Abstract
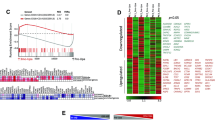
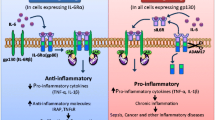
Nuclear orphan receptors 4A (NR4A) are early responsive genes that belong to the superfamily of hormone receptors and comprise NR4A1, NR4A2 and NR4A3. They have been associated to transcriptional activation of multiple genes involved in inflammation, apoptosis and cell cycle control. Here, we establish a link between NR4As and adenosine, a paradoxical inflammatory molecule that can contribute to persistence of inflammation or mediate inflammatory shutdown. Transcriptomics screening of the human mast cell-line HMC-1 revealed a sharp induction of transcriptionally active NR4A2 and NR4A3 by the adenosine analogue NECA. The concomitant treatment of NECA and the adenosine receptor A2A (A2AAR) selective antagonist SCH-58261 exaggerated this effect, suggesting that upregulation of these factors in mast cells is mediated by other AR subtypes (A2B and A3) and that A2AAR activation counteracts NR4A2 and NR4A3 induction. In agreement with this, A2AAR-silencing amplified NR4A induction by NECA. Interestingly, a similar A2AAR modulatory effect was observed on ERK1/2 phosphorylation because A2AAR blockage exacerbated NECA-mediated phosphorylation of ERK1/2. In addition, PKC or MEK1/2 inhibition prevented ERK1/2 phosphorylation and antagonized AR-mediated induction of NR4A2 and NR4A3, suggesting the involvement of these kinases in AR to NR4A signaling. Finally, we observed that selective A2AAR activation with CGS-21680 blocked PMA-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation and modulated the overexpression of functional nuclear orphan receptors 4A. Taken together, these results establish a novel PKC/ERK/nuclear orphan receptors 4A axis for adenosinergic signaling in mast cells, which can be modulated by A2AAR activation, not only in the context of adenosine but of other mast cell activating stimuli as well.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AR:
-
Adenosine receptor
- HMC-1:
-
Human mast cell line 1
- NBRE-LUC:
-
Nerve-growth factor I-B responsive element-luciferase reporter gene
- NR4A1:
-
Nuclear orphan receptor 4 A1
- NR4A2:
-
Nuclear orphan receptor 4 A2
- NR4A3:
-
Nuclear orphan receptor 4 A3
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction
References
Blatner NR, Bonertz A, Beckhove P, Cheon EC, Krantz SB, Strouch M, Weitz J, Koch M, Halverson AL, Bentrem DJ, Khazaie K (2010) In colorectal cancer mast cells contribute to systemic regulatory T-cell dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:6430–6435
Brightling CE, Bradding P, Pavord ID, Wardlaw AJ (2003) New insights into the role of the mast cell in asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 33:550–556
Chang EY, Szallasi Z, Acs P, Raizada V, Wolfe PC, Fewtrell C, Blumberg PM, Rivera J (1997) Functional effects of overexpression of protein kinase C-alpha, -beta, -delta, -epsilon, and -eta in the mast cell line RBL-2H3. J Immunol 159:2624–2632
Cho SH, You HJ, Woo CH, Yoo YJ, Kim JH (2004) Rac and protein kinase C-delta regulate ERKs and cytosolic phospholipase A2 in FcepsilonRI signaling to cysteinyl leukotriene synthesis in mast cells. J Immunol 173:624–631
Church MK, Levi-Schaffer F (1997) The human mast cell. J Allergy Clin Immunol 99:155–160
Codina A, Benoit G, Gooch JT, Neuhaus D, Perlmann T, Schwabe JW (2004) Identification of a novel co-regulator interaction surface on the ligand binding domain of Nurr1 using NMR footprinting. J Biol Chem 279:53338–53345
Driver AG, Kukoly CA, Ali S, Mustafa SJ (1993) Adenosine in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis 148:91–97
Fahrner TJ, Carroll SL, Milbrandt J (1990) The NGFI-B protein, an inducible member of the thyroid/steroid receptor family, is rapidly modified posttranslationally. Mol Cell Biol 10:6454–6459
Feoktistov I, Biaggioni I (1998) Pharmacological characterization of adenosine A2B receptors: studies in human mast cells co-expressing A2A and A2B adenosine receptor subtypes. Biochem Pharmacol 55:627–633
Feoktistov I, Goldstein AE, Biaggioni I (1999) Role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase kinase in adenosine A2B receptor-mediated interleukin-8 production in human mast cells. Mol Pharmacol 55:726–734
Feoktistov I, Ryzhov S, Goldstein AE, Biaggioni I (2003) Mast cell-mediated stimulation of angiogenesis: cooperative interaction between A2B and A3 adenosine receptors. Circ Res 92:485–492
Fozard JR (2003) The case for a role for adenosine in asthma: almost convincing? Curr Opin Pharmacol 3:264–269
Groot Kormelink T, Abudukelimu A, Redegeld FA (2009) Mast cells as target in cancer therapy. Curr Pharm Des 15:1868–1878
Harant H, Lindley IJ (2004) Negative cross-talk between the human orphan nuclear receptor Nur77/NAK-1/TR3 and nuclear factor-kappaB. Nucleic Acids Res 32:5280–5290
Huszar E, Vass G, Vizi E, Csoma Z, Barat E, Molnar Vilagos G, Herjavecz I, Horvath I (2002) Adenosine in exhaled breath condensate in healthy volunteers and in patients with asthma. Eur Respir J 20:1393–1398
Jacobson KA, Gao ZG (2006) Adenosine receptors as therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:247–264
Lammi J, Rajalin AM, Huppunen J, Aarnisalo P (2007) Cross-talk between the NR3B and NR4A families of orphan nuclear receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 359:391–397
