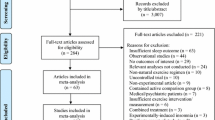
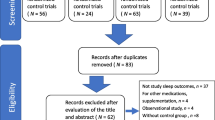
Abstract
Patients with major depressive disorders (MDD) who exercise report better quality of sleep, but there is a need for more conclusive evidence. This systematic review sought to gather data only from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that looked at how physical activity affects the quality of sleep in patients with MDD. Three e-databases (Web of Sciences, Scopus, and PubMed) were searched for relevant RCTs in January 2021. Ten RCTs (768 participants) with a total of 24 articles were deemed eligible, including RCTs with clinically diagnosed MDD. Across the studies, physical activity was found to improve sleep quality among people with MDD. However, the limitations of this systematic review include the few available trials, the small number of samples with clinically diagnosed MDD patients, and the wide range of exercise modalities. The physical activity enhanced sleep quality in people with MDD, especially in RCTs with 150 min per week moderate intensity interventions. Although more RCTs are required to examine the effects of physical activity among people with MDD, these findings are clinically useful.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article (and its additional file).
References
Archer, T., Josefsson, T., & Lindwall, M. (2014). Effects of physical exercise on depressive symptoms and biomarkers in depression. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets, 13(10), 1640–1653. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527313666141130203245
Bahmani, D. S., Razazian, N., Farnia, V., Alikhani, M., Tatari, F., & Brand, S. J. M. (2019). Compared to an active control condition, in persons with multiple sclerosis two different types of exercise training improved sleep and depression, but not fatigue,paresthesia, and intolerance of uncertainty. Multiple sclerosis and related disorders, 36, 101356.
Blumenthal, J. A., Babyak, M. A., Doraiswamy, P. M., Watkins, L., Hoffman, B. M., Barbour, K. A., & Waugh, R. J. P. (2007). Exercise and pharmacotherapy in the treatment of theajor depressive disorder. Psychosomatic medicine, 69(7), 587–596.
Brand, S., Ebner, K., Mikoteit, T., Lejri, I., Gerber, M., Beck, J., & Eckert, A. (2020). Influence of regular physical activity on mitochondrial activity and symptoms of burnout—An interventional pilot study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(3), 667.
Brand, S., Gerber, M., Beck, J., Hatzinger, M., Pühse, U., & Holsboer-Trachsler, E. (2010). High exercise levels are related to favorable sleep patterns and psychological functioning in adolescents: a comparison of athletes and controls. Journal of Adolescent Health, 46(2), 133–141.
Brupbacher, G., Gerger, H., Zander-Schellenberg, T., Straus, D., Porschke, H., Gerber, M., & Schmidt-Trucksäss, A. J. S. (2021). The effects of exercise on sleep in unipolar depression: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 101452
Brupbacher, G., Zander-Schellenberg, T., Straus, D., Porschke, H., Infanger, D., Gerber, M., & Schmidt-Trucksäss, A. (2021). The Acute Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Nocturnal and Pre-Sleep Arousal in Patients with Unipolar Depression: Preplanned Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine,10(17), 4028.
Chan, A. S., Wong, Q. Y., Sze, S. L., Kwong, P. P., Han, Y. M., & Cheung, M. C. (2012). Chinese Chan-based mind-body intervention for patients with depression. Clinical Interventions in Aging, 142(1–3), 283–289.
Combs, K., Smith, P. J., Sherwood, A., Hoffman, B., Carney, R. M., & Freedland, K. (2014). Impact of sleep complaints and depression outcomes among participants in the standard medical intervention and long-term exercise study of exercise and pharmacotherapy for depression. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 202(2), 167–171.
Craft, L. L., & Perna, F. M. (2004). The benefits of exercise for the clinically depressed. Primary care companion to the Journal of clinical psychiatry, 6(3), 104.
Driver, H. S., & Taylor, S. R. (2000). Exercise and sleep. Sleep medicine reviews, 4(4), 387–402.
Gerber, M., Beck, J., Brand, S., Cody, R., Donath, L., Eckert, A., & Holsboer-Trachsler, E. J. T. (2019). The impact of lifestyle Physical Activity Counselling in IN-PATients with major depressive disorders on physical activity, cardiorespiratory fitness, depression, and cardiovascular health risk markers: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials, 20(1), 1–21.
