. and Hochgreb, S. (1999). Mechanism of particulate matter formation in spark-ignition engines. Environ. Sci. Technol., 33, 3957–3967.
Khalek, I., Kittelson, D., Graskow, B., Wei, Q. and Brear, F. (1998). Diesel exhaust particle size: Measurement issues and trends. SAE Paper No. 980525.
Khalek, I., Kittelson, D. and Brear, F. (1999). The influence of dilution conditions on diesel exhaust particle size distribution measurements. SAE Paper No. 1999-01-1142.
Kirchner, U., Vogt, R. and Maricq, M. (2010). Investigation of EURO-5/6 level particle number emissions of European diesel light duty vehicles. SAE Paper No. 2010-01-0789.
Kittelson, D. (1998). Engines and nanoparticles: A review. J. Aerosol Sci. 29,5/6, 575–588.
Kittelson, D., Watts, W., Johnson, J., Rowntree, C., Payne, M., Goodier, S., Warrens, C., Preston, H., Zink, U., Ortiz, M., Goersmann, C., Twigg, M., Walker, A. and Caldow, R. (2006). On-road evaluation of two diesel exhaust aftertreatment devices. J. Aerosol Sci., 37, 1140–1151.
Kittelson, D., Watts, W., Johnson, J., Thorne, C., Higham, M., Payne, S., Goodier, C., Warrens, H., Preston, U., Zink, D. and Boddy, R. (2008). Effect of fuel and lube oil sulfur on the performance of a diesel exhaust gas continuously regenerating trap. Environ. Sci. Technol., 42, 9276–9282.
Kobayashi, M., Aoyagi, Y., Adachi, T., Murayama, T., Hashimoto, M., Goto, Y. and Suzuki, H. (2011). Effective BSFC and NOx reduction on super clean diesel of heavy duty diesel engine by high boosting and high EGR rate. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-0369.
Kunde, O., Hansen, J., Zenner, T., Kapus, P., Obst, C., Queenan, B. and Bjornesson, H. (2010). The new 2.0 SCTi EcoBoost gasoline engine from Ford. 19th Aachen Colloquium.
Kwak, H., Myung, C. and Park, S. (2007). Experimental investigation on the time resolved THC emission characteristics of liquid phase LPG injection (LPLi) engine during cold start. Fuel, 86, 1475–1482.
Lee, H., Kim, J., Myung, C. and Park, S. (2009). Experimental investigation of nanoparticle formation characteristics from advanced gasoline and diesel fueled light duty vehicles under different certification driving modes. J. Mechanical Science and Technology, 23, 1591–1601.
Lee, J., Do, H., Kweon, S., Park, K. and Hong, J. (2010). Effect of various LPG supply systems on exhaust particle emission in spark-ignited combustion engine. Int. J. Automotive Technology 11,6, 793–800.
Lee, J., Jung, Y., Jung, M., Cha, K., Kwon, S., Kim, J. and Park, S. (2008). Experimental investigation and comparison of nano-particle emission characteristics in light-duty vehicles for two different fuels. Int. J. Automotive Technology 9,4, 397–403.
Lee, K. and Lee, C. (2004). An experimental study on the spray behavior and fuel distribution of GDI injectors using the entropy analysis and PIV method. Fuel, 83, 971–980.
Lee, Y., Hong, K., Song, S., Chun, K., Lee, K., Min, S. and Chung, D. (2011). Evaluation of SOF effects on deposit characteristics of the EGR cooler using a PM generator. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-1156.
Li, X., Yang, L., Pang, M. and Liang, X. (2010). Effect of LPG injection methods on engine performance. Advanced Materials Research, 97-101, 2279–2282.
Lohfink, C., Baecker, H. and Tichy, M. (2008). Experimental investigation on catalyst-heating strategies and potential of GDI combustion systems. SAE Paper No. 2008-01-2517.
