Abstract
Epstein-Barr virus-positive Inflammatory follicular dendritic cell/fibroblastic reticular cell tumour (EBV-IFDC/FRCT) is a rare neoplasm that occurs almost exclusively in the liver or spleen. Extra-hepatosplenic presentation is infrequent and exceptional cases have been described arising in the gastrointestinal tract or in the pharynx. However, EBV-IFDC/FRCT cases have not been previously reported in the larynx.
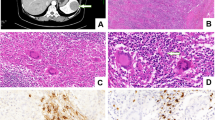
This report describes a case of a 32-year-old woman who arrived to the emergency department due to progressive dyspnea with associated inspiratory stridor and non-productive cough. Direct laryngoscopy showed a nodular tumour arising on the left posterior subglottic mucosa obstructing 90% of the airway. A preoperative dual energy contrast enhanced computed tomography (CECT) was performed demonstrating a low attenuation lesion on virtual non-contrast (VNC) images and vivid iodine uptake on the iodine map. The tumour was excised and the histopathological analysis led to the diagnosis of an EBV-IFDC/FRCT. A fibre-optic laryngoscopy six months after the surgery did not show any abnormalities.
Although the vast majority of EBV-IFDC/FRCT occur in the liver or spleen, some extra hepatosplenic tumours have been reported affecting the head and neck region. We describe here the first case arising in the larynx, as well as the usefulness of preoperative dual energy imaging techniques to assess these lesions, thus providing information that could have management implications.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EBV-IFDC/FRCT:
-
Epstein-Barr virus-positive Inflammatory follicular dendritic cell/fibroblastic reticular cell tumour
- CECT:
-
Contrast enhanced Computed Tomography
- VNC:
-
Virtual non-contrast
- HU:
-
Hounsfield unit
- FDCS:
-
Follicular dendritic cell sarcomas
- SMA:
-
Smooth muscle actin
References
Ge R, Liu C, Yin X, Chen J, Zhou X, Huang C, Yu W, Shen X (2014) Clinicopathologic characteristics of inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell sarcoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7(5):2421–2429
Jiang XN, Zhang Y, Xue T, Chen JY, Chan ACL, Cheuk W, Chan JKC, Li XQ (2021) New clinicopathologic scenarios of EBV + inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: report of 9 extrahepatosplenic cases. Am J Surg Pathol 45(6):765–772. https://doi.org/10.1097/pas.0000000000001632
Bui PL, Vicens RA, Westin JR, Jensen CT (2015) Multimodality imaging of Epstein-Barr virus-associated inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell tumor of the spleen: case report and literature review. Clin Imaging 39(3):525–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinimag.2014.12.021
Mao S, Dong J, Wang Y, Zhang C, Dong A, Shen J (2021) Follicular dendritic cell sarcomas: CT and MRI findings in 20 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 216(3):835–843. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.19.22759
Long-Hua Q, Qin X, Ya-Jia G, Jian W, Xiao-Yuan F (2011) Imaging findings of follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: report of four cases. Korean J Radiol 12(1):122–128. https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2011.12.1.122
Gong S, Auer I, Duggal R, Pittaluga S, Raffeld M, Jaffe ES (2015) Epstein-Barr virus-associated inflammatory pseudotumor presenting as a colonic mass. Hum Pathol 46:1956–1961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2015.08.011
Lorenzi L, Döring C, Rausch T, Benes V, Lonardi S, Bugatti M, Campo E, Cabeçadas J, Simonitsch-Klupp I, Borges A, Mehta J, Agostinelli C, Pileri SA, Facchetti F, Hansmann ML, Hartmann S (2017) Identification of novel follicular dendritic cell sarcoma markers, FDCSP and SRGN, by whole transcriptome sequencing. Oncotarget 8(10):16463–16472. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14864
Vermi W, Giurisato E, Lonardi S, Balzarini P, Rossi E, Medicina D, Bosisio D, Sozzani S, Pellegrini W, Doglioni C, Marchetti A, Rossi G, Pileri S, Facchetti F (2013) Ligand-dependent activation of EGFR in follicular dendritic cells sarcoma is sustained by local production of cognate ligands. Clin Cancer Res 19(18):5027–5038. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-13-1275
Heesters BA, van Megesen K, Tomris I, de Vries RP, Magri G, Spits H (2021) Characterization of human FDCs reveals regulation of T cells and antigen presentation to B cells. J Exp Med 218(10):e20210790. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20210790
Choe JY, Go H, Jeon YK, Yun JY, Kim YA, Kim HJ et al (2013) Inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell sarcoma of the spleen: a report of six cases with increased IgG4-positive plasma cells. Pathol Int 63(5):245–251. https://doi.org/10.1111/pin.12057
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Isabel Vilaseca examined the patient, performed the fibre-laryngoscopy and the resection of the lesion. Laura Oleaga and Alex Gil interpreted the imaging data. Natalia Castrejon de Anta, Gerard Frigola and Elias Campo performed the histological examination. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics Approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gil, A., Castrejon-de-Anta, N., Vilaseca, I. et al. Laryngeal EBV-positive Inflammatory Follicular Dendritic cell/fibroblastic Reticular cell Tumour. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 75, 3941–3944 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03937-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03937-5