Abstract
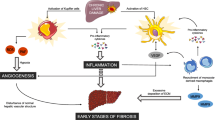
Angiogenesis, defined as the formation of new microvasculature from preexisting blood vessels and mature endothelial cells, plays a major role in wound healing and scar formation, and it is associated with inflammatory responses. Angiogenesis can occur in physiological conditions, such as during liver regeneration, and in pathological situations, such as during the progression of fibrosis to cirrhosis and also during tumor angiogenesis. Cellular cross-talk among liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs), hepatic stellate cells and hepatocytes is believed to play an important role in the angiogenesis process during both liver regeneration and development of cirrhosis. In addition to mature endothelial cells, bone marrow (BM)-derived circulating endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) have been recently identified for their contribution to post-natal vasculogenesis/angiogenesis. In vivo, EPCs are mobilized into the peripheral blood in response to tissue ischemia or traumatic injury, migrate to the sites of injured endothelium and differentiate into mature endothelial cells. In our recent studies, we have explored the role of EPC-mediated angiogenesis in liver regeneration and/or cirrhosis. Results have demonstrated significantly increased endogenous levels of circulating EPCs in cirrhotic patients in comparison to the controls. Also, EPCs from cirrhotic patients have been observed to stimulate substantial angiogenesis by resident LSECs in vitro via paracrine factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor. This review gives an overview of the angiogenesis process in liver regeneration and disease and discusses a new mechanism for intrahepatic angiogenesis mediated by BM-derived EPCs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Michalopoulos GK. Liver regeneration. J Cell Physiol 2007;213:286–300
Michalopoulos GK. Liver regeneration: alternative epithelial pathways. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2011;43:173–179
Drixler TA, Vogten MJ, Ritchie ED, van Vroonhoven TJ, Gebbink MF, Voest EE, et al. Liver regeneration is an angiogenesis-associated phenomenon. Ann Surg 2002;236:703–711
Vanheule E, Geerts AM, Van Huysse J, Schelfhout D, Praet M, Van Vlierberghe H, et al. An intravital microscopic study of the hepatic microcirculation in cirrhotic mice models: relationship between fibrosis and angiogenesis. Int J Exp Pathol 2008;89:419–432
Carmeliet P. Mechanisms of angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. Nat Med 2000;6:389–395
Kirton JP, Xu Q. Endothelial precursors in vascular repair. Microvasc Res 2010;79:193–199
Kaur S, Jayakumar K, Kartha CC. The potential of circulating endothelial progenitor cells to form colonies is inversely proportional to total vascular risk score in patients with coronary artery disease. Indian Heart J 2007;59:475–481
Kaur S, Tripathi D, Dongre K, Garg V, Rooge S, Mukopadhyay A, et al. Increased number and function of endothelial progenitor cells stimulate angiogenesis by resident liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (SECs) in cirrhosis through paracrine factors. J Hepatol 2012;57:1193–1198
Kmieć Z. Cooperation of liver cells in health and disease. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 2001;61:1–151
Sakamoto T, Liu Z, Murase N, Ezure T, Yokomuro S, Poli V, et al. Mitosis and apoptosis in the liver of interleukin-6-deficient mice after partial hepatectomy. Hepatology 1999;29:403–411
Rabes HM. Kinetics of hepatocellular proliferation as a function of the microvascular structure and functional state of the liver. Ciba Found Symp 1977;55:31–53
Webber EM, Bruix J, Pierce RH, Fausto N. Tumor necrosis factor primes hepatocytes for DNA replication in the rat. Hepatology 1998;28:1226–1234
Van Sweringen HL, Sakai N, Tevar AD, Burns JM, Edwards MJ, Lentsch AB. CXC chemokine signaling in the liver: impact on repair and regeneration. Hepatology 2011;54:1445–1453
Wisse E, De Zanger RB, Charels K, Van Der Smissen P, McCuskey RS. The liver sieve: considerations concerning the structure and function of endothelial fenestrae, the sinusoidal wall and the space of Disse. Hepatology 1985;5:683–692
Martinez-Hernandez A, Amenta PS. The extracellular matrix in hepatic regeneration. FASEB J 1995;9:1401–410