Gerber, M., Minghetti, A., Beck, J., Zahner, L., & Donath, L. (2019). Is improved fitness following a 12-week exercise program associated with decreased symptom severity, better well-being, and fewer sleep complaints in patients with major depressive disorders? A secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Psychiatric Research,113, 58–64.
Gerber, M., & Pühse, U. (2009). Review article: do exercise and fitness protect against stress-induced health complaints? A review of the literature. Scandinavian Journal of Public Health, 37(8), 801–819.
Giese, M., Unternährer, E., Hüttig, H., Beck, J., Brand, S., Calabrese, P., & Eckert, A. (2014). BDNF: an indicator of insomnia? Molecular Psychiatry, 19(2), 151–15.2
Gökçe, E., Güneş, E., & Nalçaci, E. (2019). Effect of exercise on major depressive disorder and schizophrenia: a BDNF focused approach. Noropsikiyatri Arsivi, 56(4), 302.
Gordon, B. R., McDowell, C. P., Hallgren, M., Meyer, J. D., Lyons, M., & Herring, M. P. (2018). Association of the efficacy of resistance exercise training with depressive symptoms: a meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis of randomized clinical trials. JAMA Psychiatry,75(6), 566.
Gourgouvelis, J., Yielder, P., Clarke, S. T., Behbahani, H., & Murphy, B. A. (2018). Exercise leads to better clinical outcomes in those receiving medication plus cognitive behavioral therapy for major depressive disorder. Frontiers in Psychiatry,9, 37.
Hallgren, M., Vancampfort, D., & Stubbs, B. (2016). Exercise is medicine for depression: even when the “pill” is small. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment,12, 2715.
Hasin, D. S., Goodwin, R. D., Stinson, F. S., & Grant, B. F. (2005). Epidemiology of major depressive disorder: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcoholism and Related Conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry, 62(10), 1097–1106.
Ignácio, Z. M., da Silva, R. S., Plissari, M. E., Quevedo, J., & Réus, G. Z. (2019). Physical exercise and neuroinflammation in major depressive disorder. Mol Neurobiol,56(12), 8323–8335.
Imboden, C., Gerber, M., Beck, J., Eckert, A., Lejri, I., Pühse, U., & Hatzinger, M. J. B. S. (2021). Aerobic Exercise and Stretching as Add-On to Inpatient Treatment for Depression Have No Differential Effects on Stress-Axis Activity, Serum-BDNF, TNF-Alpha and Objective Sleep Measures. Brain Sciences, 11(4), 411.
Junior, J. F. S., Eckeli, A. L., Ribeiro, C. C. C., Batista, R. F. L., da Silva, A. A. M., & Alves, C. M. C. J. S. M (2021). Influence of excessive daily sleeping and sleep quality on BDNF and NGF serum levels in adolescents. Sleep Medicine, 84, 415–423.
Kadoya, M., Koyama, H., Kurajoh, M., Naka, M., Miyoshi, A., Kanzaki, A., & Yamamoto, T. J. P. (2016). Associationsf sleep quality and awake physical activity with fluctuations in nocturnal blood pressure in patients with cardiovascular risk factors. PLoS One, 11(5), e0155116.
Kalak, N., Gerber, M., Kirov, R., Mikoteit, T., Yordanova, J., Pühse, U., & Brand, S. (2012). Daily morning running for 3 weeks improved sleep and psychological functioning in healthy adolescents compared with controls. J Adolesc Health,51(6), 615–622.
Kredlow, M. A., Capozzoli, M. C., Hearon, B. A., Calkins, A. W., & Otto, M. W. (2015). The effects of physical activity on sleep: a meta-analytic review. Journal of behavioral medicine,38(3), 427–449.
Krystal, A. D., & Edinger, J. D. (2008). Measuring sleep quality. Sleep medicine, 9, S10–S17.
Lallukka, T., Sivertsen, B., Kronholm, E., Bin, Y. S., Øverland, S., & Glozier, N. (2018). Association of sleep duration and sleep quality with the physical, social, and emotional functioning among Australian adults. Sleep Health, 4(2), 194–200.
Lang, C., Kalak, N., Brand, S., Holsboer-Trachsler, E., Pühse, U., & Gerber, M. (2016). The relationship between physical activity and sleep from mid-adolescence to early adulthood. A systematic review of methodological approaches and meta-analysis. Sleep medicine reviews, 28, 32–45.
