Abstract
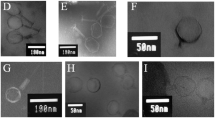
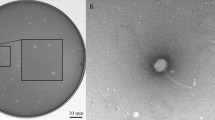
In this study, Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida was isolated, identified by 16S RNA sequencing and its potential lytic phage (ASP-1) was isolated and characterized. The bacterium was positive for virulence genes (ascV, fla, ahyB, gcaT, lip, alt and act) and phenotypic parameters (haemolysis, slime production, lipase activity, DNase test, gelatinase activity and protease activity) were tested. The bacterium was resistant to 27%, intermediate resistant to 14% and susceptible to 59% of tested common antibiotics. Transmission electron microscopy analysis revealed that lytic ASP-1 belongs to the Myoviridae family. The isolated phage was more specific against A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida (efficiency of plating index = 1), but also had infectivity to A. hydrophila lab strain 1. The bacteriolytic effect of ASP-1 was tested at early exponential phase culture of A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida, and bacteria growth was apparently decreased with time and MOI dependent manner. One-step growth of ASP-1 showed approximately 30 min of latent period, 16 PFU/infected cells of burst size and 40 min of rise period. The adsorption rate was determined as 3.61 × 108 PFU mL−1 min−1 for 3 min, and rate decreased with time. The ASP-1 genome size was estimated to be approximately 55–60 kD. The phage was stable over wide-range of temperatures, pH and salinity, thus could withstand at severe environmental conditions, indicating that ASP-1 has a potential to develop as an alternative antibiotic to use in ornamental and aquaculture industry.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaix G, Roger F, Berthe T, Lamy B, Jumas-Bilak E, Lafite R, Forget-Leray J, Petit F (2017) Distinct Aeromonas populations in water column and associated with copepods from estuarine environment (Seine, France). Front Microbiol 8:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01259
Janda JM, Abbott SL (2010) The genus Aeromonas: taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clin Microbiol Rev 23:35–73. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00039-09
Krishnakumar K, Raghavan R, Prasad G, Bijukumar A, Sekharan M, Pereira B, Ali A (2009) When pets become pests-exotic aquarium fish and biological invasions in Kerala, India. Curr Sci 97:474–476. https://www.jstor.org/stable/24111872
Bergh O (2008) Bacterial diseases of fish. In: Eiras JC, Segner H, Wahli T, Kapoor BG (eds) Fish diseases, vol 1. Science Publishers, Enfield, New Hampshire, USA, pp 239–277
Long M, Nielsen TK, Leisner JJ, Hansen LH, Shen ZX, Zhang QQ, Li A (2016) Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida strains isolated from Chinese freshwater fish contain a novel genomic island and possible regional-specific mobile genetic elements profiles. FEMS Microbiol Lett 363:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnw190
Wiklund T, Dalsgaard I (1998) Occurrence and significance of atypical Aeromonas salmonicida in non-salmonid and salmonid fish species: a review. Dis Aquat Organ 32:49–69. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao032049
Santos Y, Garcia-Marquez Z, Pereira PG, Pazos F, Riaza A, Silva R, EI Morabit A, Ubeira FM (2005) Efficacy of furunculosis vaccines in turbot, Scopthalmus maximus (L): evaluation of immersion, oral and injection delivery. J Fish Dis 28:165–172. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.2005.00610.x
Austin B, Austin DA (2007) Bacterial fish pathogens: diseases of farmed and wild fish. Springer, Cham, pp 147–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-32674-0
EI Morabit A, Garcia-Marquez S, Santos Y (2004) Is sea lamprey a potential source of infection with Aeromonas salmonicida for wild and farmed fish? Bull Eur Assoc Fish Pathol 24:100–103
Magarinos B, Devesa S, Gonzalez A, Castro N, Toranzo AE (2011) Furunculosis in Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) cultured in a recirculation system. Vet Rec 168:431. https://doi.org/10.1136/vr.c6754
Fernandez-Alvarez C, Gijon D, Alvarez M, Santos Y (2016) First isolation of Aeromonas salmonicida subspecies salmonicida from diseased sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax (L.), cultured in Spain. Aquac Rep 4:36–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2016.05.006
Coscelli GA, Bermdez R, Losada AP, Failde LD, Santos Y, Quiroga MI (2014) Acute Aeromonas salmonicida infection in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L). Histopathological and immunohistochemical studies. Aquaculture 430:79–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.04.002
Kim JH, Hwang SY, Son JS, Han JE, Jun JW, Shin SP, Choresca C Jr, Choi YJ, Park YH, Park SC (2011) Molecular characterization of tetracycline- and quinolone-resistant Aeromonas salmonicida isolated in Korea. J Vet Sci 12:41–48. https://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2011.12.1.41