Wack KE, Ross MA, Zegarra V, Sysko LR, Watkins SC, Stolz DB. Sinusoidal ultrastructure evaluated during the revascularization of regenerating rat liver. Hepatology 2001;33:363–378
Ross MA, Sander CM, Kleeb TB, Watkins SC, Stolz DB. Spatiotemporal expression of angiogenesis growth factor receptors during the revascularization of regenerating rat liver. Hepatology 2001;34:1135–1148
Maeno H, Ono T, Dhar DK, Sato T, Yamanoi A, Nagasue N. Expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha during liver regeneration induced by partial hepatectomy in rats. Liver Int 2005;25:1002–1009
Redaelli CA, Semela D, Carrick FE, Ledermann M, Candinas D, Sauter B, et al. Effect of vascular endothelial growth factor on functional recovery after hepatectomy in lean and obese mice. J Hepatol 2004;40:305–312
Taniguchi E, Sakisaka S, Matsuo K, Tanikawa K, Sata M. Expression and role of vascular endothelial growth factor in liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in rats. J Histochem Cytochem 2001;49:121–130
Shimizu H, Miyazaki M, Wakabayashi Y, Mitsuhashi N, Kato A, Ito H, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor secreted by replicating hepatocytes induces sinusoidal endothelial cell proliferation during regeneration after partial hepatectomy in rats. J Hepatol 2001;34:683–689
Yokomori H, Oda M, Yoshimura K, Nagai T, Ogi M, Nomura M, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor increases fenestral permeability in hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells. Liver Int 2003;23:467–475
Ding BS, Nolan DJ, Butler JM, James D, Babazadeh AO, Rosenwaks Z, et al. Inductive angiocrine signals from sinusoidal endothelium are required for liver regeneration. Nature 2010;468:310–315
LeCouter J, Moritz DR, Li B, Phillips GL, Liang XH, Gerber HP, et al. Angiogenesis-independent endothelial protection of liver: role of VEGFR-1. Science 2003;299:890–893
Balabaud C, Bioulac-Sage P, Desmouliere A. The role of hepatic stellate cells in liver regeneration. J Hepatol 2004;40:1023–1026
Budny T, Palmes D, Stratmann U, Minin E, Herbst H, Spiegel HU. Morphologic features in the regenerating liver—a comparative intravital, lightmicroscopical and ultrastructural analysis with focus on hepatic stellate cells. Virchows Arch 2007;451:781–791
Neufeld G, Kessler O, Herzog Y. The interaction of Neuropilin-1 and Neuropilin-2 with tyrosine-kinase receptors for VEGF. Adv Exp Med Biol 2002;515:81–90
Unemori EN, Ferrara N, Bauer EA, Amento EP. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces interstitial collagenase expression in human endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol 1992;153:557–562
Zucker S, Mirza H, Conner CE, Lorenz AF, Drews MH, Bahou WF, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces tissue factor and matrix metalloproteinase production in endothelial cells: conversion of prothrombin to thrombin results in progelatinase A activation and cell proliferation. Int J Cancer 1998;75:780–786
Pepper MS, Ferrara N, Orci L, Montesano R. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induces plasminogen activators and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in microvascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1991;181:902–906
Sato T, El-Assal ON, Ono T, Yamanoi A, Dhar DK, Nagasue N. Sinusoidal endothelial cell proliferation and expression of angiopoietin/Tie family in regenerating rat liver. J Hepatol 2001;34:690–698
Sato TN, Tozawa Y, Deutsch U, Wolburg-Buchholz K, Fujiwara Y, Gendron-Maguire M, et al. Distinct roles of the receptor tyrosine kinases Tie-1 and Tie-2 in blood vessel formation. Nature 1995;376:70–74
Maisonpierre PC, Suri C, Jones PF, Bartunkova S, Wiegand SJ, Radziejewski C, et al. Angiopoietin-2, a natural antagonist for Tie2 that disrupts in vivo angiogenesis. Science 1997;277:55–60
Holash J, Wiegand SJ, Yancopoulos GD. New model of tumor angiogenesis: dynamic balance between vessel regression and growth mediated by angiopoietins and VEGF. Oncogene 1999;18:5356–5362
Greene AK, Wiener S, Puder M, Yoshida A, Shi B, Perez-Atayde AR, et al. Endothelial-directed hepatic regeneration after partial hepatectomy. Ann Surg 2003;237:530–535
Boulton R, Woodman A, Calnan D, Selden C, Tam F, Hodgson H. Nonparenchymal cells from regenerating rat liver generates interleukin-1alpha and -1beta: a mechanism of negative regulation of hepatocyte proliferation. Hepatology 1997;26:49–58