Lavretsky, H., Holstein, L. L., Olmstead, R. E., Ercoli, L. M., Riparetti-Brown, M., Cyr, N. S., & Irwin, M. (2011). Complementary use of tai chi chih augments escitalopram treatment of geriatric depression: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry, 19(10), 839–850.
Levinson, D. F. J. B. p (2006). The genetics of depression: a review. Biological Psychiatry, 60(2), 84–92.
Lopresti, A. L., Hood, S. D., & Drummond, P. (2013). A review of lifestyle factors that contribute to important pathways associated with major depression: diet, sleep, and exercise. J Affect Disord,148(1), 12–27.
Ludyga, S., Gerber, M., Brand, S., Holsboer-Trachsler, E., & Pühse, U. J. P. (2016). Acute effects of moderate aerobic exercise on specific aspects of executive function in different age and fitness groups: A meta‐analysis. Psychophysiology, 53(11), 1611–1626.
Mandolesi, L., Polverino, A., Montuori, S., Foti, F., Ferraioli, G., Sorrentino, P., & Sorrentino, G. J. F. (2018). Effects of physical exercise on cognitive functioning and wellbeing: biological and psychological benefits. Front Psychol,9, 509.
Martinowich, K., Manji, H., & Lu, B. (2007). New insights into BDNF function in depression and anxiety. Nat Neurosci, 10(9), 1089–1093.
Mellion, M. B. J. P. (1985). Exercise therapy for anxiety and depression: 1. Does the evidence justify its recommendation? Postgrad Med,77(3), 59–66.
Mikoteit, T., Brand, S., Eckert, A., Holsboer-Trachsler, E., & Beck, J. 2019). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is a biomarker for subjective insomnia but not objectively assessable poor sleep continuity. J Psychiatr Res,110, 103–109.
Miller, K. J., Gonçalves-Bradley, D. C., Areerob, P., Hennessy, D., Mesagno, C., & Grace, F. J. A. R. R. (2020). Comparative effectiveness of three exercise types to treat clinical depression in older adults: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Aging Res Rev, 58, 100999.
Moher, D., Altman, D. G., Liberati, A., & Tetzlaff, J. J. E. (2011). PRISMA statement. BMJ, 22(1), 128.
Murphy, M., & Peterson, M. (2015). Sleep disturbances in depression. Sleep Med Clin,10(1), 17.
Murri, M. B., Pariante, C., Mondelli, V., Masotti, M., Atti, A. R., Mellacqua, Z., & Zanetidou, S. J. P. (2014). HPA axis and aging in depression: systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 41, 46–62.
Murawski, B., Plotnikoff, R. C., Rayward, A. T., Vandelanotte, C., Brown, W. J., & Duncan, M. J. (2018). Randomised controlled trial using a theory-based m-health intervention to improve physical activity and sleep health in adults: the Synergy Study protocol. BMJ open, 8(2), e018997.
North, T. C., McCullagh, P., Tran, Z. V., Lavallee, D. E., Williams, J. M., Jones, M. V., & Papathomas, A. C. (2008). Effect of exercise on depression. In D. Lavallee, J. M. Williams, M. V. Jones, M. Allen, C. Spray, H. Peters, M. Eys, G. Morgan, V. Krane, C. Douglas, M. I. Jones, A. Papathomas, & C. Scherzer (Eds.), K. Goodger (Collaborators), Key studies in sport and exercise psychology (pp. 258–284). Open University Press.
Pariante, C. M., & Lightman, S. (2008). The HPA axis in major depression: classical theories and new developments. Trends Neurosci,31(9), 464–468.
Park, S. D., & Yu, S. H. J. (2015). The effects of Nordic and general walking on depression disorder patients’ depression, sleep, and body composition. J Phys Ther Sci,27(8), 2481–2485.
Phillips, C. J. N. (2017). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, depression, andhysical activity: making the neuroplastic connection. Neural Plast,2017.
Ryan, M. P. (2008). The antidepressant effects of physical activity: Mediating self-esteem and self-efficacy mechanisms. Psychology & Health, 23(3), 279–307.
Rethorst, C., Sunderajan, P., Greer, T., Grannemann, B., Nakonezny, P., Carmody, T., & Trivedi, M. J. P. (2013). Does exercise improve self-reported sleep quality in non-remittedajor depressive disorder? Psychol Med,43(4), 699 – 70.
