Abstract
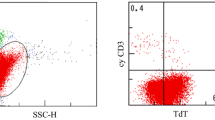
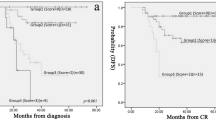
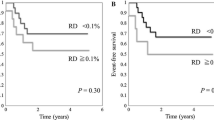
To examine the prognostic significance of minimal residual disease (MRD) in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia (AML), 96 bone marrow samples from 26 Japanese patients in complete remission (CR) were analyzed regarding the RUNX1/MTG8 transcript using real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction assay. All patients were treated with intensive chemotherapy. The median copy number of the RUNX1/MTG8 transcript, measured after each treatment course decreased over time. However, an increase in the MRD level was documented in three patients after the second consolidation, and all of them subsequently relapsed. The relapse-free survival (RFS) did not differ between the patients whose MRD levels were below or above 1,000 copies/µg after the first consolidation, with respective 2-year rates of 62 and 86% (P = 0.21). With respect to the MRD level after induction therapy, our data also failed to show any favorable effect of a lower MRD on RFS. Although these findings need to be confirmed with a larger number of patients, our data indicate that the MRD level at a given time during the early course in CR does not predict the outcome in Japanese patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferrara F, Del Vecchio L. Acute myeloid leukemia with t(8;21)/AML1/ETO: a distinct biological and clinical entity. Haematologica. 2002;87:306–19.
Grimwade D, Walker H, Oliver F, et al. The importance of diagnostic cytogenetics on outcome in AML: analysis of 1, 612 patients entered into the MRC AML 10 trial. The Medical Research Council Adult and Children’s Leukaemia Working Parties. Blood. 1998;92:2322–33.
Byrd JC, Mrozek K, Dodge RK, et al. Pretreatment cytogenetic abnormalities are predictive of induction success, cumulative incidence of relapse, and overall survival in adult patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia: results from Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB 8461). Blood. 2002;100:4325–36.
Heid CA, Stevens J, Livak KJ, Williams PM. Real time quantitative PCR. Genome Res. 1996;6:986–94.
Krauter J, Gorlich K, Ottmann O, et al. Prognostic value of minimal residual disease quantification by real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction in patients with core binding factor leukemias. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:4413–22.
Tobal K, Newton J, Macheta M, et al. Molecular quantitation of minimal residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia with t(8;21) can identify patients in durable remission and predict clinical relapse. Blood. 2000;95:815–9.
Leroy H, de Botton S, Grardel-Duflos N, et al. Prognostic value of real-time quantitative PCR (RQ-PCR) in AML with t(8;21). Leukemia. 2005;19:367–72.
Perea G, Lasa A, Aventin A, et al. Prognostic value of minimal residual disease (MRD) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with favorable cytogenetics [t(8;21) and inv(16)]. Leukemia. 2006;20:87–94.
Weisser M, Haferlach C, Hiddemann W, Schnittger S. The quality of molecular response to chemotherapy is predictive for the outcome of AML1-ETO-positive AML and is independent of pretreatment risk factors. Leukemia. 2007;21:1177–82.
Narimatsu H, Yokozawa T, Iida H, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes in patients with t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia in Japan. Leukemia. 2008;22:428–32.
Marcucci G, Mrozek K, Ruppert AS, et al. Prognostic factors and outcome of core binding factor acute myeloid leukemia patients with t(8;21) differ from those of patients with inv(16): a Cancer and Leukemia Group B study. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:5705–17.
Osumi K, Fukui T, Kiyoi H, et al. Rapid screening of leukemia fusion transcripts in acute leukemia by real-time PCR. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002;43:2291–9.
Nanri T, Matsuno N, Kawakita T, et al. Mutations in the receptor tyrosine kinase pathway are associated with clinical outcome in patients with acute myeloblastic leukemia harboring t(8;21)(q22;q22). Leukemia. 2005;19:1361–6.
Schnittger S, Kohl TM, Haferlach T, et al. KIT-D816 mutations in AML1-ETO-positive AML are associated with impaired event-free and overall survival. Blood. 2006;107:1791–9.
Paschka P, Marcucci G, Ruppert AS, et al. Adverse prognostic significance of KIT mutations in adult acute myeloid leukemia with inv(16) and t(8;21): a Cancer and Leukemia Group B Study. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:3904–11.
Miyamoto T, Weissman IL, Akashi K. AML1/ETO-expressing nonleukemic stem cells in acute myelogenous leukemia with 8;21 chromosomal translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:7521–6.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank all the staff and resident members of the participating institutions. A complete list of participating institutions appears in the Appendix.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
This study was conducted at the following institutions: Toyohashi Municipal Hospital, Toyohashi; Yamanashi Prefectural Central Hospital, Kofu; National Hospital Organization Nagoya Medical Center, Nagoya; Komaki City Hospital, Komaki; Nagoya University Hospital, Nagoya; Yokkaichi Municipal Hospital, Yokkaichi; Okazaki City Hospital, Okazaki; Meitetsu Hospital, Nagoya; Fujita Health University Hospital, Toyoake, Japan.
About this article
Cite this article
Narimatsu, H., Iino, M., Ichihashi, T. et al. Clinical significance of minimal residual disease in patients with t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia in Japan. Int J Hematol 88, 154–158 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-008-0108-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-008-0108-1