Abstract
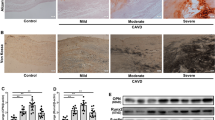
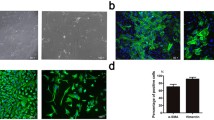
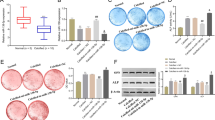
Calcified aortic valve disease (CAVD) is a major non-rheumatic heart valve disease in the world, with a high mortality rate and without suitable pharmaceutical therapy due to its complex mechanisms. Src-associated in mitosis 68-KD (Sam68), an RNA binding protein, has been reported as a signaling adaptor in numerous signaling pathways (Huot in Mol Cell Biol, 29(7), 1933-1943, 2009), particularly in inflammatory signaling pathways. The effects of Sam68 on the osteogenic differentiation process of hVICs and its regulation on signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling pathway have been investigated in this study. Human aortic valve samples detection found that Sam68 expression was up-regulated in human calcific aortic valves. We used tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) as an activator for osteogenic differentiation in vitro and the result indicated that Sam68 was highly expressed after TNF-α stimulation. Overexpression of Sam68 promoted osteogenic differentiation of hVICs while Sam68 knockdown reversed this effect. Sam68 interaction with STAT3 was predicted by using String database and was verified in this study. Sam68 knockdown reduced phosphorylation of STAT3 activated by TNF-α and the downstream gene expression, which further influenced autophagy flux in hVICs. STAT3 knockdown alleviated the osteogenic differentiation and calcium deposition promoted by Sam68 overexpression. In conclusion, Sam68 interacts with STAT3 and participates in its phosphorylation to promote osteogenic differentiation of hVICs to induce valve calcification. Thus, Sam68 may be a new therapeutic target for CAVD.
Graphical abstract

Regulatory of Sam68 in TNF-α/STAT3/Autophagy Axis in promoting osteogenesis of hVICs






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abboud D, Daly AF, Dupuis N, Bahri MA, Inoue A, Chevigne A et al (2020) GPR101 drives growth hormone hypersecretion and gigantism in mice via constitutive activation of Gs and Gq/11. Nat Commun 11(1):4752
Alushi B, Curini L, Christopher MR, Grubitzch H, Landmesser U, Amedei A et al (2020) Calcific aortic valve disease-natural history and future therapeutic strategies. Front Pharmacol 11:685
Bian W, Wang Z, Sun C, Zhang DM (2021) Pathogenesis and molecular immune mechanism of calcified aortic valve disease. Front Cardiovas Med 8:1975
Chen Q, Lv J, Yang W, Xu B, Wang Z, Yu Z et al (2019) Targeted inhibition of STAT3 as a potential treatment strategy for atherosclerosis. Theranostics 9(22):6424–6442
Comità S, Femmino S, Thairi C, Alloatti G, Boengler K, Pagliaro PAO et al (2021) Regulation of STAT3 and its role in cardioprotection by conditioning: focus on non-genomic roles targeting mitochondrial function. Basic Res Cardiol 116:1–31
Coté N, Mahmut A, Bosse Y, Couture C, Pagé S, Trahan S et al (2013) Inflammation is associated with the remodeling of calcific aortic valve disease. Inflammation 36(3):573–581
Cui J, Xu H, Yu J, Li Y, Chen Z, Zou Y et al (2021) IL-4 inhibits regulatory T cells differentiation by HDAC9-mediated epigenetic regulation. Cell Death Dis 12(6):501
de Araujo ED, Orlova AA-O, Neubauer HA-O, Bajusz DA-O, Seo HA-O, Dhe-Paganon S et al (2019) Structural implications of STAT3 and STAT5 SH2 domain mutations. Cancers 11(11):1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111757
Dutzmann J, Daniel JM, Bauersachs J, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Sedding DG (2015) Emerging translational approaches to target STAT3 signalling and its impact on vascular disease. Cardiovasc Res 106(3):365–374
El Husseini D, Boulanger MC, Mahmut A, Bouchareb R, Laflamme MH, Fournier D et al (2014) P2Y2 receptor represses IL-6 expression by valve interstitial cells through Akt: implication for calcific aortic valve disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol 72:146–156
