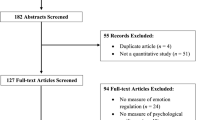
Abstract
Relationships between memory and social inference (SI) have been documented in clinical literature, and these relationships may be affected by specific symptomatology within clinical groups. Among healthy individuals, two commonly studied emotion regulation (ER) strategies, cognitive reappraisal and suppression, have been found to correlate with memory and social skills, but have not been examined in relation to SI specifically. Therefore, the aim of this study was to examine relationships between various types of memory and SI in healthy young adults, and to explore whether individual differences in ER moderate the relationship between memory and SI skills. Ninety-seven participants completed computerized tasks of memory (verbal, face, and working memory), The Awareness of Social Inference Test (TASIT), and a trait ER questionnaire. Correlational analyses showed that verbal memory was positively related to SI and cognitive reappraisal was positively related to face memory. Moderation analyses showed a positive relationship between face memory and SI only for individuals who reported high trait use of cognitive reappraisal. These findings suggest that the relationship between face memory and social cognitive abilities in healthy college students may be affected by individual differences in habitual ER strategy use.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreotti, C., Thigpen, J. E., Dunn, M. J., Watson, K., Potts, J., Reising, M. M., Robinson, K. E., Rodriguez, E. M., Roubinov, D., Luecken, L., & Compas, B. E. (2013). Cognitive reappraisal and secondary control coping: Associations with working memory, positive and negative affect, and symptoms of anxiety/depression. Anxiety, Stress, and Coping, 26(1), 20–35.
Calkins, M. E., Gur, R. C., Ragland, J. D., & Gur, R. E. (2005). Face recognition memory deficits and visual object memory performance in patients with schizophrenia and their relatives. American Journal of Psychiatry, 162(10), 1963–1966. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.162.10.1963.
Carlson, S. M., Moses, L. J., & Breton, C. (2002). How specific is the relation between executive function and theory of mind? Contributions of inhibitory control and working memory. Infant and Child Development, 11(2), 73–92.
Egloff, B., Schmukle, S. C., Burns, L. R., & Schwerdtfeger, A. (2006). Spontaneous emotion regulation during evaluated speaking tasks: Associations with negative affect, anxiety expression, memory, and physiological responding. Emotion, 6(3), 356–366.
Ellis, H. D., Ellis, D. M., Fraser, W., & Deb, S. (1994). A preliminary study of right hemisphere cognitive deficits and impaired social judgments among young people with Asperger syndrome. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 3(4), 255–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01978114.
English, T., John, O. P., Srivastava, S., & Gross, J. J. (2012). Emotion regulation and peer-rated social functioning: A 4-year longitudinal study. Journal of Research in Personality, 46(6), 780–784.
Gilbert, D. T., Krull, D. S., & Pelham, B. W. (1988). Of thoughts unspoken: Social inference and the self-regulation of behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 55(5), 685–694. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.55.5.685.
Green, M. F., Bearden, C. E., Cannon, T. D., Fiske, A. P., Hellemann, G. S., Horan, W. P., Kee, K., Kern, R. S., Lee, J., Sergi, M. J., Subotnik, K. L., Sugar, C. A., Ventura, J., Yee, C. M., & Nuechterlein, K. H. (2012). Social cognition in schizophrenia, part 1: Performance across phase of illness. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 38(4), 854–864. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbq171.
Gross, J. J. (2002). Emotion regulation: Affective, cognitive, and social consequences. Psychophysiology, 39(3), 281–291. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0048577201393198.
Gross, J. J., & John, O. P. (1998). Mapping the domain of expressivity: Multimethod evidence for a hierarchical model. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 74(1), 170–191. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.74.1.170.
Gross, J. J., & John, O. P. (2003). Individual differences in two emotion regulation processes: Implications for affect, relationships, and well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 85(2), 348–362. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.85.2.348.
Gross, J. J., Carstensen, L. L., Pasupathi, M., Tsai, J., Götestam Skorpen, C., & Hsu, A. Y. (1997). Emotion and aging: Experience, expression, and control. Psychology and Aging, 12(4), 590–599. https://doi.org/10.1037/0882-7974.12.4.590.
Gur, R. C., Ragland, J. D., Moberg, P. J., Turner, T. H., Bilker, W. B., Kohler, C., Siegel, S. J., & Gur, R. E. (2001). Computerized neurocognitive scanning: I. Methodology and validation in healthy people. Neuropsychopharmacology, 25(5), 766–776. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(01)00278-0.
