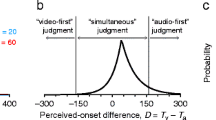
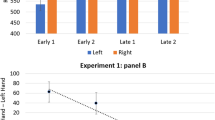
Abstract
Previous studies have demonstrated that spatial location impacts temporal order perception, and that the effect of spatial location on temporal order perception varies across cultures. English and Spanish speakers can perceive left-side stimuli occur earlier than right-side stimuli, while native Hebrew speakers do not express this characteristic. Likewise, only a few studies have investigated the effect of spatial location on temporal order perception in Chinese culture, which would be the main aim of this research. In Experiments 1–3, a temporal order judgment (TOJ) task, simultaneity judgment (SJ) task, and TOJ-SJ dual-task were used to test the effect of spatial location on temporal order perception. On the horizontal axis, the effect of spatial location on temporal order perception was observed only in the TOJ task, with Mandarin speakers perceiving left-side stimuli occur earlier than right-side stimuli. On the vertical axis, Mandarin speakers consistently perceived the top-side stimuli occur earlier than the bottom-side stimuli in every task. In Experiment 4, an ‘orthogonal’ (location-unrelated) TOJ task was used, where the participants were required to judge the color order that appeared. We also observed the effect of spatial location (top or left) on temporal order perception in this experiment. The results indicated that the effects of spatial location on temporal order perception were robust in both horizontal and vertical directions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beracci, A., Rescott, M. L., Natale, V., & Fabbri, M. (2022). The vertical space–time association. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 75(9), 1674–1693. https://doi.org/10.1177/17470218211057031
Bergen, B. K., & Chan Lau, T. T. (2012). Writing direction affects how people map space onto time. Frontiers in Psychology, 3, 109. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00109
Binder, M. (2015). Neural correlates of audiovisual temporal processing—comparison of temporal order and simultaneity judgments. Neuroscience, 300, 432–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.05.011
Bonato, M., Zorzi, M., & Umiltà, C. (2012). When time is space: Evidence for a mental time line. Neuroscience and Biobehavioural Reviews, 36(10), 2257–2273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.08.007
Boroditsky, L. (2011). How languages construct time. In S. Dehaene & E. Brannon (Eds.), Space, time and number in the brain: Searching for the foundations of mathematical thought (pp. 333–341). Burlington, MA: Elsevier/Academic Press.
Bowers, D., & Heilman, K. M. (1980). Pseudoneglect: Effects of hemispace on a tactile line bisection task. Neuropsychologia.18(4–5), 491–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/0028-3932(80)90151-7
Chan, T. T., & Bergen, B. (2005). Writing direction influences spatial cognition. Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh Annual Conference of Cognitive Science Society. 27, 412–417.
Chokron, S., & Imbert, M. (1993). Influence of reading habits on line bisection. Cognitive Brain Research, 1(4), 219–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/0926-6410(93)90005-P
Constable, M. D., Welsh, T., Pratt, J., & Huffman, G. (2018). I before U: temporal order judgements reveal bias for self-owned objects. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 72(3), 589–598. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747021818762010
Cui-Hua, B. I., Lu-Lou, G. U. O., & Jia, Y. U. (2021). Sensorimotor experience affects the formation of Mental Timeline: The evidence from Blind. Journal of Psychological Science, 44(5), 1064–1072. https://doi.org/10.16719/j.cnki.1671-6981.20210506
Dalmaso, M., Schnapper, Y., & Vicovaro, M. (2022). When time stands upright: STEARC effects along the vertical axis. Psychological Research, 19, 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-022-01693-9
Dean, C. L., Eggleston, B. A., Gibney, K. D., Aligbe, E., Blackwell, M., & Kwakye, L. D. (2017). Auditory and visual distractors disrupt multisensory temporal acuity in the crossmodal temporal order judgment task. PLoS One, 12(7), e0179564. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179564
Ding, X., Feng, N., Cheng, X., Liu, H., & Fan, Z. (2015). Are past and future symmetric in mental time line? Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 208. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00208
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A. G., & Buchner, A. (2007). G* Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39(2), 175–191. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03193146
Friedrich, T. E., & Elias, L. J. (2014). Behavioural asymmetries on the greyscales task: The influence of native reading direction. Culture and Brain, 2, 161–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40167-014-0019-3
