Abstract
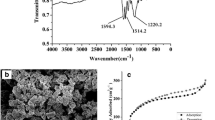
A novel aptamer solid-phase microextraction (SPME) fibre-based on poly (methacrylic acid-co-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) for lysozyme-specific recognition has been successfully prepared. The prepared SPME fibres were characterised by various instrumental methods, including scanning electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and Fourier-transform infrared spectrometry. The results showed that the SPME fibre exhibited a porous structure, which is beneficial for the enrichment of the aptamer. The solid-phase microextraction-high-performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection (SPME-HPLC-FLD) with the superior selectivity and sensitivity responded linearly to the concentration of lysozyme over the 0.025–10 mg/L range, and the limit of detection was low at 6.8 μg/L, with a linearity of 0.9995. The method showed excellent reproducibility, and the relative standard deviations (RSDs) were less than 5.5%, which facilitated the analysis. The method was applied for the analysis of lysozyme in cow milk and papaya samples, and the recoveries ranged from 86.7–93.5% with RSDs of 4.3–6.1%, which clearly state that the proposed lysozyme aptamer SPME-HPLC-FLD method is a promising analytical tool for the analysis of lysozyme in food samples.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves M, Vieira NSM, Rebelo LPN, Araújo JMM, Pereiro AB, Archer M (2017) Fluorinated ionic liquids for protein drug delivery systems: investigating their impact on the structure and function of lysozyme. Int J Pharm 526:309–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.05.002
Chen Y, Chen M, Chi J, Yu X, Chen Y, Lin X, Xie Z (2018) Aptamer-based polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS)-containing hybrid affinity monolith prepared via a “one-pot” process for selective extraction of ochratoxin A. J Chromatogr A 1563:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.05.044
Dragoni I, Balzaretti C, Rossini S, Rossi L, Dell’Orto V, Baldi A (2011) Detection of hen lysozyme on proteic profiles of grana padano cheese through SELDI-TOF MS high-throughput technology during the ripening process. Food Anal Methods 4:233–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-010-9146-4
Guan Y-F, Lai S-Y, Lin C-S, Suen S-Y, Wang M-Y (2019) Purification of lysozyme from chicken egg white using diatom frustules. Food Chem 286:483–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.02.023
Guarino C, Fuselli F, Mantia AL, Longo L (2011) Development of an RP-HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of benzoic acid, sorbic acid, natamycin and lysozyme in hard and pasta filata cheeses. Food Chem 127:1294–1299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.01.086
Han B, Zhao C, Yin J, Wang H (2012) High performance aptamer affinity chromatography for single-step selective extraction and screening of basic protein lysozyme. J Chromatogr B 903:112–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.07.003
Hou M, Zhang M, Chen L, Gong K, Pan C, Wang Y (2019) Amplification of lysozyme signal detected in capillary electrophoresis using mixed polymer brushes coating with switchable properties. Talanta 202:426–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.05.014
Kaur H, Bruno JG, Kumar A, Sharma TK (2018) Aptamers in the therapeutics and diagnostics pipelines. Theranostics 8:4016–4032. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.25958
Kerkaert B, Mestdagh F, Meulenaer BD (2010) Detection of hen’s egg white lysozyme in food: comparison between a sensitive HPLC and a commercial ELISA method. Food Chem 120:580–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.10.027
Lamrabet O, Jauslin T, Lima WC, Leippe M, Cosson P (2020) The multifarious lysozyme arsenal of Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Comp Immunol 107:103645–103651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2020.103645
Li J, Fan N, Wang X, He Z (2017) Cellular level evaluation and lysozyme adsorption regulation of bimodal nanoporous silica. Mater Sci Eng C 76:509–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.096
Li Z, Su C, Wu D, Zhang Z (2018) Gold nanoparticles decorated hematite photoelectrode for sensitive and selective photoelectrochemical aptasensing of lysozyme. Anal Chem 90:961–967. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04015
Lou T, Qiang H, Chen Z (2017) Core-shell Cu@Au nanoparticles-based colorimetric aptasensor for the determination of lysozyme. Talanta 163:132–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.10.095
Luo X, Wu S, Yang Y-Q, Jin N, Liu S, Huang B (2017) Deposition of titanium coating on SiC fiber by chemical vapor deposition with Ti-I2 system. Appl Surf Sci 406:62–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.02.141
Martini M, Salari F, Licitra R, Motta CL, Altomonte I (2019) Lysozyme activity in donkey milk. Int Dairy J 96:98–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2019.04.009
Mihai I, Vezeanu A, Polonschii C, Albu C, Radu G-L, Vasilescu A (2015) Label-free detection of lysozyme in wines using an aptamer based biosensor and SPR detection. Sensor Actuators B Chem 206:198–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.09.050
Mirzajani R, Ramezani Z, Kardani F (2016) Selective determination of thidiazuron herbicide in fruit and vegetable samples using molecularly imprinted polymer fiber solid phase microextraction with ion mobility spectrometry detection (MIPF-SPME-IMS). Microchem J 130:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2016.08.009