Éva Sikura K, Combi Z, Potor L, Szerafin T, Hendrik Z, Méhes G et al (2021) Hydrogen sulfide inhibits aortic valve calcification in heart via regulating RUNX2 by NF-κB, a link between inflammation and mineralization. J Adv Res 27:165–176
Feng Y, Ke C, Tang Q, Dong H, Zheng X, Lin W et al (2014) Metformin promotes autophagy and apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by downregulating Stat3 signaling. Cell Death Dis 5(2):e1088
Fu K, Sun XA-O, Wier EM, Hodgson A, Hobbs RP, Wan FAO (2016a) Sam68/KHDRBS1-dependent NF-κB activation confers radioprotection to the colon epithelium in γ-irradiated mice. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.21957
Fu K, Sun XA-O, Wier EM, Hodgson A, Liu Y, Sears CL et al (2016b) Sam68/KHDRBS1 is critical for colon tumorigenesis by regulating genotoxic stress-induced NF-κB activation. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.15018
García-Rodríguez C, Parra-Izquierdo I, Castaños-Mollor I, López J, San Román JA, Sánchez CM (2018) Toll-like receptors, inflammation, and calcific aortic valve disease. Front Physiol 9:201
Green DR, Galluzzi L, Kroemer G (2011) Mitochondria and the autophagy-inflammation-cell death axis in organismal aging. Science (new York, NY) 333(6046):1109–1112
Greenberg HZE, Zhao G, Shah AA-O, Zhang MA-O (2022) Role of oxidative stress in calcific aortic valve disease and its therapeutic implications. Cardiovas Res 118(6):1433–1451
Grivennikov SI, Karin M (2010) Dangerous liaisons: STAT3 and NF-kappaB collaboration and crosstalk in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Revi. 21(1):11–19
Han S, Xu S, Zhou J, Qiao A, Boriboun C, Ma W et al (2019) Sam68 impedes the recovery of arterial injury by augmenting inflammatory response. J Mol Cell Cardiol 137:82–92
Huot MÉ, Brown CM, Lamarche-Vane N, Richard S (2009) An adaptor role for cytoplasmic Sam68 in modulating Src activity during cell polarization. Mol Cellular Biol 29(7):1933–1943
Huot M, Vogel G, Zabarauskas A, Ngo CT, Coulombe-Huntington J, Majewski J et al (2012) The Sam68 STAR RNA-binding protein regulates mTOR alternative splicing during adipogenesis. Mol Cell 46(2):187–199
Isoda K, Matsuki T, Fau Kondo H, Kondo H, Fau Iwakura Y, Iwakura Y, Fau Ohsuzu F, Ohsuzu F (2010) Deficiency of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist induces aortic valve disease in BALB/c mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vas Biol 30(4):708–715
Jang YH, Choi KY, Min DS (2014) Phospholipase D-mediated autophagic regulation is a potential target for cancer therapy. Cell Death Differ 21(4):533–546
Kaden JJ, Kiliç R, Sarikoç A, Hagl S, Lang S, Hoffmann U et al (2005) Tumor necrosis factor alpha promotes an osteoblast-like phenotype in human aortic valve myofibroblasts: a potential regulatory mechanism of valvular calcification. Int J Mol Med 16(5):869–872
Kasembeli MM, Singhmar P, Ma J, Edralin J, Tang Y, Adams C 3rd et al (2021) TTI-101: A competitive inhibitor of STAT3 that spares oxidative phosphorylation and reverses mechanical allodynia in mouse models of neuropathic pain. Biochem Pharmacol 192:114688
Kostyunin AE, Yuzhalin AE, Ovcharenko EA, Kutikhin AG (2019) Development of calcific aortic valve disease: Do we know enough for new clinical trials? J Mol Cell Cardiol 132:189–209
Kurozumi A, Nakano K, Yamagata K, Okada Y, Nakayamada S, Tanaka Y (2019) IL-6 and sIL-6R induces STAT3-dependent differentiation of human VSMCs into osteoblast-like cells through JMJD2B-mediated histone demethylation of RUNX2. Bone 124:53–61
Li F, Song R, Ao L, Reece TB, Cleveland JC Jr, Dong N et al (2017) ADAMTS5 deficiency in calcified aortic valves is associated with elevated pro-osteogenic activity in valvular interstitial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 37(7):1339–1351
