Abstract
Background/aim
The number of amino acid (AA) mutations in the interferon sensitivity determining region (ISDR) of NS5A is reported to affect the response to interferon (IFN) therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C (CHC). The aim of this study was to clarify whether host immunity is influenced by the number of AA mutations in the ISDR.
Patients and methods
Subjects included 44 patients with CHC infected with genotype 1b and high viral load. The number of AA mutations in the ISDR was retrospectively determined using stored serum samples taken immediately before starting therapy. All patients received IFN-alpha 2b or pegylated-IFN (PEG-IFN)-alpha 2b and ribavirin. When serum hepatitis C virus-ribonucleic acid (HCV-RNA) was negative at 4 or 12 weeks after starting therapy, the patient was defined as having rapid viral response (RVR) or early viral response (EVR), respectively. CD4+ T cell (Th1 or Th2) in peripheral blood (PB) before and until day 56 of treatment was analyzed.
Results
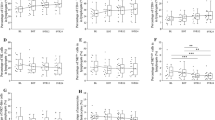
Rates of RVR and EVR were 0 (0/21) and 14% (3/21), respectively, in patients with one or fewer AA mutations in the ISDR (ISDR0-1), and 30 (7/23), and 74% (17/23), respectively, with two or more AA mutations in the ISDR (ISDR > 2). Although the percentage of PB Th1 cells did not differ between the two groups during the study period, the percentage of PB Th2 cells was significantly lower in the ISDR0-1 group than in the ISDR > 2 group at baseline and on days 3, 7, 14, and 28 of treatment.
Conclusion
The number of AA mutations in the ISDR influenced PB Th2 cells before and until day 28, and was associated with higher RVR and EVR rates.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dustin LB, Rice CM. Flying under the radar: the immunobiology of hepatitis C. Annu Rev Immunol 2007;25:71–99
Gerlach JT, Diepolder HM, Jung MC, Gruener NH, Schraut WW, Zachoval R, Hoffmann R, Schirren CA, Santantonio T, Pape GR. Recurrence of hepatitis C virus after loss of virus-specific CD4(+) T-cell response in acute hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 1999;117:933–941
Grakoui Shoukry NH, Woollard DJ, Han JH, Hanson HL, Ghrayeb J, Murthy KK, Rice CM, Walker CM. HCV persistence and immune evasion in the absence of memory T cell help. Science 2003;302:659–662
Shoukry NH, Cawthon AC, Walker CM. Cell-mediated immunity and the outcome of hepatitis C virus infection. Annu Rev Microbiol 2004;58:391–424
Thimme R, Oldach D, Chang K, Steiger C, Ray SC, Chisari FV. Determinants of viral clearance and persistence during acute hepatitis C virus infection. J Exp Med 2001;194:1395–1406
Ishii K, Takamura N, Shinohara M, Shin H, Ikehara T, Hata S, Kawafune T, Sumino Y. Intracellular cytokines analysis of CD4 positive T cells predictive of sustained response to interferon therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis C. Dig Dis Sci 2002;47:778–783
Shinohara M, Ishii K, Takamura N. Long-term changes of peripheral blood CD4-positive T cell subsets (Th1, Th2) in chronic hepatitis C patients with a sustained response or no response to IFN. Hepatol Res 2003;27:260–265
Ishii K, Matsumaru K, Higami K, Fujita Y, Sasao K, Wakui N, Momiyama K, Shinohara M, Nagai H, Watanabe M, Miki K, Sumino Y. Early immune-mediated response to ribavirin combined with IFN in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatol Res 2006;34:15–22
Tanaka Y, Nishida N, Sugiyama M, Kurosaki M, Matsuura K, Sakamoto N, Nakagawa M, Korenaga M, Hino K, Hige S, Ito Y, Mita E, Tanaka E, Mochida S, Murawaki Y, Honda M, Sakai A, Hiasa Y, Nishiguchi S, Koike A, Sakaida I, Imamura M, Ito K, Yano K, Masaki N, Sugauchi F, Izumi N, Tokunaga K, Mizokami M. Genome-wide association of IL28B with response to pegylated interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Nat Genet 2009;41:1105–1109
Ge D, Fellay J, Thompson AJ, Simon JS, Shianna KV, Urban TJ, Heinzen EL, Qiu P, Bertelsen AH, Muir AJ, Sulkowski M, McHutchison JG, Goldstein DB. Genetic variation in IL28B predicts hepatitis C treatment-induced viral clearance. Nature 2009;461:399–401
Bruno S, Cammà C, Di Marco V, Rumi M, Vinci M, Camozzi M, Rebucci C, Di Bona D, Colombo M, Craxì A, Mondelli MU, Pinzello G. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for naïve patients with genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C: a randomized controlled trial. J Hepatol 2004;41:474–481
Manns MP, McHutchinson JG, Gordon SC, Rustigi VK, Shiffman M, Reindollar R, Goodman ZD, Koury K, Ling M, Albrecht JK. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet 2001;358:958–965
Akuta N, Suzuki F, Sezaki H, Suzuki Y, Hosaka T, Someya T, Kobayashi M, Saitoh S, Watahiki S, Sato J, Matsuda M, Kobayashi M, Arase Y, Ikeda K, Kumada H. Association of amino acid substitution pattern in core protein of hepatitis C virus genotype 1b high viral load and non-virological response to interferon-ribavirin combination therapy. Intervirology 2005;48:372–380