Gur, R. C., Richard, J., Hughett, P., Calkins, M. E., Macy, L., Bilker, W. B., Brensinger, C., & Gur, R. E. (2010). A cognitive neuroscience-based computerized battery for efficient measurement of individual differences: Standardization and initial construct validation. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 187(2), 254–262.
Hayes, A. F. (2013). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach. Guilford Press.
IBM. (2013). SPSS statistics for windows, version 22.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp.
Ihnen, G. H., Penn, D. L., Corrigan, P. W., & Martin, J. (1998). Social perception and social skill in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research, 80(3), 275–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-1781(98)00079-1.
Ilieva, I. P., Hook, C. J., & Farah, M. J. (2015). Prescription Stimulants' effects on healthy inhibitory control, working memory, and episodic memory: A meta-analysis. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 27, 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_00776.
John, O. P., & Gross, J. J. (2004). Healthy and unhealthy emotion regulation: Personality processes, individual differences, and life span development. Journal of Personality, 72(6), 1301–1333. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6494.2004.00298.x.
Kausler, D. H. (1994). Learning and memory in normal aging. San Diego, CA: Academic Press.
Lopez, B. R., Lincoln, A. J., Ozonoff, S., & Lai, Z. (2005). Examining the relationship between executive functions and restricted, repetitive symptoms of autistic disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 35(4), 445–460.
Martin, I., & McDonald, S. (2004). An exploration of causes of non-literal language problems in individuals with Asperger syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 34(3), 311–328. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JADD.0000029553.52889.15.
McDonald, S., Flanagan, S., Rollins, J., & Kinch, J. (2003). TASIT: A new clinical tool for assessing social perception after traumatic brain injury. The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation, 18(3), 219–238.
McDonald, S., Bornhofen, C., Shum, D., Long, E., Saunders, C., & Neulinger, K. (2006). Reliability and validity of the awareness of social inference test (TASIT): A clinical test of social perception. Disability and Rehabilitation, 28(24), 1529–1542. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638280600646185.
Menon, V., Anagnoson, R., Mathalon, D., Glover, G., & Pfefferbaum, A. (2001). Functional neuroanatomy of auditory working memory in schizophrenia: Relation to positive and negative symptoms. NeuroImage, 13(3), 433–446.
Morrison, R. L., & Bellack, A. S. (1981). The role of social perception in social skill. Behavior Therapy, 12(1), 69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-7894(81)80107-4.
Philippot, P., & Feldman, R. S. (1990). Age and social competence in preschoolers' decoding of facial expression. British Journal of Social Psychology, 29(1), 43–54.
Richards, J. M., & Gross, J. J. (2000). Emotion regulation and memory: The cognitive costs of keeping one's cool. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 79(3), 410–424. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.79.3.410.
Sabatelli, R. M., Buck, R., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). A social relations analysis of nonverbal communication accuracy in married couples. Journal of Personality, 54(3), 513–527.
Schenkel, L. S., Marlow-O'Connor, M., Moss, M., Sweeney, J. A., & Pavuluri, M. N. (2008). Theory of mind and social inference in children and adolescents with bipolar disorder. Psychological Medicine, 38(6), 791–800. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0033291707002541.
Schmeichel, B. J., Volokhov, R. N., & Demaree, H. A. (2008). Working memory capacity and the self-regulation of emotional expression and experience. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 95(6), 1526–1540. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0013345.
Turner, B. J., Chapman, A. L., & Layden, B. K. (2012). Intrapersonal and interpersonal functions of non suicidal self-injury: Associations with emotional and social functioning. Suicide and Life-threatening Behavior, 42(1), 36–55.
Vakil, E. (2005). The effect of moderate to severe traumatic brain injury (TBI) on different aspects of memory: A selective review. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 27(8), 977–1021.
Acknowledgements
The data collected for this research was originally submitted in partial fulfillment of requirements for a graduate degree awarded by The Catholic University of America. We would like to thank Rosa Heryak, MaryGrace Cruser, and Conor Wilson for assistance with data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of Interest
Kelly E. Ferreira declares that she has no conflict of interest. Nancy E. Adleman declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreira, K.E., Adleman, N.E. Memory, emotion regulation, and social inference skills in college students. Curr Psychol 39, 1269–1276 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-018-9833-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-018-9833-7