Fuhrman, O., & Boroditsky, L. (2010). Cross-cultural differences in mental representations of time: Evidence from an implicit nonlinguistic task. Cognitive Science, 34(8), 1430–1451. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-6709.2010.01105.x
Fuhrman, O., McCormick, K., Chen, E., Jiang, H., Shu, D., Mao, S., & Boroditsky, L. (2011). How linguistic and cultural forces shape conceptions of time: English and mandarin time in 3D. Cognitive Science, 35(7), 1305–1328. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-6709.2011.01193.x
Fujisaki, W., & Nishida, S. (2010). A common perceptual temporal limit of binding synchronous inputs across different sensory attributes and modalities. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 277(1692), 2281–2290. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2010.0243
García-Pérez, M. A., & Alcalá-Quintana, R. (2012). On the discrepant results in synchrony judgment and temporal-order judgment tasks: a quantitative model. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 19(5), 820–846. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-012-0278-y
Grasso, C., Ziegler, J., Mirault, J., Coull, J., & Montant, M. (2021). As time goes by: Space-time compatibility effects in word recognition. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 48(2), 304. https://doi.org/10.1037/xlm0001007
Gu, Y. Y., & Zhang, Z. J. (2012). The horizontal and the vertical mental timeline in Chinese context. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 44(8), 1015–1024. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2012.01015
Guerrini, C., Berlucchi, G., Bricolo, E., & Aglioti, S. M. (2003). Temporal modulation of spatial tactile extinction in right-brain-damaged patients. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 15(4), 523–536. https://doi.org/10.1162/089892903321662912
He, J., Bi, C., Jiang, H., & Meng, J. (2021). The variability of mental timeline in vertical dimension. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 6209. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.782975
Heber, I. A., Siebertz, S., Wolter, M., Kuhlen, T., & Fimm, B. (2010). Horizontal and vertical pseudoneglect in peri- and extrapersonal space. Brain and Cognition, 73(3), 160–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandc.2010.04.006
Jewell, G., & McCourt, M. E. (2000). Pseudoneglect: A review and meta-analysis of performance factors in line bisection tasks. Neuropsychologia, 38(1), 93–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0028-3932(99)00045-7
Kolesari, J., & Carlson, L. (2018). How the physicality of space affects how we think about time. Memory & Cognition, 46(3), 438–449. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13421-017-0776-2
Li, Q., Liu, P., Huang, S., & Huang, X. (2018). The effect of phasic alertness on temporal precision. Attention, Perception, and Psychophysics, 80, 262–274. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-017-1418-2
Love, S. A., Petrini, K., Cheng, A., & Pollick, F. E. (2013). A psychophysical investigation of differences between synchrony and temporal order judgments. PloS One, 8(1), e54798. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0054798
Love, S. A., Petrini, K., Pernet, C. R., Latinus, M., & Pollick, F. E. (2018). Overlapping but divergent neural Correlates Underpinning Audiovisual Synchrony and temporal order judgments. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 12, 274. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2018.00274
Matthews, N., Welch, L., Achtman, R., Fenton, R., & FitzGerald, B. (2016). Simultaneity and temporal order judgments exhibit distinct reaction times and training effects. PloS One, 11(1), e0145926. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0145926
Mayzner, M. S., & Agresti, W. W. (1978). On an illusion of visual temporal order. Bulletin of the Psychonomic Society, 12(6), 451–452. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03329734
Miles, L. K., Tan, L., Noble, G. D., Lumsden, J., & Macrae, C. N. (2011). Can a mind have two time lines? Exploring space–time mapping in Mandarin and English speakers. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 18(3), 598–604. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-011-0068-y
Miyazaki, M., Kadota, H., Matsuzaki, K. S., Takeuchi, S., Sekiguchi, H., Aoyama, T., & Kochiyama, T. (2016). Dissociating the neural correlates of tactile temporal order and simultaneity judgements. Scientific Reports, 6, 23323. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23323
Pérez, A., García, L., Valdés-Sosa, M., & Jaśkowski, P. (2011). Influence of the learnt direction of reading on TemporalOrder Judgments. Psychology, 02(02), 103–108. https://doi.org/10.4236/psych.2011.22017
Pérez, A., García Pentón, L., & Valdés-Sosa, M. (2008). Rightward shift in temporal order judgements in the wake of the attentional blink. Psicológica, 29(1). 35–54.