Mack M, Rosenkranz AR (2009) Basophils and mast cells in renal injury. Kidney Int 76:1142–1147
Manna PR, Dyson MT, Eubank DW, Clark BJ, Lalli E, Sassone-Corsi P, Zeleznik AJ, Stocco DM (2002) Regulation of steroidogenesis and the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein by a member of the cAMP response-element binding protein family. Mol Endocrinol 16:184–199
Martinez-Gonzalez J, Badimon L (2005) The NR4A subfamily of nuclear receptors: new early genes regulated by growth factors in vascular cells. Cardiovasc Res 65:609–618
McEvoy AN, Murphy EA, Ponnio T, Conneely OM, Bresnihan B, FitzGerald O, Murphy EP (2002) Activation of nuclear orphan receptor NURR1 transcription by NF-kappa B and cyclic adenosine 5′-monophosphate response element-binding protein in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue. J Immunol 168:2979–2987
Murphy EP, McEvoy A, Conneely OM, Bresnihan B, FitzGerald O (2001) Involvement of the nuclear orphan receptor NURR1 in the regulation of corticotropin-releasing hormone expression and actions in human inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 44:782–793
Nilsson G, Blom T, Kusche-Gullberg M, Kjellen L, Butterfield JH, Sundstrom C, Nilsson K, Hellman L (1994) Phenotypic characterization of the human mast-cell line HMC-1. Scand J Immunol 39:489–498
Ohta A, Sitkovsky M (2001) Role of G-protein-coupled adenosine receptors in downregulation of inflammation and protection from tissue damage. Nature 414:916–920
Palmer TM, Trevethick MA (2008) Suppression of inflammatory and immune responses by the A(2A) adenosine receptor: an introduction. Br J Pharmacol 153(Suppl 1):S27–S34
Pei L, Castrillo A, Chen M, Hoffmann A, Tontonoz P (2005) Induction of NR4A orphan nuclear receptor expression in macrophages in response to inflammatory stimuli. J Biol Chem 280:29256–29262
Pei L, Castrillo A, Tontonoz P (2006a) Regulation of macrophage inflammatory gene expression by the orphan nuclear receptor Nur77. Mol Endocrinol 20:786–794
Pei L, Waki H, Vaitheesvaran B, Wilpitz DC, Kurland IJ, Tontonoz P (2006b) NR4A orphan nuclear receptors are transcriptional regulators of hepatic glucose metabolism. Nat Med 12:1048–1055
Ralph JA, McEvoy AN, Kane D, Bresnihan B, FitzGerald O, Murphy EP (2005) Modulation of orphan nuclear receptor NURR1 expression by methotrexate in human inflammatory joint disease involves adenosine A2A receptor-mediated responses. J Immunol 175:555–565
Rivera J, Gilfillan AM (2006) Molecular regulation of mast cell activation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 117:1214–1225, quiz 1226
Ryzhov S, Goldstein AE, Matafonov A, Zeng D, Biaggioni I, Feoktistov I (2004) Adenosine-activated mast cells induce IgE synthesis by B lymphocytes: an A2B-mediated process involving Th2 cytokines IL-4 and IL-13 with implications for asthma. J Immunol 172:7726–7733
Ryzhov S, Goldstein AE, Biaggioni I, Feoktistov I (2006) Cross-talk between G(s)- and G(q)-coupled pathways in regulation of interleukin-4 by A(2B) adenosine receptors in human mast cells. Mol Pharmacol 70:727–735
Spicuzza L, Di Maria G, Polosa R (2006) Adenosine in the airways: implications and applications. Eur J Pharmacol 533:77–88
Suzuki H, Takei M, Nakahata T, Fukamachi H (1998) Inhibitory effect of adenosine on degranulation of human cultured mast cells upon cross-linking of Fc epsilon RI. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 242:697–702
Wallen-Mackenzie A, Mata de Urquiza A, Petersson S, Rodriguez FJ, Friling S, Wagner J, Ordentlich P, Lengqvist J, Heyman RA, Arenas E, Perlmann T (2003) Nurr1-RXR heterodimers mediate RXR ligand-induced signaling in neuronal cells. Genes Dev 17:3036–3047
Wang Z, Benoit G, Liu J, Prasad S, Aarnisalo P, Liu X, Xu H, Walker NP, Perlmann T (2003) Structure and function of Nurr1 identifies a class of ligand-independent nuclear receptors. Nature 423:555–560
Winoto A, Littman DR (2002) Nuclear hormone receptors in T lymphocytes. Cell 109(Suppl):S57–S66
Zetterstrom RH, Solomin L, Jansson L, Hoffer BJ, Olson L, Perlmann T (1997) Dopamine neuron agenesis in Nurr1-deficient mice. Science 276:248–250
Zhou QY, Li C, Olah ME, Johnson RA, Stiles GL, Civelli O (1992) Molecular cloning and characterization of an adenosine receptor: the A3 adenosine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:7432–7436
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Felix R. Althaus for his support, and the Functional Genomics Center Zurich (University of Zurich-Irchel) for the assistance with RNA profiling studies. This work has been financed by the Foundation for Scientific Research of the University of Zurich (Stiftung für wissenschaftliche Forschung).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Concise summary
Non-selective AR engagement triggers robust induction NR4A orphan receptors in mast cells. Induction of these early responsive genes can be blocked by selective activation of the anti-inflammatory A2AAR not only in the context of adenosine but also of PMA signaling, suggesting a general mechanism of mast cell regulation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Paine, C. & Dip, R. Selective regulation of nuclear orphan receptors 4A by adenosine receptor subtypes in human mast cells. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 4, 173–183 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-010-0104-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-010-0104-0