Margraf, J., Schrewe, K. and Steigert, S. (2011). Enhancement of diesel soot combustion with oxygen on particulate filters after injection of dicyclopentadienyl iron (ferrocene) in the exhaust pipe. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-0303.
Maricq, M., Podsiadlik, D. and Chase, R. (1999). Gasoline vehicle particle size distributions: Comparison of steady state, FTP, and US06 measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol., 33, 2007–2015.
May, J., Bosteels, D., Nicol, A., Andersson, J. and Such, C. (2007). The application of emissions control technologies to a low-emissions engine to evaluate the capabilities of future systems for European and world-harmonised regulations. 16th Aachen Colloquium.
May, J., Bosteels, D., Such, C., Nicol, A. and Andersson, J. (2008). Heavy-duty engine particulate emissions: Application of PMP methodology to measure particle number and particulate mass. SAE Paper No. 2008-01-1176.
McMahon, W., Zhang, S., Ayala, A., Rieger, P. and Chang, O. (2011). Fuel and technology effects on particulate matter emissions for light-duty gasoline vehicles. 20th CRC Real World Emissions Workshop.
Mikulic, I., Koelman, H., Majkowski, S. and Vosejpka, P. (2010). A study about particle filter application on a state-of-the-art homogeneous turbocharged 2L DI gasoline engine. 19th Aachen Colloquium.
Mizutani, T., Iwasaki, S., Miyairi, Y., Yuuki, K., Makino, M. and Kurachi, H. (2010). Performance verification of next generation diesel particulate filter. SAE Paper No. 2010-01-0531.
Moon, G., Lee, Y., Choi, K. and Jeong, D. (2009). Experimental study on characteristics of diesel particulate emissions with diesel, GTL and blended fuels. SAE Paper No. 2009-24-0098.
Myung, C., Lee, H., Choi, K., Lee, Y. and Park, S. (2009a). Effects of gasoline, diesel, LPG and low-carbon fuels and various certification modes on nanoparticle emission characteristics in light-duty vehicles. Int. J. Automotive Technology 10,5, 537–544.
Myung, C., Lee, H., Kwon, S., Lee, S., Jun, J., Lee, Y., Woo, Y., Lee, M., Bae, G. and Park, S. (2009b). Interlaboratory correlation exercise on a light-duty diesel passenger vehicle to verify nano-particle emission characteristics by Korea particle measurement program. J. Mechanical Science and Technology, 23, 729–738.
Myung, C., Kim, J., Kwon, S., Choi, K., Ko, A. and Park, S. (2011). Nano-particle emission characteristics of European and worldwide harmonized test cycles for heavy-duty diesel engines. Int. J. Automotive Technology 12,3, 331–377.
Ntziachristos, L., Mamakos, A., Samaras, Z., Mathis, U., Mohr, M., Thompson, N., Strandling, R. and Forti, L. (2004). Overview of the European “Particulates” project on the characterization of exhaust particulate emissions from road vehicles: Results for light-duty vehicles. SAE Paper No. 2004-01-1985.
Ntziachristos, L., Mamakos, A., Samaras, Z., Rexeis, M. and Hausberger, S. (2006). Diesel particle exhaust emissions from light duty vehicles and heavy duty engines. SAE Paper No. 2006-01-0866.
Nuszkowski, J., Flaim, K. and Thompson, G. (2011). The effect of cetane improvers and biodiesel on diesel particulate matter size. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-0330.
Oh, S., Lee, S., Choi, Y., Kang, K., Cho, J. and Cha, K. (2010). Combustion and emission characteristics in a direct injection LPG/gasoline spark ignition engine. SAE Paper No. 2010-01-1461.
Ostro, B. (1984). A research for a threshold in the relationship of air pollution to mortality: A reanalysis of London winters. Environ. Health Perspect., 58, 397–399.
Paule, M., Mackensen, A., Binz, R. and Enderle, C. (2011). Challenges for the next generation of blue TEC emission technology. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-0294.