Liang L, Hui K, Hu C, Wen Y, Yang S, Zhu P et al (2019) Autophagy inhibition potentiates the anti-angiogenic property of multikinase inhibitor anlotinib through JAK2/STAT3/VEGFA signaling in non-small cell lung cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:1–13
Lin S, Yang L, Yao Y, Xu L, Xiang Y, Zhao H et al (2019) Flubendazole demonstrates valid antitumor effects by inhibiting STAT3 and activating autophagy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:1–13
Lindman BR, Clavel MA, Mathieu P, Iung B, Lancellotti P, Otto CM et al (2016) Calcific aortic stenosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2:16006
Liu Z, Wang Y, Shi J, Chen S, Xu L, Li F et al (2020) IL-21 promotes osteoblastic differentiation of human valvular interstitial cells through the JAK3/STAT3 pathway. Int J Med Sci 17(18):3065–3072
Luo Z, Xu X, Sho T, Zhang J, Xu W, Yao J et al (2019) ROS-induced autophagy regulates porcine trophectoderm cell apoptosis, proliferation, and differentiation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 316(2):C198-c209
Martin-Romero C, Sanchez-Margalet V (2001) Human leptin activates PI3K and MAPK pathways in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: possible role of Sam68. Cell Immunol 212(2):83–91
Mukhopadhyay S, Panda PK, Sinha N, Das DN, Bhutia SK (2014) Autophagy and apoptosis: where do they meet? Apoptosis Int J Program Cell Death 19(4):555–566
Myasoedova VA, Ravani AL, Frigerio B, Valerio V, Moschetta D, Songia P et al (2018) Novel pharmacological targets for calcific aortic valve disease: prevention and treatments. Pharmacol Res 136:74–82
Nishimura RA, Otto CM, Bonow RO, Carabello BA, Erwin JP 3rd, Guyton RA et al (2014) 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation 129(23):2440–2492
O’Brien KD, Kuusisto J, Reichenbach DD, Ferguson M, Giachelli C, Alpers CE et al (1995) Osteopontin is expressed in human aortic valvular lesions. Circulation 92(8):2163–2168
Paronetto MP, Messina V, Barchi M, Geremia R, Richard S, Sette C (2011) Sam68 marks the transcriptionally active stages of spermatogenesis and modulates alternative splicing in male germ cells. Nucleic Acids Res 39(12):4961–4974
Pawade TA, Newby DE, Dweck MR (2015) Calcification in aortic stenosis: the skeleton key. J Am Coll Cardiol 66(5):561–577
Qiao A, Zhou J, Xu S, Ma W, Boriboun C, Kim T et al (2021) Sam68 promotes hepatic gluconeogenesis via CRTC2. Nat Commun 12(1):3340
Raddatz MA, Huffstater T, Bersi MR, Reinfeld BI, Madden MZ, Booton SE et al (2020) Macrophages promote aortic valve cell calcification and alter STAT3 splicing. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 40(6):e153–e165
Rajamannan NM, Evans FJ, Aikawa E, Grande-Allen KJ, Demer LL, Heistad DD et al (2011) Calcific aortic valve disease: not simply a degenerative process: a review and agenda for research from the National Heart and Lung and Blood Institute Aortic Stenosis Working Group. Executive summary: Calcific aortic valve disease-2011 update. Circulation 124(16):1783–1791
Ramakrishnan P, Baltimore D (2011) Sam68 is required for both NF-κB activation and apoptosis signaling by the TNF receptor. Mol Cell 43(2):167–179
Sanchez-Margalet V, Martin-Romero C (2001) Human leptin signaling in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: activation of the JAK-STAT pathway. Cell Immunol 211(1):30–36
Small A, Kiss D, Giri J, Anwaruddin S, Siddiqi H, Guerraty M et al (2017) Biomarkers of calcific aortic valve disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 37(4):623–632
Sonderskov PS, Lindholt JS, Hallas J, Gerke O, Hasific S, Lambrechtsen J et al (2020) Association of aortic valve calcification and vitamin K antagonist treatment. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imag 21(7):718–724