Rosenbaum, S., Tiedemann, A., Sherrington, C., Curtis, J., & Ward, P. B. (2014). Physical activity interventions for people with mental illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Psychiatry,75(9), 0–0.
Salmon, P. (2001). Effects of physical exercise on anxiety, depression, and sensitivity to stress: a unifying theory. Clinical psychology review, 21(1), 33–61.
Schunk, D. H., & DiBenedetto, M. K. J. C. E. P. (2020). Motivation and social cognitive theory. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 60, 101832.
Sedov, I. D., Cameron, E. E., Madigan, S., & Tomfohr-Madsen, L. M. (2018). Sleep quality during pregnancy: a meta-analysis. Sleep medicine reviews, 38, 168–176.
Simpson, N., & Dinges, D. F. (2007). Sleep and inflammation. Nutr Rev,65(suppl_3), S244–S252.
Singh, N. A., Clements, K. M., & Fiatarone, M. A. J. S. (1997). A randomized controlled trial of the effect of exercise on sleep. Sleep, 20(2), 95–101.
Singh, N. A., Stavrinos, T. M., Scarbek, Y., Galambos, G., Liber, C., Singh, F., M. A., & Morley, J. (2005). A randomized controlled trial of high versus low-intensity weight training versus general practitioner care for clinical depression in older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci,60(6), 768–776.
Smith, K. J. N. N. (2014). Mental health: a world of depression. Nature, 515(7526), 180.
Smith, P. J., & Merwin, R. M. (2021). The role of exercise in the management of mental health disorders: an integrative review. Annual review of medicine, 72, 45.
Su, Y., Wang, S. B., Zheng, H., Tan, W. Y., Li, X., Huang, Z. H., & Jia, F. J. (2021). The role of anxiety and depression in the relationship between physical activity and sleep quality: A serial multiple mediation model. Journal of Affective Disorders, 290, 219–226.
Vancampfort, D., Firth, J., Schuch, F. B., Rosenbaum, S., Mugisha, J., Hallgren, M., & De Hert, M. J. W. P. (2017). Sedentary behavior and physical activity levels in people with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder: a global systematic review and meta-analysis. World Psychiatry, 16(3), 308–315.
Werneck, A. O., Silva, D. R., Malta, D. C., Lima, M. G., Souza-Júnior, P. R., Azevedo, L. O., & Szwarcwald, C. L. (2020). The mediation role of sleep quality in the association between the incidence of unhealthy movement behaviors during the COVID-19 quarantine and mental health. Sleep medicine, 76, 10–15.
Yang, P. Y., Ho, K. H., Chen, H. C., & Chien, M. Y. (2012). Exercise training improves sleep quality in middle-aged and older adults with sleep problems: a systematic review. J Physiother,58(3), 157–163.
Yuan, Y., Heizhati, M., Wang, L., Li, M., Lin, M., Gan, L., & Li, N. (2021). Poor sleep quality is associated with new-onset hypertension in a diverse young and middle-aged population. Sleep Medicine, 88, 189–196.
Yu, H., & Chen, Z. J. A. P. S. (2011). The role of BDNF in deprisiousedis baseded on its location in the neural circuitry. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 32(1), 3–11.
Yun, L., Fagan, M., Subramaniapillai, M., Lee, Y., Park, C., Mansur, R. B., & Faulkner, G. E. (2020). Are early increases in physical activity a behavioralmarker for successful antidepressant treatment? J Affect Disord, 260, 287–291.
Acknowledgements
We wish to express our gratitude to Reza Fadaei (Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences, Iran) for assist in data collection.
Funding
This study has been fund by Iran National Science Foundation (ISNF) with budget number: (99019689).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Habibolah Khazaie, Ebrahim Norouzi, Leeba Rezaie and Roya Safari-Faramani participated in the design of the study, carried out the data, analyzed the data, interpreted the results, and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Review Board of the Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences (Kermanshah, Iran) approved the study, which was performed in accordance with the ethical principles laid down in the seventh and current edition (2013) of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
For all details include data and images relating to an individual person, written informed consent for the publication of these details and any potentially identifiable images were obtained from that person.
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any interests that might be interpreted as influencing the research, and ethical standards were followed in the conduct of the study. All authors declare no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khazaie, H., Norouzi, E., Rezaie, L. et al. Effect of physical activity on sleep quality in patients with major depression disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Curr Psychol 42, 28846–28856 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03810-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03810-8