Weir M, Rajic A, Dutil L, Uhland C, Bruneau N (2012) Zoonotic bacteria and antimicrobial resistance in aquaculture: opportunities for surveillance in Canada. Can Vet J 53:619–622
Dobiasova H, Kutilova I, Piackova V (2014) Ornamental fish as a source of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes and antibiotic resistance plasmids. Vet Microbiol 171:413–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.02.011
Beilstein F, Dreiseikelmann B (2008) Temperate bacteriophage PhiO18P from an Aeromonas media isolate: characterization and complete genome sequence. Virology 373:25–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2007.11.016
Kim JH, Son JS, Choi YJ, Choresca CH, Shin SP, Han JE, Jun JW, Kang DH, Oh C, Heo SJ, Park SC (2012) Isolation and characterization of a lytic Myoviridae bacteriophage PAS-1 with broad infectivity in Aeromonas salmonicida. Curr Microbiol 64:418–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-012-0091-x
Kim JH, Son JS, Choi YJ, Choresca CH, Shin SP, Han JE, Jun JW, Park SC (2012) Complete genomic sequence of a T4-like bacteriophage, phiAS4, infecting Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida. Arch Virol 157:391–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-011-1175-9
Chen L, Yuan S, Liu Q, Mai G, Yang J, Deng D, Zhang B, Liu C, Ma Y (2018) In vitro design and evaluation of phage cocktails against Aeromonas salmonicida. Front Microbiol 9:1476. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01476
Le TS, Nguyen TH, Vo PH, Doan VC, Nguyen HL, Tran MT, Tran TT, Southgate PC, Kurtboke Dİ (2018) Protective effects of bacteriophages against Aeromonas hydrophila causing motile Aeromonas Septicemia (MAS) in Striped Catfish. Antibiotics (Basel) 7:16. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics7010016
Imbeault S, Parent S, Lagace M, Uhland CF, Blais JF (2006) Using bacteriophages to prevent furunculosis caused by Aeromonas salmonicida in farmed brook trout. J Aquat Anim Health 18:203–214. https://doi.org/10.1577/H06-019.1
Verner-Jeffreys DW, Algoet M, Pond MJ, Virdee HK, Bagwell NJ, Roberts EG (2007) Furunculosis in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) is not readily controllable by bacteriophage therapy. Aquaculture 270:475–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.05.023
Kim JH, Choresca CH, Shin SP, Han JE, Jun JW, Park SC (2015) Biological control of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida infection in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) using Aeromonas phage PAS-1. Transbound Emerg Dis 62:81–86. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbed.12088
Silva YJ, Moreirinha C, Pereira C, Costa L, Rocha RJM, Cunha A, Gomes NCM, Calado R, Almeida A (2016) Biological control of Aeromonas salmonicida infection in juvenile Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) with Phage AS-A. Aquaculture 450:225–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.07.025
Carvalho-Castro GA, Lopes CO, Leal CAG, Cardoso PG, Leite RC, Figueiredo HCP (2010) Detection of type III secretion system genes in Aeromonas hydrophila and their relationship with virulence in Nile tilapia. Vet Microbiol 144:371–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2010.01.021
Sen K, Rodgers M (2004) Distribution of six virulence factors in Aeromonas species isolated from US drinking water utilities: a PCR identification. J Appl Microbiol 94:1077–1086. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2004.02398.x
Nawaz M, Khan SA, Khan AA, Sung K, Tran Q, Kerdahi K, Steele R (2010) Detection and characterization of virulence genes and integrons in Aeromonas veronii isolated from catfish. Food Microbiol 27:327–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2009.11.007
Chacon MR, Figueras MJ, Castro-Escarpulli G, Soler L, Guarro J (2003) Distribution of virulence genes in clinical and environmental isolates of Aeromonas spp. Ant van Leeuwenhoek 84:269–278. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026042125243
Igbinosa IH, Igumbor EU, Aghdasi F, Tom M, Okoh AI (2012) Emerging Aeromonas species infections and their significance in public health. Sci World J 2012:625023. https://doi.org/10.1100/2012/625023
Freeman DJ, Falkiner FR, Keane CT (1989) New method for detecting slime production by coagulase negative staphylococci. J Clin Pathol 42:872–874
Harley JP, Prescott LM (2002) Laboratory exercise in microbiology. The McGraw-Hill Companies, New York
Collins CH, Lyne PM, Grange JM (1995) Identification methods. In: Collins CH, Lyne PM, Grange JM (eds) Collins and Lyne’s microbiological methods, 8th edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, UK, p 95
Cruz T, Torres JM (2012) Gelatin hydrolysis test protocol. Microbial library American society for microbiology, Washington
