Abstract
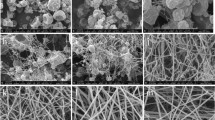
In this research we propose a new type of smart microfibers, distinguished by moisture management and proactive temperature and pH controlled release activity. Hydrogel with submicron-sized particles based on poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (poly-NiPAAm) and chitosan (PNCS hydrogel) was incorporated into the structure of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) microfibers using the electrospinning technique. Composites with different PLA to PNCS hydrogel ratios were prepared, and the chemical and morphological properties of the samples were studied using SEM, FT-IR and Raman mapping. Additionally, the moisture management properties, which were provided by the temperature and pH-related phase change transition of the incorporated PNCS hydrogel, were studied by determining the temperature-related static contact angle, thin-layer wicking, moisture content and pH-related water uptake. The loading and release abilities of the incorporated PNCS hydrogel were studied using fluorescent microscopy. The increased concentration of the PNCS hydrogel in spinning solutions resulted in greater variations in fiber thickness and deterioration of the mechanical properties of the fibers; thus, the highest concentration of the PNCS hydrogel that could be incorporated within the fibers was found to be 20 % of the spinning mass. The composite sample showed temperature and pH responsiveness, a successful fluorescent-dye loading ability and its controlled release at predetermined conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. C. Koetting, J. T. Peters, S. D. Steichen, and N. A. Peppas, Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep., 93, 1 (2015).
D. Jocić, Tekstilec, 59, 107 (2016).
B. Liu and J. Hu, Fibres Text. East. Eur., 13, 45 (2005).
E. A. Kamoun, E. S. Kenawy, and X. Chen, J. Adv. Res., 8, 217 (2017).
S. K. Samal, M. Dash, P. Dubruel, and S. Van Vlierberghe in “Smart Polymers and Their Applications” (M. R. Aguilar De Armas and J. S. Román Eds.), pp.237–270, Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing, 2014.
J. Qu, X. Zhao, P. X. Ma, and B. Guo, Acta Biomater, 58, 168 (2017).
Z. Deng, T. Hu, Q. Lei, J. He, P. X. Ma, and B. Guo, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 11, 6796 (2019).
A. Kulkarni, A. Tourrette, M. M. C. G. Warmoeskerken, and D. Jocić, Carbohydr. Polym., 82, 1306 (2010).
A. Tourrette in “Surface Modification Systems for Creating Stimuli Responsiveness of Textiles” (D. Jocić Ed.), pp.77–92, Workshop Proceedings: 6th Framework Programe ADVANBIOTEX of the EU, 2010.
P. Križman Lavrič, M. M. C. G. Warmoeskerken, and D. Jocić, Cellulose, 19, 257 (2011).
P. Križman Lavrič, B. Tomšič, B. Simončič, M. M. C. G. Warmoeskerken, and D. Jocić, Cellulose, 19, 273 (2012).
B. Tomšič, P. Križman Lavrič, B. Simončič, B. Orel, and D. Jocić, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol., 61, 463 (2012).
D. Štular, I. Jerman, I. Naglič, B. Simončič, and B. Tomšič, Carbohydr. Polym., 159, 161 (2017).
D. Štular, J. Vasiljević, M. Čolović, M. Mihelčič, J. Medved, J. Kovač, I. Jerman, B. Simončič, and B. Tomšič, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol, 83, 19 (2017).
A. S. Patil, A. P. Gadad, R. D. Hiremath, and S. D. Joshi, J. Polym. Res., 25, 77 (2018).
D. Štular, B. Tomšič, I. Jerman, B. Simončič, M. Mihelčič, L. Noč, and I. German Ilić, Prog. Org. Coat., 124, 213 (2018).
S. Jin, Z. Chen, B. Xin, T. Xi, and N. Meng, Fiber. Polym., 18, 1160 (2017).
C. Huang and N. L. Thomas, Eur. Polym. J., 99, 464 (2018).
T. Grothe, D. Wehlage, T. Böhm, A. Remche, and A. Ehrmann, Tekstilec, 60, 290 (2017).
J. Li, W. Xu, D. Li, T. Liu, Y. S. Zhang, J. Ding, and X. Chen, ACS Nano, 12, 6685 (2018).
J. Ding, J. Zhang, J. Li, D. Li, C. Xiao, H. Xiao, H. Yang, X. Zhuang, and X. Chen, Prog. Polym. Sci., 90, 1 (2019).
D. Kehren, A. C. Molano Lopez, and A. Pich, Polymer, 55, 2153 (2014).
A. Balaceanu, Y. Verkh, D. Kehren, W. Tillmann, and A. Pich, Z Phys. Chem., 228, 253 (2014).
D. Kehren and A. Pich, Macromol. Mater. Eng., 298, 1282 (2013).
J. E. Díaz, A. Barrero, M. Marquez, A. Fernandez-Nieves, and I. G. Loscertales, Macromol. Rapid. Comm., 31, 183 (2010).
P. Wilke, V. Coger, M. Nachev, S. Schachschal, N. Million, S. Barcikowski, B. Sures, K. Reimers, P. M. Vogt, and A. Pich, Polymer, 61, 163 (2015).
C. F. Lee, C. J. Wen, and W. Y. Chiu, J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem., 41, 2053 (2003).
C. T. Rueden, J. Schindelin, M. C. Hiner, B. E. DeZonia, A. E. Walter, E. T. Arena, and K. W. Eliceiri, BMC Bioinformatics, 18, 26 (2017).
E. Chibowski and F. González-Caballero, Langmuir, 9, 330 (1993).
B. Simončič and V. Rozman, Colloid Surface A, 292, 236 (2007).
D. H. Reneker and A. L. Yarin, Polymer, 49, 2387 (2008).
G. Socrates, “Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies”, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2001.
Y. Tsuboi, M. Nishino, and N. Kitamura, Polym. J., 40, 367 (2008).
D. Klinger and K. Landfester, Polymer, 53, 5209 (2012).
S. L. Percival, S. McCarty, J. A. Hunt, and E. J. Woods, Wound. Repair. Regen., 22, 174 (2014).
B. Simončič and B. Tomšič in “Textile Finishing: Recent Developments and Future Trends, (Adhesion and Adhesives)” (K. L. Mittal and T. Bahners Eds.), pp.3–50, Hoboken: Wiley; Beverly: Scrivener Publishing, 2017.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Slovenian Research Agency (Program P2-0213, Infrastructural Centre RIC UL-NTF, grant for the doctoral student, D.Š. and Program P2-0207 in ARRS grant J3-8201).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Štular, D., Kruse, M., Župunski, V. et al. Smart Stimuli-Responsive Polylactic Acid-Hydrogel Fibers Produced via Electrospinning. Fibers Polym 20, 1857–1868 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-019-9157-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-019-9157-8