Abstract
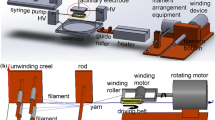
Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofiber filaments were manufactured continuously for several hours by a homemade multi-needle electrospinning device. The yarns were continuously obtained by plying and twisting nanofiber filaments using a self-made twisting device. The structures and mechanical properties of yarns were investigated. The influences of twist setting temperatures and periods of time on morphology and mechanical properties were discussed. The results showed that the alignment degree of nanofibers along the filament axis could reach 70.9 %. The twist angle increased with increasing twists and the number of filaments. With increasing twists, the breaking stress and strain increased initially and then decreased; the maximum breaking stress and strain were 34.7 MPa and 26.1 %, respectively; the initial modulus decreased with increasing twists and plies, the maximum modulus was 391.3 MPa. Both the breaking stress and strain increased with the increase of twist setting temperatures and times. The optimal setting temperature and time were 90 °C and 30 min, respectively, the maximum breaking stress and strain were 32.8 MPa and 20.8 %, meanwhile, the crystallinity improved from 34.5 % to 39.9 %. This study demonstrates the possibility of continuously and stably manufacturing PAN nanofiber yarns.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Bhardwaj and S. C. Kundu, Biotechnol. Adv., 28, 325 (2010).
S. Agarwal, A. Greiner, and J. H. Wendorff, Prog. Polym. Sci., 38, 963 (2013).
S. Agarwal, J. H. Wendorff, and A. Greiner, Polymer, 49, 5603 (2008).
L. Huang, S. S. Manickam, and J. R. McCutcheon, J. Membr. Sci., 436, 213 (2013).
N. R. Dhineshbabu, G. Karunakaran, R. Suriyaprabha, P. Manivasakan, and V. Rajendran, Nano-micro Lett., 6, 46 (2014).
B. Ding, M. Wang, J. Yu, and G. Sun, Sensors, 9, 1609 (2009).
X. Zhuang, K. Jia, B. Cheng, X. Feng, S. Shi, and B. Zhang, Chem. Eng. J., 237, 308 (2014).
J. Li, L. Tian, N. Pan, and Z. J. Pan, Polym. Eng. Sci., 54, 1618 (2014).
E. Smit, U. Bttner, and R. D. Sanderson, Polymer, 46, 2419 (2005).
J. Liu, G. Chen, H. Gao, L. Zhang, S. Ma, J. Liang, and H. Fong, Carbon, 50, 1262 (2012).
W. E. Teo, R. Gopal, R. Ramaseshan, K. Fujihara, and S. Ramakrishna, Polymer, 48, 3400 (2007).
H. Matsumoto, S. Imaizumi, Y. Konosu, M. Ashizawa, M. Minagawa, A. Tanioka, W. Lu, and J. Tour, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 5, 6225 (2013).
S. C. Moon and R. J. Farris, Carbon, 47, 2829 (2009).
X. Wang, K. Zhang, M. Zhu, H. Yu, Z. Zhou, Y. Chen, and B. S. Hsiao, Polymer, 49, 2755 (2008).
H. Yan, L. Liu, and Z. Zhang, Mater. Lett., 65, 2419 (2011).
F. Dabirian, Y. Hosseini, and S. A. H. Ravandi, J. Text. Inst., 98, 237 (2007).
M. S. M. Jad, S. A. H. Ravandi, H. Tavanai, and R. H. Sanatgar, Fiber. Polym., 12, 801 (2011).
S. F. Fennessey and R. J. Farris, Polymer, 45, 4217 (2004).
Z. Xie, H. Niu, and T. Lin, RSC Adv., 5, 15147 (2015).
J. He, K. Qi, Y. Zhou, and S. Cui, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 131, 8 (2014).
S. Y. Gu, J. Ren, and Q. L. Wu, Synth. Met., 155, 157 (2005).
L. Tian, T. Yan, and Z. J. Pan, J. Mater. Sci., 50, 7137 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, T., Tian, L. & Pan, Z. Structures and mechanical properties of plied and twisted polyacrylonitrile nanofiber yarns fabricated by a multi-needle electrospinning device. Fibers Polym 17, 1627–1633 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-016-6553-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-016-6553-1