Peckham, M. S., Finch, A. and Campbell, B. (2011a). Analysis of transient HC, CO, NOx and CO2 emissions from a GDI engine using fast response gas analyzers. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-1227.
Peckham, M. S., Finch, A., Campbell, B., Price, P. and Davies, M. T. (2011b). Study of particle number emissions from a turbocharged gasoline direct injection (GDI) engine including data from a fast-response particle size spectrometer. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-1224.
Piock, W., Hoffmann, G., Berndorfer, A., Salemi, P. and Fusshoeller, B. (2011). Strategies towards meeting future particulate matter emission requirements in homogeneous gasoline direct injection engines. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-1212.
Piscaglia, F. and Ferrari, G. (2009). A novel 1D approach for the simulation of unsteady reacting flows in diesel exhaust after-treatment systems. Energy, 34, 2051–2062.
Pope, C., Schwartz, J. and Ransom, M. (1992). Daily mortality and PM10 pollution in utah valley. Arch. Environ. Health 47,3, 211–217.
Price, P., Stone, R., Collier, T. and Davies, M. (2006). Particulate matter and hydrocarbon emissions measurements: Comparing first and second generation DISI with PFI in single cylinder optical engines. SAE Paper No. 2006-01-1263.
Rajamani, P., Palani, S. and Subramanian, S. (2010). Optimization of geometry and parameter affecting combustion for four stroke LPG engine using CFD. SAE Paper No. 2010-32-0009.
Rakopoulos, C. and Giakoumis, E. (2009). Diesel Engine Transient Operation — Principles of Operation and Simulation Analysis. Springer. UK.
Ristimaki, J., Keskinen, J., Virtanen, A., Maricq, M. and Virtanen, P. (2005). Cold temperature PM emissions measurement: Method evaluation and application to light duty vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol., 39, 9424–9430.
Ristovski, Z. D., Morawska, L., Hitchins, J., Thomas, S., Greenaway, C. and Gilbert, D. (2000). Particle emissions from compressed natural gas engines. J. Aerosol Sci. 31,4, 403–413.
Ristovski, Z., Jayaratne, E., Morawska, L., Ayoko, G. and Lim, M. (2005). Particle and carbon dioxide emissions from passenger vehicles operating on unleaded petrol and LPG fuel. Science of the Total Environment, 345, 93–98.
Roberto, C., Volker, S., Rainer, V. and Thorsten, B. (2007). Measurement of nucleation and soot mode particle emission from a diesel passenger car in real world and laboratory in situ dilution. Atmo. Environ., 41, 2125–2135.
Rocher, L., Seguelong, T., Harle, V., Lallemand, M., Pudlarz, M. and Macduff, M. (2011). New generation fuel borne catalyst for reliable DPF operation in globally diverse fuel. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-0297.
Rofail, R. and Henein, N. (2011). Simulation of the effect of recirculated gases on ignition delay during cold starting of a direct injection diesel engine. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-0838.
Sabathil, D., Koenigstein, A., Schaffner, P., Fritzsche, J. and Doehler, A. (2011). The influence of DISI engine operating parameters on particle number emissions. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-0143.
Sakurai, H., Tobias, H., Park, K., Zarling, D., Docherty, K., Kittelson, D., McMurry, P. and Ziemann, P. (2003). Online measurements of diesel nanoparticle composition and volatility. Atmos. Environ., 37, 1199–1210.
Samuel, S., Hassaneen, A. and Morrey, D. (2010). Particulate matter emissions and the role of catalytic converter during cold start of GDI engine. SAE Paper No. 2010-01-2122.
Sappok, A., Morrow, R., Wong, V., Pazar, J., Doustar, I. and Zisholtz, E. (2010). Unraveling DPF degradation using chemical tracers and opportunities for extending filter life. DEER Conf.
