Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the role of dexamethasone therapy in neonatal meningitis in a randomized placebo controlled trial.
Methods
The participants were eighty neonates with meningitis randomized to receive dexamethasone or saline placebo. Dexamethasone was started prior to the first dose of antibiotics in the dose of 0.15 mg/kg intravenous 6 hourly for 2 d. Primary outcome measure was mortality. Secondary outcome measures included progression of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) up to 48 h, differences in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cytokines between baseline levels and 24 h after enrolment and brain stem auditory evoked response (BAER) after 4 to 6 wk of discharge.
Results
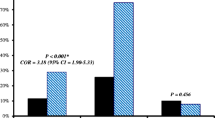
Baseline variables were comparable in both the groups. Mortality was significantly decreased in dexamethasone group (p = 0.005) and the absolute risk difference was 27.5 % (95 % CI 9.5–45.8 %). There was a significant reduction in cells per mm3 (62.5 vs. 100) and proteins (162 vs. 217.5 mg/dl) after 24 h of treatment in the dexamethasone group. IL-1β was significantly reduced after 24 h in dexamethasone group (290 vs 665 pg/ml). TNF- α was significantly lower (157.5 vs 427.5 pg/ml) and sugar significantly higher (50 vs 38 mg/dl) in the dexamethasone group after 24 h. Significant difference was noted between dexamethasone and saline groups in the progression of SIRS.
Conclusions
Dexamethasone significantly reduced fatality, progression of SIRS and CSF inflammatory indices.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Unhanand M, Mustafa MM, McCracken GH, Nelson JD. Gram negative enteric bacillary meningitis: a twenty- one- year experience. J Pediatr. 1993;122:15.
Yang YJ, Liu CC, Wang SM. Group B streptococcal infections in children: the changing spectrumof infections in infants. J Microbial Immunol Infant. 1998;31:107.
Tuomanen E, Hungstler B, Rich R, Bray MA, Zak O, Tomasz A. Non steroidal anti inflammatory agents in the therapy for experimental pneumococcal meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1987;155:985–90.
Van de Beek D, de Gans J, McIntyre P, Prasad K. Corticosteroids for acute bacterial meningitis . Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007;1:CD004405.
Peltola H, Roine I, Fernandez J, et al. Adjuvant glycerol and/or dexamethasone to improve the outcomes of childhood bacterial meningitis: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45:1277–86.
Molyneux EM, Walsh AL, Forsyth H, et al. Dexamethasone treatment in childhood bacterial meningitis in Malawi: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;360:211–8.
Van de Beek D, Farrar JJ, de Gans J, et al. Adjunctive dexamethasone in bacterial meningitis: a meta-analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:254–63.
Kim YS, Sheldon RA, Elliot BR, Liu Q, Ferriero DM, Tauber MG. Brain injury in experimental neonatal meningitis due to Group B streptococci. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1995;54:531–9.
Ahmed A, Hickey SM, Ehrell S. Cerebrospinal fluid in the term neonate. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1996;15:298–303.
Dear P. Neonatal infection. In: Rennie JM, ed. Roberton’s textbook of neonatologyPhiladelphia: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone; 2005:pp. 1011–92.
Manroe BL, Weinberg AG, Rosenfeld CR, Browne R. The neonatal blood count in health and disease. I. Reference values for neutrophilic cells. J Pediatr. 1979;95:89–98.
Adler SM, Denton RL. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate in the newborn period. J Pediatr. 1975;86:942–8.
Gerdes JS, Polin RA. Sepsis screen in neonates with evaluation of plasma fibronectin. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987;6:443–6.
Saez-Llorens X, McCracken Jr GH. Sepsis syndrome and septic shock in pediatrics: current concepts of terminology, pathophysiology and management. J Pediatr. 1993;123:497–508.
Yu JS, Grauaug A. Purulent meningitis in the neonatal period. Arch Dis Child. 1963;38:391–6.
Daoud AS, Batieha A, Al-Sheyyab M, Abuekteish F, Obeidat A, Mahafza T. Lack of effectiveness of dexamethasone in neonatal bacterial meningitis. Eur J Pediatr. 1999;158:230–3.
Quagliarello VJ, Scheld WM. Bacterial meningitis: pathogenesis, pathophysiology, and progress. N Engl J Med. 1992;327:864–72.
Nudelman Y, Tunkel AR. Bacterial meningitis: epidemiology, pathogenesis and management update. Drugs. 2009;69:2577–96.
King SM, Law B, Langley JM, et al. Dexamethasone therapy for bacterial meningitis. Better never than late. Can J Infect Dis. 1994;5:210–5.
Odio CM, Faingezicht I, Paris M. The beneficial effects of early dexamethasone administration in infants and children with bacterial meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:1525–31.
Wald ER, Kaplan SL, Mason EO, Sabo D, Ross L, Arditi M. Dexamethasone therapy for children with bacterial meningitis. Paediatrics. 1995;95:21–8.
Lebel MH, Freij BJ, Syrogiannopoulos GA, et al. Dexamethasone therapy for bacterial meningitis: results of two double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. N Engl J Med. 1988;319:964–71.
Beutler B, Krochin N, Milsark IW. Control of cachectin (tumour necrosis factor) synthesis: mechanisms of endotoxin resistance. Science. 1986;232:977–80.
Kern JA, Lamb RJ, Reed JC, Daniele RP, Nowell PC. Dexamethasone inhibition of Interleukin-1β production by human monocytes. J Clin invest. 1988;81:237–44.
Tauber MG, Khayan-Bashi H, Sande MA. Effects of Ampicillin and corticosteroids on brain water content, CSF pressures, CSF lactate in experimental pneumococcal meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1985;151:528–34.
Mustafa MM, Ramilo O, Mertsola J, Risser RC, Beutler B, Hansen EJ. Modulation of inflammation and cachectin activity in relation to treatment of experimental Haemophilus influenzae Type b meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1989;160:818–25.
Vergnano S, Sharland M, Kazembe P, Mwansambo C, Heath PT. Neonatal sepsis: an international perspective. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2005;90:F220–4.
Airede KI, Adeyemi O, Ibrahim T. Neonatal bacterial meningitis and dexamethasone adjunctive usage in Nigeria. Niger J Clin Pract. 2008;11:235–45.
Adams RD, Kubik CS, Bronner FJ. Clinical and pathological aspects of influenzal meningitis. Arch Pediatr. 1948;65:354–76,408–41.
Smith PB, Garges HP, Cotton CM, Walsh TJ, Clark RH, Benjamin Jr DK. Meningitis in preterm neonates: importance of cerebrospinal fluid parameters. Am J Perinatol. 2008;25:421–6.
Greenberg RG, Smith PB, Cotton CM, Moody MA, Clark RH, Benjamin DK. Traumatic lumbar puncture in neonates: test performance of the Cerebrospinal fluid white blood cell count. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2008;27:1047–51.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Role of Funding Source
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mathur, N.B., Garg, A. & Mishra, T.K. Role of Dexamethasone in Neonatal Meningitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Indian J Pediatr 80, 102–107 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-012-0875-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-012-0875-9