Pitt, B., & Casasanto, D. (2020). The correlations in experience principle: How culture shapes concepts of time and number. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 149(6), 1048–1070. https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0000696
Rajsic, J., Perera, H., & Pratt, J. (2017). Learned value and object perception: accelerated perception or biased decisions? Attention Perception and Psychophysics, 79(2), 603–613. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-016-1242-0
Rinaldi, L., Locati, F., Parolin, L., Bernardi, N. F., & Girelli, L. (2016). Walking on a mental time line: temporal processing affects step movements along the sagittal space. Cortex; a Journal Devoted to the Study of the Nervous System and Behavior, 78, 170–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2016.02.013
Schneider, K. A., & Bavelier, D. (2003). Components of visual prior entry. Cognitive Psychology, 47(4), 333–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-0285(03)00035-5
Sekuler, R., Tynan, P., & Levinson, E. (1973). Visual temporal order: a new illusion. Science, 180(4082), 210–212. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.180.4082.210
Shore, D. I., Gray, K., Spry, E., & Spence, C. (2005). Spatial modulation of tactile temporal-order judgments. Perception, 34(10), 1251–1262. https://doi.org/10.1068/p3313
Shore, D. I., Spence, C., & Klein, R. M. (2001). Visual prior entry. American Psychological Society, 1(3), 205–212. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic960259b
Spence, C., & Parise, C. (2010). Prior-entry: A review. Consciousness and Cognition, 19(1), 364–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.concog.2009.12.001
Stevenson, R. A., & Wallace, M. T. (2013). Multisensory temporal integration: Task and stimulus dependencies. Experimental Brain Research, 227, 249-261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-013-3507-3
Suavansri, K., Falchook, A. D., Williamson, J. B., & Heilman, K. M. (2012). Right up there: Hemispatial and hand asymmetries of altitudinal pseudoneglect. Brain and Cognition, 79(3), 216-220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandc.2012.03.003
Tiippana, K., & Salmela, V. R. (2018). Stimulus duration has little effect on auditory, visual and audiovisual temporal order judgement. Experimental Brain Research, 236(5),1273-1282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-018-5218-2
Ulrich, R. (1987). Threshold models of temporal-order judgments evaluated by a ternary response task. Perception & Psychophysics, 42(3), 224–239. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03203074
Ulrich, R., Eikmeier, V., de la Vega, I., Ruiz Fernández, S., Alex-Ruf, S., & Maienborn, C. (2012). With the past behind and the future ahead: Back-to-front representation of past and future sentences. Memory & Cognition, 40(3), 483–495. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13421-011-0162-4
Vallesi, A., Weisblatt, Y., Semenza, C., & Shaki, S. (2014). Cultural modulations of space–time compatibility effects. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 21(3), 666–669. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-013-0540-y
Van Eijk, R. L. J., Kohlrausch, A., Juola, J. F., & Van De Par, S. (2008). Audiovisual synchrony and temporal order judgments: Effects of experimental method and stimulus type. Perception and Psychophysics, 70(6), 955–968. https://doi.org/10.3758/PP.70.6.955
Vatakis, A., Navarra, J., Soto-Faraco, S., & Spence, C. (2008). Audiovisual temporal adaptation of speech: temporal order versus simultaneity judgments. Experimental Brain Research, 185(3), 521–529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-007-1168-9
Wagenmakers, E. J., Love, J., Marsman, M., Jamil, T., Ly, A., Verhagen, J., Selker, R., Gronau, Q. F., Dropmann, D., Boutin, B., Meerhoff, F., Knight, P., Raj, A., van Kesteren, E. J., van Doorn, J., Šmíra, M., Epskamp, S., Etz, A., Matzke, D., & Morey, R. D. (2018). Bayesian inference for psychology. Part II: Example applications with JASP. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 25(1), 58–76. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-017-1323-7
West, G. L., Anderson, A. A. K., & Pratt, J. (2009). Motivationally significant stimuli show visual prior entry: evidence for attentional capture. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 35(4), 1032–1042. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0014493
Wise, A., & Barnett-Cowan, M. (2018). Perceived simultaneity and temporal order of Audiovisual events following concussion. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 12, 139. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2018.00139
Yang, W., & Sun, Y. (2016). A monolingual mind can have two time lines: Exploring space-time mappings in Mandarin monolinguals. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 23(3), 857–864. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-015-0964-7
Yarrow, K., Jahn, N., Durant, S., & Arnold, D. H. (2011). Shifts of criteria or neural timing? The assumptions underlying timing perception studies. Consciousness and Cognition, 20(4), 1518–1531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.concog.2011.07.003
Yates, M. J., & Nicholls, M. E. (2009). Somatosensory prior entry. Attention Perception Psychophysics, 71(4), 847–859. https://doi.org/10.3758/APP.71.4.847
Yates, M. J., & Nicholls, M. E. R. (2011). Somatosensory prior entry assessed with temporal order judgments and simultaneity judgments. Attention Perception & Psychophysics, 73(5), 1586–1603. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-011-0117-7
Yin, T., & Huan, X. (2009). Research methods of temporal order perception and influencing factors. Psychological Exploration, 29(5), 22–26. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1003-5184.2009.05.005
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, L., Huang, X. The influence of spatial location on temporal order perception. Curr Psychol 43, 2052–2061 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-04225-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-04225-1