Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the prevalence of thrombocytopenia in neonates born to mothers with pregnancy induced hypertension (PIH) and identify the associated material and neonatal characteristics.
Methods
In the current, prospective study, platelet counts were assessed serially. Maternal and neonatal characteristic were recorded in pre-designed proforma. Primary outcome measures were thrombocytopenia defined as platelet count of <150000/mm3 and severe thrombocytopenia if counts were <30000/mm3 or <50000/mm3 with bleeding.
Results
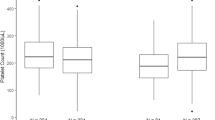
Of 97 neonates born to PIH mothers 35 (36.1%) had thrombocytopenia. In 20 (20.6%) thrombocytopenia was severe. Higher percentage of thrombocytopenia was associated with male gender (47.7%), low birth weight (71.4%) and prematurity (67.4%). Severe thrombocytopenia was significantly associated with low birth weight (OR: 4.58; 95% CI: 0.98–21.3; p<0.03) and prematurity (OR: 2.52; 95% CI: 0.87–7.24; p<0.05). Material parity, onset of PIH, and medications did not seem to be associated significantly.
Conclusion
Premature and low birth weight neonates born to mothers with pregnancy induced hypertension would require scrutiny for thrombocytopenia during early neonatal period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pritchard JA, Cunningham FG, Pritchard SA, Mason RA. How often does maternal preeclampsia-eclampsia incite thrombocytopenia in the fetus. Obstet Gynecol 1987; 69: 292–295.
Roberts I, Murray NA. Neonatal thrombocytopenia: causes and management. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2003; 88: F359–F364.
Burrows RF, Andrew M. Neonatal thrombocytopenia in the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 1990; 76: 234–238.
Murray NA Evaluation and treatment of thrombocytopenia in the neonatal intensive care unit. Acta Paediatr Suppl 2002; 91: 74–81.
Burrows RF, Kelton JG. Thrombocytopenia at delivery: a prospective survey of 6715 Deliveries. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990; 162: 731–734.
Tsao PN, Teng RJ, Chou HC, Tsou KI. The thrombopoietin level in the cord blood in premature infants born to mothers with pregnancy-induced hypertension. Biol Neonate 2002; 82: 217–221.
Engle WD, Rosenfeld CR. Neutropenia in high risk neonates. J Pediatr 1984; 105: 982–985.
Brazy JE, Grimm JK, Little VA. Neonatal manifestations of severe maternal hypertension occurring before the thirty sixth week of pregnancy. J Pediatr 1982; 100: 265–269.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramesh Bhat, Y., Cherian, C.S. Neonatal thrombocytopenia associated with maternal pregnancy induced hypertension. Indian J Pediatr 75, 571–573 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-008-0110-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-008-0110-x