Mirzajani R, Kardani F, Ramezani Z (2019) Preparation and characterization of magnetic metal–organic framework nanocomposite as solid-phase microextraction fibers coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography for determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in biological fluids and tablet formulation samples. Microchem J 144:270–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.09.014
Ocaña C, Hayat A, Mishra R, Vasilescu A, Valle M, Marty J-L (2015) A novel electrochemical aptamer-antibody sandwich assay for lysozyme detection. Analyst 140:4148–4153. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5an00243e
Palmer WJ, Duarte A, Schrader M, Day JP, Kilner R, Jiggins FM (2016) A gene associated with social immunity in the burying beetle Nicrophorus vespilloides. Proc R Soc B 283:20152733–20152740. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2015.2733
Pan J, Hu Y, Liang T, Li G (2012) Preparation of solid-phase microextraction fibers by in-mold coating strategy for derivatization analysis of 24-epibrassinolide in pollen samples. J Chromatogr A 1262:49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2012.09.008
Schneider N, Werkmeister K, Becker C-M, Pischetsrieder M (2011) Prevalence and stability of lysozyme in cheese. Food Chem 128:145–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.03.010
Shakoori M, Hoseinifar SH, Paknejad H, Jafari V, Safari R, Doan HV, Mozanzadeh MT (2019) Enrichment of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fingerlings diet with microbial lysozyme: Effects on growth performance, serum and skin mucus immune parameters. Fish Shellfish Immun 86:480–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.11.077
Song S-H, Gao Z-F, Guo X, Chen G-H (2019) Aptamer-based detection methodology studies in food safety. Food Anal Methods 12:966–990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-019-01437-3
Sun W, Zhao N, Niu X, Wang Y, Jiao K (2009) Linear sweep voltammetric studies on the supramolecular complex of alizarin red S with lysozyme and determination of lysozyme. J Chem Sci 121:217–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-009-0025-8
Tian M-M, Su R-Y, Jia Q, Bao C-L, Quan X-J (2011) Spectrophotometric determination of lysozyme by on-line preconcentration with a microcolumn containing La3+-TiO2-Zeolite. Chin J Anal Chem 39:103–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2040(10)60411-2
Valderrama L, Merib J, Março PH, Valderrama P, Garasek E (2020) Emerging micropollutants determination by NIR spectroscopy using pseudo-univariate calibration and TF-SPME coupled with 96-well plate system. Microchem J 155:104789–104797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.104789
Valeur E, Bradley M (2009) Amide bond formation: beyond the myth of coupling reagents. Chem Soc Rev 606:606–631. https://doi.org/10.1039/b701677h
Wang F, Wang X, Zhang M, Huang A, Ma L (2018) Conformational change of lysozyme on the interaction with gene carrier polyethyleneimine. Int J Biol Macromol 117:532–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.05.194
Wilken LR, Nikolov ZL (2006) Factors influencing recombinant human lysozyme extraction and cation exchange adsorption. Biotechnol Prog 22:745–752. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp0600536
Wu H, Cao D, Liu T, Zhao J, Hu X, Li N (2015) Purification and characterization of recombinant human lysozyme from eggs of transgenic chickens. PLoS One 10:146032–146048. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0146032
Zhang C, Zhang Z, Li G (2014) Preparation of sulfonated graphene/polypyrrole solid-phase microextraction coating by in situ electrochemical polymerization for analysis of trace terpenes. J Chromatogr A 1346:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.04.043
Zhang Q, Yang Y, Zhang C, Zheng Y, Wu Y, Wang X (2021) Development of an aptamer-functionalized capillary monolithic column for the highly-selective and highly-efficient recognition of patulin. Food Control 119:107461–107467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107461
Zhu C, Yang G, Ghulam M, Li L, Qu F (2019) Evolution of multi-functional capillary electrophoresis for high-efficiency selection of aptamers. Biotechnol Adv 37:107432–107447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.107432
Funding
This study was financed by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21505115), the Top Scientific and Technological Talents in Universities of Guizhou Province (KY2018078), the Higher Education Improvement Project of Guizhou Province (2017014) and the Professor Programs Foundation of Xingyi Normal University for Nationalities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and informed consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in this work.
Conflict of interest
Qianchun Zhang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Junyu Chen declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yutong Wang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Guangping Xia declares that she has no conflict of interest. Yuguo Zheng declares that he has no conflict of interest. Xingyi Wang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Yun Wu declares that she has no conflict of interest. Changbo Zhang declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 498 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Chen, J., Wang, Y. et al. Preparation and application of lysozyme aptamer fibre for specific recognition of lysozyme in food samples. Food Anal. Methods 14, 1464–1471 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-021-01993-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-021-01993-7