Shimizu, M., Yageta, K., Matsui, Y. and Yoshida, T. (2011). Development of new 1.6 liter four cylinder turbocharged direct injection gasoline engine with intake and exhaust valve timing control system. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-0419.
Soewono, A. and Rogak, S. (2009). Morphology and microstructure of engine-emitted particulates. SAE Paper No. 2009-01-1906.
Sogawa, Y., Hattori, H., Yamashita, T., Yanagisawa, N., Hosoya, M., Shoji, T., Iwakiri, Y., Yamashita, T., Ikeda, T., Tanaka, S., Takahashi, K., Suzuki, T., Nakajima, T. and Tonegawa, Y. (2007). Nano particle emission evaluation of state of the art diesel aftertreatment technologies (DPF, urea-SCR and DOC), gasoline combustion systems (Lean Burn/Stoichiometric DISI and MPI) and fuel qualities effects (EtOH, ETBE, FAME, Aromatics and Distillation). SAE Paper No. 2007-01-4083.
Surenhalli, H., Premchand, K., Johnson, J. and Parker, G. (2011). Modeling study of active regeneration of a catalyzed particulate filter using one dimensional DOC and CPF models. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-1242.
Takeda, K., Yaegashi, T., Sekiguchi, K., Saito, K. and Imatake, N. (1995). Mixture preparation and HC emission of a 4-valve engine during cold start and warmup. SAE Paper No. 950074.
Theis, J. R., Dearth, M. and McCabe, R. (2011). LNT+SCR catalyst systems optimized for NOx conversion on diesel applications. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-0305.
Uchiyama, M., Fraidel, G., Kapus, P., Ogris, M. and Hollerer, P. (2011). Solutions for EU 6 particulate number in gasoline DI engines. JSAE Paper No. 20115251.
Vaaraslahti, K., Keskinen, J., Giechaskiel, B., Murtonen, T. and Solla, A. (2005). Effect of lubricant on the formation of heavy-duty diesel exhaust nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol., 39, 8497–8504.
Walter, P., Guy, H., Axel, B., Patrick, S. and Bernd, F. (2011). Strategies towards meeting future particulate matter emission requirements in homogeneous gasoline direct injection engines. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-1212.
Wei, Q., Ziegler, F. and Winkler, W. (2010). PM emissions from light-duty diesel vehicles retrofitted with diesel particulate filters. SAE Paper No. 2010-01-0788.
Wu, X., Daniel, R., Tian, G., Xu, H., Huang, Z. and Richardson, D. (2011). Dual-injection: The flexible, bifuel concept for spark-ignition engines fuelled with various gasoline and biofuel blends. Applied Energy, 88, 2305–2314.
Yamakawa, M., Youso, T., Fujikawa, T., Nishimoto, T., Wada, Y., Sato, K. and Yokohata, H. (2011). Combustion technology development for a high compression ratio gasoline engine. JSAE Paper No. 20115067.
Yamamoto, K., Oohori, S., Yamashita, H. and Daido, S. (2009). Simulation on soot deposition and combustion in diesel particulate filter. Proc. Combustion Institute, 32, 1965–1972.
Zhang, S. and McMahon, W. (2010). Particulate emissions and size distributions for California LEV II certified gasoline direct injection vehicles. CRC Mobile Source Air Toxics Workshop.
Zhang, X., Tennison, P. and Yi, J. (2011). 3-D numerical study of fluid flow and pressure loss characteristics through a DPF with asymmetrical channel size. SAE Paper No. 2011-01-0818.
Zhao, F., Lai, M. and Harrington, D. (1999). Automotive spark-ignited direct-injection gasoline engines. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 25, 437–562.
Zinola, S. and Lavy, J. (2009). Detailed particulate characterization from HCCI combustion for future DPF development. SAE Paper No. 2009-01-1185.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Myung, C.L., Park, S. Exhaust nanoparticle emissions from internal combustion engines: A review. Int.J Automot. Technol. 13, 9–22 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-012-0002-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-012-0002-y