Abstract
Background
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is a useful tool for the treatment of hematologic malignancies. However, transplantation-related complications are the main cause of non-relapse mortality. Previous reports suggest that endothelial damage is related to early complications after HSCT. Non-invasive reactive hyperemia peripheral arterial tonometry (RH-PAT) was performed to evaluate endothelial function as a predictive marker for these complications.
Methods
The reactive hyperemia index (RHI) obtained from RH-PAT was evaluated before the conditioning regimen. The relationship between the RHI and the appearance of engraftment syndrome, thrombotic microangiopathy, and acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD) was assessed. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed that an RHI value of 1.58 was the optimal cut-off for predicting transplantation-related complications.
Results
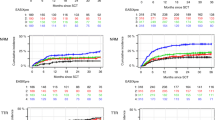
In total, 49 patients (22 acute myelogenous leukemia, 7 acute lymphocytic leukemia, 6 myelodysplastic syndrome, 6 adult T-cell leukemia, 6 non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and 2 others) were enrolled; 34 had a normal RHI (≥ 1.59), and 15 had an abnormally low RHI (≤ 1.58). Thrombotic microangiopathy (20.2% vs 0.0%, P = 0.025) and aGVHD (80.0% vs 41.2%, P = 0.015) were significantly more frequent in patients with a low RHI.
Conclusion
Endothelial dysfunction assessed by RH-PAT before HSCT was able to predict transplantation-related complications.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
Data available on reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
Nassereddine S, Rafei H, Elbahesh E, Tabbara I. Acute graft versus host disease: a comprehensive review. Anticancer Res. 2017;37:1547–55.
Spitzer TR. Engraftment syndrome: double-edged sword of hematopoietic cell transplants. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2015;50:469–75.
Daly AS, Xenocostas A, Lipton JH. Transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: twenty-two years later. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002;30:709–15.
Ferrara JL, Levine JE, Reddy P, Holler E. Graft-versus-host disease. Lancet. 2009;373:1550–61.
Biedermann BC. Vascular endothelium and graft-versus-host disease. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2008;21:129–38.
Schots R, Kaufman L, Van Riet I, Ben Othman T, De Waele M, Van Camp B, et al. Proinflammatory cytokines and their role in the development of major transplant-related complications in the early phase after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Leukemia. 2003;17:1150–6.
Carreras E, Diaz-Ricart M. The role of the endothelium in the short-term complications of hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2011;46:1495–502.
Tichelli A, Gratwohl A. Vascular endothelium as “novel” target of graft-versus-host disease. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2008;21:139–48.
Mir E, Palomo M, Rovira M, Pereira A, Escolar G, Penack O, et al. Endothelial damage is aggravated in acute GvHD and could predict its development. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017;52:1317–25.
Ueda N, Chihara D, Kohno A, Tatekawa S, Ozeki K, Watamoto K, et al. Predictive value of circulating angiopoietin-2 for endothelial damage-related complications in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20:1335–40.
Palomo M, Diaz-Ricart M, Carbo C, Rovira M, Fernandez-Aviles F, Martine C, et al. Endothelial dysfunction after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: role of the conditioning regimen and the type of transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010;16:985–93.
Hamburg NM, Keyes MJ, Larson MG, Vasan RS, Schnabel R, Pryde MM, et al. Cross-sectional relations of digital vascular function to cardiovascular risk factors in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2008;117:2467–74.
Matsuzawa Y, Kwon TG, Lennon RJ, Lerman LO, Lerman A. Prognostic value of flow-mediated vasodilation in brachial artery and fingertip artery for cardiovascular events: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2015; 4.
Spitzer TR. Engraftment syndrome following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001;27:893–8.
Ho VT, Cutler C, Carter S, Martin P, Adams R, Horowitz M, et al. Blood and marrow transplant clinical trials network toxicity committee consensus summary: thrombotic microangiopathy after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005;11:571–5.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J, et al. 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995; 15:825–8
Shimpo M, Morrow DA, Weinberg EO, Sabatine MS, Murphy SA, Antman EM, et al. Serum levels of the interleukin-1 receptor family member ST2 predict mortality and clinical outcome in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2004;109:2186–90.
