Abstract
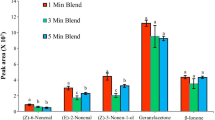
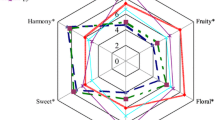
Since the aroma is one of the essential factors for evaluating fruit quality, a headspace–solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry method for the identification and quantification of the aroma volatile constituents in melon fruits has been developed. Two different varieties of Cucumis melo L., reticulatus and inodorus, have been analyzed and 66 volatile compounds have been identified and quantified; among these, the impact aroma compounds are included too. The volatile compounds have been identified by linear retention index, mass spectra, standard injection, and reference data; the quantification has been carried out by the standard addition technique. The method proposed showed good linearity within the concentration range tested; the precision, CV was <15% for all the components identified, and the limits of quantification was very low for most of the components, for example, 1.7 ng/g for ethyl octanoate and 1.5 ng/g for limonene. The results emphasized each fruit variety could be distinguished by a different qualitative and quantitative volatile fraction composition; as example, reticulatus samples were characterized by a high amount of esters (192.8 μg/Kg), which were present as traces in inodorus. Sensory analysis was performed on the samples and quantitative volatile and sensory data were correlated using multivariate analysis. The developed method allowed us to obtain reliable quantitative data of the melon volatile constituents which are necessary for the fruit quality evaluation since the aroma contribution of a particular substance is assessed by knowledge of the ratio between its amount and odor threshold level.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arvanitoyannis IS, Vlachos A (2007) Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 47(5):441–498
Ashurst PR (1999) Food flavorings, 3rd edn. pp. 116–145
Aubert C, Bourger N, Agric J (2004) Food Chem 52:4522–4528
Beaulieu JC (2005) Within-season volatile and quality differences in stored fresh-cut cantaloupe cultivars. J Agric Food Chem 53(22):8679–8687
Beaulieu JC, Aura J (2006) Soc Hoar Sci 131(1):127–139
Beaulieu JC, Grimm CC, Agric J (2001) Food Chem 49:1345–1352
Beaulieu JC, Lancaster VA, Agric J (2007) Food Chem 55:9503–9513
Jordan MJ, Shaw PE, Goodner KL (2001) J Agric Food Chem 49:5929–5933
Kourkoutas D, Elmore JS, Mottram DS (2006) Food Chem 97:95–102
Lamikanra O, Richard OA, Agric J (2002) Food Chem 50:4043–4047
Lanza CM, Scacco A, Mazzaglia A, Pagliarini E (2008) Vitic Enol 2(3–4):467–472
Obando-Ulloa JM, Moreno E, Garcıa-Mas J, Nicolai B, Lammertync J, Monforte AJ, Fernandez-Trujillo JP (2008) Postharvest Biol Technol 49:27–37
Obando-Ulloa JM, Ruiz J, Monforte AJ, Fernández-Trujillo JP (2010) Food Chem 118:815–822
Perry PL, Wang Y, Lin J (2009) Flavour Frag J 24:341–347
Saftner R, Abbott JA, Lester G, Vinyard B (2006) Postharvest Biol Technol 42:150–160
Tzouros NE, Arvanitoyannis IS (2001) Agric Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 41(4):287–319
Verzera A, Ziino M, Scacco A, Lanza CM, Mazzaglia A, Romeo V, Condurso C (2008) Food Anal Methods 1:144–151
Wyllie SG, Leach DN (1990) J Agric Food Chem 38:2042–2044
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verzera, A., Dima, G., Tripodi, G. et al. Fast Quantitative Determination of Aroma Volatile Constituents in Melon Fruits by Headspace–Solid-Phase Microextraction and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 4, 141–149 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-010-9159-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-010-9159-z