Oe S, Lemmer ER, Conner EA, Factor VM, Levéen P, Larsson J, et al. Intact signaling by transforming growth factor beta is not required for termination of liver regeneration in mice. Hepatology 2004;40:1098–1105
Fernández M, Semela D, Bruix J, Colle I, Pinzani M, Bosch J. Angiogenesis in liver disease. J Hepatol 2009;50:604–620
Rosmorduc O, Wendum D, Corpechot C, Galy B, Sebbagh N, Raleigh J, et al. Hepatocellular hypoxia induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression and angiogenesis in experimental biliary cirrhosis. Am J Pathol 1999;155:1065–1073
Corpechot C, Barbu V, Wendum D, Kinnman N, Rey C, Poupon R, et al. Hypoxia-induced VEGF and collagen I expressions are associated with angiogenesis and fibrogenesis in experimental cirrhosis. Hepatology 2002;35:1010–1021
Taura K, De Minicis S, Seki E, Hatano E, Iwaisako K, Osterreicher CH, et al. Hepatic stellate cells secrete angiopoietin 1 that induces angiogenesis in liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 2008;135:1729–1738
Thabut D, Shah V. Intrahepatic angiogenesis and sinusoidal remodeling in chronic liver disease: new targets for the treatment of portal hypertension? J Hepatol 2010;53:976–980
Ankoma-Sey V, Wang Y, Dai Z. Hypoxic stimulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in activated rat hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2000;31:141–148
Novo E, Cannito S, Zamara E, Valfrè di Bonzo L, Caligiuri A, Cravanzola C, et al. Proangiogenic cytokines as hypoxia-dependent factors stimulating migration of human hepatic stellate cells. Am J Pathol 2007;170:1942–1953
Moon JO, Welch TP, Gonzalez FJ, Copple BL. Reduced liver fibrosis in hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2009;296:G582–G592
Copple BL, Kaska S, Wentling C. Hypoxia-inducible factor activation in myeloid cells contributes to the development of liver fibrosis in cholestatic mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2012;341:307–316
Rockey DC. Vascular mediators in the injured liver. Hepatology 2003;37:4–12
Fernandez M, Mejias M, Angermayr B, Garcia-Pagan JC, Rodes J, Bosch J. Inhibition of VEGF receptor-2 decreases the development of hyperdynamic splanchnic circulation and portal-systemic collateral vessels in portal hypertensive rats. J Hepatol 2005;43:98–103
Cejudo-Martin P, Ros J, Navasa M, Fernandez J, Fernandez-Varo G, Ruiz-del-Arbol L, et al. Increased production of vascular endothelial growth factor in peritoneal macrophages of cirrhotic patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Hepatology 2001;34:487–493
Tsugawa K, Hashizume M, Tomikawa M, Migou S, Kawanaka H, Shiraishi S, et al. Immunohistochemical localization of vascular endothelial growth factor in the rat portal hypertensive gastropathy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2001;16:429–437
Cha C, Dematteo RP. Molecular mechanisms in hepatocellular carcinoma development. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2005;19:25–37
Pang R, Poon RT. Angiogenesis and antiangiogenic therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 2006;242:151–167
Tugues S, Fernandez-Varo G, Muñoz-Luque J, Ros J, Arroyo V, Rodés J, et al. Antiangiogenic treatment with sunitinib ameliorates inflammatory infiltrate, fibrosis, and portal pressure in cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 2007;46:1919–1926
Rosmorduc O. Antiangiogenic therapies in portal hypertension: a breakthrough in hepatology. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 2010;34:446–449
Patsenker E, Popov Y, Stickel F, Schneider V, Ledermann M, Sägesser H, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of integrin alphavbeta3 aggravates experimental liver fibrosis and suppresses hepatic angiogenesis. Hepatology 2009;50:1501–1511
Parlakgumus A, Colakoglu T, Kayaselcuk F, Colakoglu S, Ezer A, Calıskan K, et al. Two drugs with paradoxical effects on liver regeneration through antiangiogenesis and antifibrosis: Losartan and Spironolactone: a pharmacologic dilemma on hepatocyte proliferation. J Surg Res 2013;179:60–65
Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, Silver M, van der Zee R, Li T, et al. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science 1997;275:964–967
Shi Q, Rafii S, Wu MH, Wijelath ES, Yu C, Ishida A, et al. Evidence for circulating bone marrow-derived endothelial cells. Blood 1998;92:362–367