Enomoto N, Sakuma I, Asahina Y, Kurosaki M, Murakami T, Yamamoto C, Ogura Y, Izumi N, Marumo F, Sato C. Mutations in the nonstructural protein 5A gene and response to interferon in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus 1b infection. N Engl J Med 1996;334:77–81
Hung CH, Lee CM, Lu SN, Lee JF, Wang JH, Tung HD, Chen TM, Hu TH, Chen WJ, Changchien CS. Mutations in the NS5A and E2-PePHD region of hepatitis C virus type 1b and correlation with the response to combination therapy with interferon and ribavirin. J Viral Hepat 2003;10:87–94
Shen C, Hu T, Shen L, Gao L, Xie W, Zhang J. Mutation in ISDR of NS5A gene influence interferon efficacy in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1b infection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;22:1898–1903
Pascu M, Martus P, Hohne M, Höhne M, Wiedenmann B, Hopf U, Schreier E, Berg T. Sustained virological response in hepatitis C virus type 1b infected patients is predicted by the number of mutations within the NS5A-ISDR: a meta-analysis focused on geographical differences. Gut 2004;53:1345–1351
Schiappa DA, Mittal C, Brown JA, Mika BP. Relationship of hepatitis C genotype 1 NS5A sequence mutations to early phase viral kinetics. J Infect Dis 2002;185:868–877
Knodell RG, Ishak KG, Black WC, Chen TS, Craig R, Kaplowitz N, Kiernan TW, Wollman J. Formulation and application of a numerical scoring system for assessing histological activity in asymptomatic chronic hepatitis. Hepatology 1981;1:431–435
Desmet VJ, Gerber M, Hoofnagle JH, Manns M, Scheuer PJ. Classification of chronic hepatitis: diagnosis, grading and staging. Hepatology 1994;19:1513–1520
Jung T, Schauer U, Heusser C, Neumann C, Rieger C. Detection of intracellular cytokines by flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods 1993;159:197–207
Nakagawa M, Sakamoto N, Ueyama M, Mogushi K, Nagaie S, Itsui Y, Azuma S, Kakinuma S, Tanaka H, Enomoto N, Watanabe M. Mutation in the interferon sensitivity determining region and virological response to combination therapy with pegylated-interferon alpha 2b plus ribavirin in patients with chronic hepatitis C-1b infection. J Gastroenterol 2010;45:656–665
Paterson M, Laxton CD, Thomas HC, Ackrill AM, Foster GR. Ahepatits C virus NS5A protein inhibits interferon antiviral activity, but the effects do not correlate with clinical response. Gastroenterology 1999;117:1187–1197
Gale MJ, Korth MJ, Tang NM, Tan SL, Hopkins DA, Dever TE, Polyak SJ, Gretch DR, Katze MG. Evidence that hepatitis C virus resistance to interferon is mediated through repression of the PKR protein kinase by the nonstructural 5A protein. Virology 1997;230:217–227
Gale M, Blakely CM, Kwieciszewski B, Tan SL, Dossett M, Tang NM, Korth MJ, Polyak SJ, Gretch DR, Katze MG. Control of PKR protein kinase by hepatitis C virus nonstructural 5A protein: Molecular mechanisms of kinase regulation. Mol Cell Biol 1998;18:5208–5218
Abe T, Kaname Y, Hamamoto I, Tsuda Y, Wen XY, Taguwa S, Wen X, Taguwa S, Moriishi K, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Kanto T, Hayashi N, Akira S, Matsuura Y. Hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A modulates the toll-like receptor-MyD88-dependent signaling pathway in macrophage cell lines. J Virol 2007;81:8953–8966
Masaki N, Fukushima S, Hayashi S. Lower th-1/th-2 ratio before interferon therapy may favor long-term virological responses in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Dig Dis Sci 2002;47:2163–2169
Ogawa K, Hige S, Nakanishi M, Yamamoto Y, Chuma M, Nagasaka A, Asaka M. Immunological and mutagenic actions of ribavirin monotherapy preceding combination therapy with interferon for patients with chronic hepatitis C. Antivir Ther 2009;14:513–522
Shirakawa H, Matsumoto A, Joshita S, Komatsu M, Tanaka N, Umemura T, Ichijo T, Yoshizawa K, Kiyosawa K, Tanaka E, Nagano Interferon Treatment Research Group. Pretreatment prediction of virological response to peginterferon plus ribavirin therapy in chronic hepatitis C patients using viral and host factors. Hepatology 2008;48:1753–1760
Kmieciak D, Kruszyna L, Migdalski P, Lancinski M, Juszczyk J, Trzeciak WH. Mutation within protein kinase R-binding domain of NS5A protein of hepatitis C virus (HCV) and specificity of HCV antibodies in pretreatment sera of HCV-chronically infected patients and their effect on results of treatment. Jpn J Infect Dis 2006;59:92–99
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishii, K., Shinohara, M., Kogame, M. et al. Effects of mutation number in interferon sensitivity determining region on peripheral blood CD4+ T cell subsets (Th1, Th2) in chronic hepatitis C patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 1b and high viral load. Hepatol Int 6, 468–474 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-011-9305-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-011-9305-8