Abstract
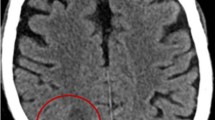
Nocardiosis is an acute or chronic infectious disease caused by the soil-borne filamentous bacteria belonging to the genus Nocardia. The organisms opportunistically infect both immunocompromised and immunocompetent individuals. The lungs are the primary site of infection and brain abscess is, by far, the most common complication following nocardial metastasis from pulmonary lesions. Although surgical intervention must always be considered in the treatment of nocardial brain abscess, it can obviously be cured by antibiotic therapy alone. This report describes a case infected by Nocardia cyriacigeorgica. Identification of the infectious agent was achieved by conventional and semi-nested PCR techniques. A 55-year-old woman with fever was referred to the infect disclinic of Imam Khomeini hospital in Tehran and was hospitalized after clinical assessment. She was a kidney transplant recipient for 4 years and was taking immunosuppressive treatment including azathioprine and methylprednisolone. Follow-up of the patient by CT scan revealed pulmonary infection and cerebral lesions. Specimens of the brain lesions contained filamentous bacteria. The patient received a combination of co-trimoxazole and ceftriaxone and brain abscesses as well as lung inflammation disappeared gradually during the course of antibiotic therapy within 3 months. The patient was discharged from the hospital after 2 months of therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arduino RC, Johnson PC (1993) Nocardiosis in renal transplant recipients undergoing immunosuppression with cyclosporine. Clin Infect dis 16(4):505–512
Barnaud G, Deschamps C, Manceron V, Mortier E, Laurent F, Bert F, Boiron P, Vinceneux P, Branger C (2005) Brain abscess caused by Nocardia cyriacigeorgica in a patient with human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Clin microbiol 43(9):4895–4897
Batista MV, Pierrotti LC, Abdala E, Clemente WT, Girao ES, Rosa DR, Ianhez LE, Bonazzi PR, Lima AS, Fernandes PF, Padua-Neto MV, Bacchella T, Oliveira AP, Viana CF, Ferreira MS, Shikanai-Yasuda MA (2011) Endemic and opportunistic infections in Brazilian solid organ transplant recipients. Trop Med Int Health 16(9):1134–1142
Berkey P, Moore DKR (1998) In vitro susceptibilities of Nocardia species to newer antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Ch 32:1078–1079
Brown JM, Pham KN, McNeil MM, Lasker BA (2004) Rapid identification of Nocardia farcinica clinical isolates by a PCR assay targeting a 314-base-pair species-specific DNA fragment. J Clin Microbiol 42(8):3655–3660
Brown-Elliott BA, Brown JM, Conville PS, Wallace RJ Jr (2006) Clinical and laboratory features of the Nocardia spp. based on current molecular taxonomy. Clin Microbiol Rev 19(2):259–282
Cloud JL, Conville PS, Croft A, Harmsen D, Witebsky FG, Carroll KC (2004) Evaluation of partial 16S ribosomal. DNA sequencing for identification of nocardia species by using the MicroSeq 500 system with an expanded database J Clin Microbiol 42(2):578–584
Conville PS, Fischer SH, Cartwright CP, Witebsky FG (2000) Identification of nocardia species by restriction endonuclease analysis of an amplified portion of the 16S rRNA gene. J Clin Microbiol 38(1):158–164
Couble A, Rodriguez-Nava V, de Montclos MP, Boiron P, Laurent F (2005) Direct detection of Nocardia spp. in clinical samples by a rapid molecular method. J Clin microbiol 43(4):1921–1924
Duran E, Lopez L, Martinez A, Comuñas F, Boiron P, Rubio MC (2001) Primary brain abscess with Nocardia otitidiscaviarum in an intravenous drug abuser. J Med Microbiol 50:101–103
Elsayed S, Kealey A, Coffin CS, Read R, Megran D, Zhang K (2006) Nocardia cyriacigeorgica septicemia. J Clin Microbiol 44:280–282
Eshraghi SS, Talebi M, Namaki S, Mirshafiey A (2009) Nocardia. J Chinese Clin Med 4:48–66
Laurent FJ, Provost F, Boiron P (1999) Rapid identification of clinically relevant Nocardia species to genus level by 16S rRNA gene PCR. J Clin microbiol 37(1):99
Leitersdorf I, Silver J, Naparstek E, Raveh D (1997) Tetracycline derivatives, alternative treatment for nocardiosis in transplanted patients. Clin nephrol 48(1):48–51
Malincarne L, Marroni M, Farina C, Camanni G, Valente M, Belfiori B, Fiorucci S, Floridi P, Cardaccia A, Stagni G (2002) Primary brain abscess with Nocardia farcinica in an immunocompetent patient. Clin neurol and neurosurg 104(2):132–135
Maraki S, Panagiotaki E, Scoulica EM, Miari N, Hainis K, Dotis G, Katsoula I, Tselentis Y (2006) Nocardia cyriacigeorgica pleural empyema in an immunocompromised patient. Diag Microbiol Infect Dis 56:333–335
McNeil MM, Brown JM (1994) The medically important aerobic actinomycetes: epidemiology and microbiology. Clin Microbiol Rev 7(3):357–417
Mijares MCC, Mendoza MT (2001) Pulmonary nocardiosis in renal transplant recipients. Phil J Microbiol Infect Dis:144-152
Rakotoarivelo RA, Raveloson HF, Razafimahefa SH, Farbos S, Gemain MC, Bonnal F (2011) Brain abscess with Nocardia asteroides revealing lung adenocarcinoma. Rev Pneumol Clin 67(5):329–330
Reis MA, Costa RS, Ferraz AS (1995) Causes of death in renal transplant recipients: a study of 102 autopsies from 1968 to 1991. J Royal Soc Med 88(1):24–27
Roth A, Andrees S, Kroppenstedt RM, Harmsen D, Mauch H (2003) Phylogeny of the genus Nocardia based on reassessed 16S rRNA gene sequences reveals underspeciation and division of strains classified as Nocardia asteroides into three established species and two unnamed taxons. J Clin Microbiol 41(2):851–856
Tatti KM, Shieh WJ, Phillips S, Augenbraun M, Rao C, Zaki SR (2006) Molecular diagnosis of Nocardia farcinica from a cerebral abscess. Hum pathol 37(8):1117–1121
Threlkeld SC, Hooper DC (1997) Update on management of patients with Nocardia infection. Curr Clin top infec dis 17:1–23
Wallace RJ Jr, Steele LC, Sumter G, Smith JM (1988) Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of Nocardia asteroides. Antimicrob Agents Ch 32(12):1776–1779
Wilson JP, TURNER HR, Kirchner KA, Chapman SW (1989) Nocardial infections in renal transplant recipients. Medicine 68(1):38–57
Yassin AF, Rainey FA, Steiner U (2001) Nocardia cyriacigeorgica sp. nov. Int J syst evol microbiol 51(4):1419–1423
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by School of Public Health and Biotechnology Research Center, Project number 13434, Tehran University of Medical Sciences. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eshraghi, S.S., Heidarzadeh, S., Soodbakhsh, A. et al. Pulmonary nocardiosis associated with cerebral abscess successfully treated by co-trimoxazole: a case report. Folia Microbiol 59, 277–281 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-013-0298-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-013-0298-7