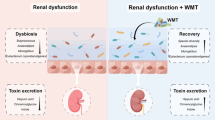
Abstract
The primary aim of this study was to investigate the alterations in the microbial community of KK-Ay mice following antibiotic treatment. A comparative analysis of the gut microbiota was conducted between KK-Ay mice treated with antibiotics and those without treatment. The microbial community dynamics in antibiotic-treated KK-Ay mice were meticulously assessed over an eight-week period using 16S rDNA sequencing analysis. Simultaneously, dynamic renal function measurements were performed. The results demonstrated a marked decrease in bacterial DNA abundance following antibiotic intervention, coupled with a substantial reduction in bacterial diversity and a profound alteration in microbial composition. These observed microbiota changes persisted in the KK-Ay mice throughout the eight-week post-antibiotic treatment period. Particularly noteworthy was the reemergence of bacterial populations after two weeks or more, resulting in a microbiota composition resembling that of untreated KK-Ay mice. This transition was characterized by a significant increase in the abundance of clostridia at the class level, Lachnospirales and Oscillospirales at the order level, and Lachnospiraceae, Oscillospiraceae, and Ruminococcaceae at the family level. Concurrently, there was a notable decrease in Clostridia_UCG-014. The observed alterations in the gut microbiota of antibiotic-treated KK-Ay mice suggest a dynamic response to antibiotic intervention and subsequent restoration towards the original untreated state.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available on request from the first authors. All sequencing data were deposited in the the NCBI SRA under accession number PRJNA1014710.
References
Bakker GJ, Schnitzler JG, Bekkering S, de Clercq NC, Koopen AM, Hartstra AV, Meessen E, Scheithauer TP, Winkelmeijer M, Dallinga-Thie GM, Cani PD, Kemper EM, Soeters MR, Kroon J, Groen AK, van Raalte DH, Herrema H, Nieuwdorp M (2019) Oral vancomycin treatment does not alter markers of postprandial inflammation in lean and obese subjects. Physiol Rep 7:e14199
Barberan A, Bates ST, Casamayor EO, Fierer N (2012) Using network analysis to explore co-occurrence patterns in soil microbial communities. ISME J 6:343–351
Bleich A, Hansen AK (2012) Time to include the gut microbiota in the hygienic standardisation of laboratory rodents. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 35:81–92
Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJ, Holmes SP (2016) DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13:581–583
Carvalho BM, Guadagnini D, Tsukumo D, Schenka AA, Latuf-Filho P, Vassallo J, Dias JC, Kubota LT, Carvalheira J, Saad M (2012) Modulation of gut microbiota by antibiotics improves insulin signalling in high-fat fed mice. Diabetologia 55:2823–2834
Chen S, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Gu J (2018) fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34:i884–i890
Cho I, Yamanishi S, Cox L, Methe BA, Zavadil J, Li K, Gao Z, Mahana D, Raju K, Teitler I, Li H, Alekseyenko AV, Blaser MJ (2012) Antibiotics in early life alter the murine colonic microbiome and adiposity. Nature 488:621–626
Cox LM, Yamanishi S, Sohn J, Alekseyenko AV, Leung JM, Cho I, Kim SG, Li H, Gao Z, Mahana D, Zarate RJ, Rogers AB, Robine N, Loke P, Blaser MJ (2014) Altering the intestinal microbiota during a critical developmental window has lasting metabolic consequences. Cell 158:705–721
Desbonnet L, Clarke G, Traplin A, O’Sullivan O, Crispie F, Moloney RD, Cotter PD, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2015) Gut microbiota depletion from early adolescence in mice: Implications for brain and behaviour. Brain Behav Immun 48:165–173
Ellekilde M, Selfjord E, Larsen CS, Jakesevic M, Rune I, Tranberg B, Vogensen FK, Nielsen DS, Bahl MI, Licht TR, Hansen AK, Hansen CH (2014) Transfer of gut microbiota from lean and obese mice to antibiotic-treated mice. Sci Rep 4:5922
Fenneman AC, Weidner M, Chen LA, Nieuwdorp M, Blaser MJ (2023) Antibiotics in the pathogenesis of diabetes and inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 20:81–100
Hansen AK (1995) Antibiotic treatment of nude rats and its impact on the aerobic bacterial flora. Lab Anim 29:37–44
Hansen CH, Krych L, Nielsen DS, Vogensen FK, Hansen LH, Sorensen SJ, Buschard K, Hansen AK (2012) Early life treatment with vancomycin propagates Akkermansia muciniphila and reduces diabetes incidence in the NOD mouse. Diabetologia 55:2285–2294