Kahla-Nakbi AB, Chaieb K, Bakhrouf A (2009) Investigation of several virulence properties among Vibrio alginolyticus strains isolated from diseased cultured fish in Tunisia. Dis Aquat Organ 86:21–28. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao02091
Adams MH (1959) Enumeration of bacteriophage particles. In: Adams MH (ed) Bacteriophages. Interscience Publishers Ltd, London, pp 27–34
Ghosh K, Senevirathne A, Kang HS, Hyun WB, Kim JE, Kim KP (2018) Complete nucleotide sequence analysis of a novel Bacillus subtilis-infecting bacteriophage BSP10 and its effect on poly-gamma-glutamic acid degradation. Viruses 10:240
Stenholm AR, Dalsgaard I, Middelboe M (2008) Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages infecting the fish pathogen Flavobacterium psychrophilum. Appl Environ Microbiol 7:4070–4078. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00428-08
Barry GT, Goebel WF (1951) The effect of chemical and physical agents on the phage receptor of phase II Shigella sonnei. J Exp Med 94:387–400
Sha J, Kozlova EV, Chopra AK (2002) Role of various enterotoxin in Aeromonas hydrophila- induced gastroenteritis: generation of enterotoxin gene deficient mutants and evaluation of their enterotoxic activity. Infect Immun 70:1924–1935. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.70.4.1924-1935.2002
Gosling PJ (1996) Pathogenic mechanisms. In: Austin B, Altwegg M, Gosling PJ, Joseph SW (eds) The genus Aeromonas. Wiley, Chichester, pp 245–265
Lago EP, Nieto TP, Farto R (2012) Virulance factors of Aeromonas salmonicida supsp. salmonicida strains associated with infection in turbot Psetta maxima. Dis Aquat Organ 99:145–151. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao02467
Chandrarathna HPSU, Nikapitiya C, Dananjaya SHS, Wijerathne CUB, Wimalasena SHMP, Kwun HJ, Heo GJ, Lee J, De Zoysa M (2018) Outcome of co-infection with opportunistic and multidrug resistant Aeromonas hydrophila and A. veronii in zebrafish: identification, characterization, pathogenicity and immune responses. Fish Shellfish Immunol 80:573–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.06.049
Hossain S, De Silva BCJ, Wimalasena SHMP, Pathirana HNKS, Dahanayake PS, Heo GJ (2018) Distribution of antimicrobial resistance genes and class 1 integron gene cassette arrays in motile Aeromonas spp. Isolated from goldfish (Carassius auratus). Microb Drug Resist 24:1217–1225. https://doi.org/10.1089/mdr.2017.0388
Duarte J, Pereira C, Moreirinha C, Salvio R, Lopes A, Wang D, Almeida A (2018) New insights on phage efficacy to control Aeromonas salmonicida in aquaculture systems: an in vitro preliminary study. Aquaculture 495:970–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.07.002
Kim JH, Son JS, Choi YJ, Choresca CH Jr, Shin SP, Han JE, Jun JW, Park SC (2012) Complete genome sequence and characterization of a broad-host range T4-like bacteriophage phiAS5 infecting Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida. Vet Microbiol 157:164–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.12.016
Ackermann HW (2009) Phage classification and characterization. In: Clokie MR, Kropinski AM (eds) Bacteriophages. Methods in molecular biology™, vol 501. Humana Press, New York City, pp 127–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-164-6_13
Vincent AT, Paquet VE, Bernatchez A, Tremblay DM, Moineau S, Charette SJ (2017) Characterization and diversity of phages infecting Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida. Sci Rep 7:7054. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-07401-7
Kelly D, McAuliffe O, Ross RP, O’Mahony J, Coffey A (2011) Development of a broad-host-range phage cocktail for biocontrol. Bioeng Bugs 2:31–37. https://doi.org/10.4161/bbug.2.1.13657
Jaiswal A, Koley H, Ghosh A, Palit A, Sarkar B (2013) Efficacy of cocktail phage therapy in treating Vibrio cholerae infection in rabbit model. Microbes Infect 15:152–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micinf.2012.11.002
Bull JJ, Gill JJ (2014) The habits of highly effective phages: population dynamics as a framework for identifying therapeutic phages. Front Microbiol 5:618. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00618
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the government of Korea (MSIT) (2017010990) and a part of the project titled ‘Fish Vaccine Research Center’ funded by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikapitiya, C., Dananjaya, S.H.S., Chandrarathna, H.P.S.U. et al. Isolation and Characterization of Multidrug Resistance Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida and Its Infecting Novel Phage ASP-1 from Goldfish (Carassius auratus). Indian J Microbiol 59, 161–170 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-019-00782-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-019-00782-5