Song J, Wang J, Tian S, Li H (2023) Discovery of STAT3 inhibitors: recent advances and future perspective. Curr Med Chem. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867329666220819093117
Stewart BF, Siscovick D, Lind BK, Gardin JM, Gottdiener JS, Smith VE et al (1997) Clinical factors associated with calcific aortic valve disease. Cardiovascular Health Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 29(3):630–634
Tai WT, Shiau CW, Chen HL, Liu CY, Lin CS, Cheng AL et al (2013) Mcl-1-dependent activation of Beclin 1 mediates autophagic cell death induced by sorafenib and SC-59 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis 4(2):e485
Tomalka JA, de Jesus TJ, Ramakrishnan P (2017) Sam68 is a regulator of Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell Mol Immunol 14(1):107–117
Vahanian AA-O, Beyersdorf F, Praz F, Milojevic M, Baldus S, Bauersachs J et al (2022) 2021 ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur Heart J 43(7):561–632
Vogel G, Richard S (2012) Emerging roles for Sam68 in adipogenesis and neuronal development. RNA Biol 9(9):1129–1133
Wang Y, Hu X, Zhang L, Zhu C, Wang J, Li Y et al (2019) Bioinspired extracellular vesicles embedded with black phosphorus for molecular recognition-guided biomineralization. Nat Commun 10(1):2829
Wang Y, Han D, Zhou T, Zhang J, Liu C, Cao F et al (2020) Melatonin ameliorates aortic valve calcification via the regulation of circular RNA CircRIC3/miR-204-5p/DPP4 signaling in valvular interstitial cells. J Pineal Res 69(2):e12666
Wang Y, Han D, Zhou T, Chen C, Cao H, Zhang JZ et al (2021) DUSP26 induces aortic valve calcification by antagonizing MDM2-mediated ubiquitination of DPP4 in human valvular interstitial cells. Eur Heart J. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab316
Xu L, Sun C, Zhang S, Xu X, Zhai L, Wang Y et al (2015) Sam68 promotes NF-κB activation and apoptosis signaling in articular chondrocytes during osteoarthritis. Inflamm Res 64(11):895–902
Yi B, Zeng W, Lv L, Hua P (2021) Changing epidemiology of calcific aortic valve disease: 30-year trends of incidence, prevalence, and deaths across 204 countries and territories. Aging 13(9):12710–12732
You L, Wang Z, Li H, Shou J, Jing Z, Xie J et al (2015) The role of STAT3 in autophagy. Autophagy 11(5):729–739
Zhang YG, Zhu X, Lu R, Messer JS, Xia Y, Chang EB et al (2019) Intestinal epithelial HMGB1 inhibits bacterial infection via STAT3 regulation of autophagy. Autophagy 15(11):1935–1953
Zhao J, Liu Z, Chang Z (2021) Osteogenic differentiation and calcification of human aortic smooth muscle cells is induced by the RCN2/STAT3/miR-155–5p feedback loop. Vas Pharmacol 136:106821
Zou S, Tong Q, Liu B, Huang W, Tian Y, Fu XAO (2020) Targeting STAT3 in cancer immunotherapy. Mol Cancer 19(1):1–19
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the technical support given by Dr. Kang Xu and Dr. Jiangyang Chi.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the grant number 81770387.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XL; QZ and JS performed study concept and design; KW; ZW. JL and HL Performed development of methodology; XL; QZ; HL and JS performed writing, review and revision of the paper; KW; XL; QZ; ZL provided acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data, and statistical analysis; ND provided technical and material support. All authors read and approved the final paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by Ethics Committee of Huazhong University of Science and technology (S036).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Zheng, Q., Wang, K. et al. Sam68 promotes osteogenic differentiation of aortic valvular interstitial cells by TNF-α/STAT3/autophagy axis. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 17, 863–879 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-023-00733-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-023-00733-2