Hansen AK, Hansen CH, Krych L, Nielsen DS (2014) Impact of the gut microbiota on rodent models of human disease. World J Gastroenterol 20:17727–17736
Li XY, Zeng ZX, Cheng ZX, Wang YL, Yuan LJ, Zhai ZY, Gong W (2023) Common pathogenic bacteria-induced reprogramming of the host proteinogenic amino acids metabolism. Amino Acids 55:1487–1499
Liu C, Zhao D, Ma W, Guo Y, Wang A, Wang Q, Lee DJ (2016) Denitrifying sulfide removal process on high-salinity wastewaters in the presence of Halomonas sp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:1421–1426
Lundberg R, Toft MF, August B, Hansen AK, Hansen CH (2016) Antibiotic-treated versus germ-free rodents for microbiota transplantation studies. Gut Microbes 7:68–74
Macpherson AJ, McCoy KD (2015) Standardised animal models of host microbial mutualism. Mucosal Immunol 8:476–486
Magoc T, Salzberg SL (2011) FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27:2957–2963
Mikkelsen KH, Frost M, Bahl MI, Licht TR, Jensen US, Rosenberg J, Pedersen O, Hansen T, Rehfeld JF, Holst JJ, Vilsboll T, Knop FK (2015) Effect of Antibiotics on Gut Microbiota, Gut Hormones and Glucose Metabolism. PLoS ONE 10:e142352
Modi SR, Lee HH, Spina CS, Collins JJ (2013) Antibiotic treatment expands the resistance reservoir and ecological network of the phage metagenome. Nature 499:219–222
Olson CA, Vuong HE, Yano JM, Liang QY, Nusbaum DJ, Hsiao EY (2018) The Gut Microbiota Mediates the Anti-Seizure Effects of the Ketogenic Diet. Cell 173:1728–1741
Rune I, Hansen CH, Ellekilde M, Nielsen DS, Skovgaard K, Rolin BC, Lykkesfeldt J, Josefsen K, Tranberg B, Kihl P, Hansen AK (2013) Ampicillin-improved glucose tolerance in diet-induced obese C57BL/6NTac mice is age dependent. J Diabetes Res 2013:319321
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Thuny F, Richet H, Casalta JP, Angelakis E, Habib G, Raoult D (2010) Vancomycin treatment of infective endocarditis is linked with recently acquired obesity. PLoS ONE 5:e9074
Vrieze A, Out C, Fuentes S, Jonker L, Reuling I, Kootte RS, van Nood E, Holleman F, Knaapen M, Romijn JA, Soeters MR, Blaak EE, Dallinga-Thie GM, Reijnders D, Ackermans MT, Serlie MJ, Knop FK, Holst JJ, van der Ley C, Kema IP, Zoetendal EG, de Vos WM, Hoekstra JB, Stroes ES, Groen AK, Nieuwdorp M (2014) Impact of oral vancomycin on gut microbiota, bile acid metabolism, and insulin sensitivity. J Hepatol 60:824–831
Wang W, Zhang N, Du Y, Gao J, Li M, Lin L, Czajkowsky DM, Li X, Yang C, Shao Z (2021) Three-dimensional quantitative imaging of native microbiota distribution in the gut. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 60:3055–3061
Zeighamy AS, Halimi S, Rezaei A, Afifirad R (2023) Association between probiotics and modulation of gut microbial community composition in colorectal cancer animal models: a systematic review (2010–2021). Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol 2023:3571184
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledged Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital and Professor Zhongdao Wu’s lab in Sun Yat-sen University for the academic supports.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82202560), the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (No.2022A1515110655), the Traditional Chinese Medicine Bureau of Guangdong Province (Nos. 20231003 and 20223001), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Nos. 2023A1515011458 and 2021A1515220050), the Science and Technology Projects in Guangzhou (No. 2024A04J4314), the National Parasitic Resource Center of China (No. NPRC-2019-194-30), and the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou (No. SL2022A04J00042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JH, FT, and WL were responsible for drafting the original manuscript. JH, YL, and MY analyzed the data and created the figures. DL and CM reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors contributed to subsequent revisions and approved the final version for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital (Approval Number: KY2023-018-01).
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, J., Fu, T., Liu, W. et al. Gut microbiota dynamics in KK-Ay mice: restoration following antibiotic treatment. Folia Microbiol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-024-01157-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-024-01157-0