Smadja DM, Guerin CL, Chocron R, Yatim N, Boussier J, Gendron N, et al. Angiopoietin-2 as a marker of endothelial activation is a good predictor factor for intensive care unit admission of COVID-19 patients. Angiogenesis. 2020;23:611–20.
Kielstein JT, Zoccali C. Asymmetric dimethylarginine: a novel marker of risk and a potential target for therapy in chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2008;17:609–15.
Gumanova NG, Deev AD, Zhang W, Kots AY, Shalnova SA. Serum nitrite and nitrate levels, NOx, can predict cardiovascular mortality in the elderly in a 3-year follow-up study. BioFactors. 2017;43:82–9.
Hink U, Li H, Mollnau H, Oelze M, Matheis E, Hartmann M, et al. Mechanisms underlying endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Circ Res. 2001;88:E14-22.
Nohria A, Gerhard-Herman M, Creager MA, Hurley S, Mitra D, Ganz P. Role of nitric oxide in the regulation of digital pulse volume amplitude in humans. J Appl Physiol. 1985;2006(101):545–8.
Dignat-George F, Sampol J. Circulating endothelial cells in vascular disorders: new insights into an old concept. Eur J Haematol. 2000;65:215–20.
Muczynski KA, Ekle DM, Coder DM, Anderson SK. Normal human kidney HLA-DR-expressing renal microvascular endothelial cells: characterization, isolation, and regulation of MHC class II expression. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14:1336–48.
Takamatsu A, Nakashima Y, Haji S, Tsuda M, Masuda T, Kimura D, et al. Circulating endothelial cells and endothelial progenitor cells as potential predictors of acute GVHD after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Eur J Haematol. 2022;109:146–53.
Barker JN, Wagner JE. Umbilical-cord blood transplantation for the treatment of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:526–32.
Matsue Y, Matsumura A, Suzuki M, Hashimoto Y, Yoshida M. Differences in action of atorvastatin and ezetimibe in lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and effect on endothelial function: randomized controlled trial. Circ J. 2013;77:1791–8.
Zeisbrich M, Becker N, Benner A, Radujkovic A, Schmitt K, Beimler J, et al. Transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy is an endothelial complication associated with refractoriness of acute GvHD. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017;52:1399–405.
Hamadani M, Awan FT, Devine SM. The impact of HMG-CoA reductase inhibition on the incidence and severity of graft-versus-host disease in patients with acute leukemia undergoing allogeneic transplantation. Blood. 2008;111:3901–2.
Acknowledgements
None to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.H., A.T., and M.S. made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, and analysis and interpretation of data. S.H., A.T., and M.S. made substantial contributions to the acquisition of data, and analysis and interpretation of data. S.H. and M.S. wrote the article, and all authors made substantial contributions to editing and revising the article. All authors have approved the final version of the article. M.S. is the guarantor of this work and, as such, had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Shojiro Haji received honoraria/lecture fees from Kyowa Kirin unrelated to this study. Motoaki Shiratsuchi received research grant support from Chugai, Kyowa Kirin, Daiichi Sankyo, MSD, and SRL, and honoraria/lecture fees from Otsuka, Chugai, Kyowa Kirin, Ono, and Sanofi, unrelated to this study. Mariko Tsuda received honoraria/lecture fees from Otsuka, unrelated to this study. Yasuhiro Nakashima received research grants from the Japanese Society of Hematology, and research grant support from Chugai, Kyowa Kirin, Daiichi Sankyo, and SRL, and honoraria/lecture fees from Otsuka, Chugai, Kyowa Kirin, Ono, and Sanofi, unrelated to this study. Yoshihiro Ogawa received research grant support from Kyowa Kirin, Taisho, Mochida, Cosmic Corporation, Fujifilm, Mitsubishi Tanabe, AstraZeneca, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Eisai, Abbott, Chugai, Pfizer, Tsumura, Otsuka, Taiho, Zeria, and Fujiyakuhin, and honoraria/lecture fees from Novo Nordisk Pharma and Taisho, unrelated to this study. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.


About this article
Cite this article
Haji, S., Shiratsuchi, M., Takamatsu, A. et al. Endothelial function testing before conditioning therapy is useful for predicting transplant-related complications after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Int J Hematol 117, 438–445 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-022-03498-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-022-03498-3