Takahashi T, Kalka C, Masuda H, Chen D, Silver M, Kearney M, et al. Ischemia- and cytokine-induced mobilization of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells for neovascularization. Nat Med 1999;5:434–438
Kawamoto A, Gwon HC, Iwaguro H, Yamaguchi JI, Uchida S, Masuda H, et al. Therapeutic potential of ex vivo expanded endothelial progenitor cells for myocardial ischemia. Circulation 2001;103:634–637
Kalka C, Masuda H, Takahashi T, Kalka-Moll WM, Silver M, Kearney M, et al. Transplantation of ex vivo expanded endothelial progenitor cells for therapeutic neovascularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000;97:3422–3427
Fan CL, Gao PJ, Che ZQ, Liu JJ, Wei J, Zhu DL. Therapeutic neovascularization by autologous transplantation with expanded endothelial progenitor cells from peripheral blood into ischemic hind limbs. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2005;26:1069–1075
Nakamura T, Torimura T, Sakamoto M, Hashimoto O, Taniguchi E, Inoue K, et al. Significance and therapeutic potential of endothelial progenitor cell transplantation in a cirrhotic liver rat model. Gastroenterology 2007;133:91–107
Nakamura T, Torimura T, Iwamoto H, Masuda H, Naitou M, Koga H, et al. Prevention of liver fibrosis and liver reconstitution of DMN-treated rat liver by transplanted EPCs. Eur J Clin Invest 2012;42:717–728
Sakamoto M, Nakamura T, Torimura T, Iwamoto H, Masuda H, Koga H, et al. Transplantation of endothelial progenitor cells ameliorates vascular dysfunction and portal hypertension in carbon tetrachloride-induced rat liver cirrhotic model. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;28:168–178
Wang L, Wang X, Xie G, Wang L, Hill CK, DeLeve LD. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell progenitor cells promote liver regeneration in rats. J Clin Invest 2012;122:1567–1573
Ho JW, Pang RW, Lau C, Sun CK, Yu WC, Fan ST, et al. Significance of circulating endothelial progenitor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2006;44:836–843
Yu D, Sun X, Qiu Y, Zhou J, Wu Y, Zhuang L, et al. Identification and clinical significance of mobilized endothelial progenitor cells in tumor vasculogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:3814–3824
Yu DC, Chen J, Sun XT, Zhuang LY, Jiang CP, Ding YT. Mechanism of endothelial progenitor cell recruitment into neo-vessels in adjacent non-tumor tissues in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2010;10:435
Yu DC, Chen J, Ding YT. Hypoxic and highly angiogenic non-tumor tissues surrounding hepatocellular carcinoma: the ‘niche’ of endothelial progenitor cells. Int J Mol Sci 2010;11:2901–2909
Abdelmoneim SS, Talwalkar J, Sethi S, Kamath P, Fathalla MM, Kipp BR, et al. A prospective pilot study of circulating endothelial cells as a potential new biomarker in portal hypertension. Liver Int 2010;30:191–197
Rautou PE. Endothelial progenitor cells in cirrhosis: The more, the merrier? J Hepatol 2012;57:1163–1165
Kaur S, Kumar TR, Uruno A, Sugawara A, Jayakumar K, Kartha CC. Genetic engineering with endothelial nitric oxide synthase improves functional properties of endothelial progenitor cells from patients with coronary artery disease: an in vitro study. Basic Res Cardiol 2009;104:739–749
Kaur S, Harikrishnan VS, Shenoy SJ, Radhakrishnan NS, Uruno A, Sugawara A, et al. Transfection of endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene improves angiogenic efficacy of endothelial progenitor cells in rabbits with hindlimb ischemia. J Clin Exp Cardiol 2011;2:140
Acknowledgements
The corresponding author is grateful to the Director, Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences, Delhi, for providing the infrastructure and facilities to perform the study of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells in liver cirrhosis. The author is also thankful to Dr. Ashok Mukopadhyay, National Institute of Immunology, Delhi, for his valuable contributions to the study.
Compliance with Ethical Requirements and Conflict of interest
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects. Savneet Kaur and K. Anita declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, S., Anita, K. Angiogenesis in liver regeneration and fibrosis: “a double-edged sword”. Hepatol Int 7, 959–968 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-013-9483-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-013-9483-7