Abstract
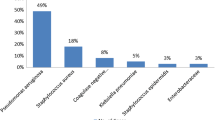
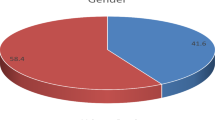
Chronic suppurative otitis media is defined as a chronic inflammation of the middle ear cleft, which presents with recurrent ear discharge through a tympanic membrane perforation. The purpose of this study was to find pattern of bacteriology in patients of atticoantral type of chronic suppurative otitis media as it will help the clinician to decide the effective antibiotics to be prescribed. This prospective and observational study was conducted in the Department of ENT in collaboration with Department of Microbiology, Government Medical College and Hospital, Chandigarh. The ear discharge specimen of all patients meeting the inclusion criteria were collected and sent for microbial examination. Culture positive samples were subjected to antibiotic sensitivity. A total of one hundred ears (mean age 27.33 years) clinically diagnosed with chronic suppurative otitis media, atticoantral type were included in this study based on the preset inclusion and exclusion. The male: female ratio in our patients was 0.94:1. Ninety-seven (96.9%) patients had unilateral disease, while 3 (3.1%) patients had bilateral disease. Twenty-eight percent of the total samples were sterile. The most common bacteria isolated were Pseudomonas aeruginosa (27.1%), Methicillin sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (23.3%) and Proteur mirabilis (6.5%). was sensitive to polymyxin B (100%) followed by ciprofloxacin (46.4%), neomycin (42.9%) and gentamicin (42.9%). Polymyxin B is the most effective antibiotic against the cultured bacteria followed by gentamicin, ciprofloxacin and neomycin.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brobby GW, Zadik P (1987) Bacteriology of otitis media in Ghana. Trop Dr 17(2):91–92
Brook I, Frazier EH (1996) Microbial dynamics of persistent purulent otitis media in children. J Pediatr 128(2):237–240
Fairbanks DN (1981) Antimicrobial therapy for chronic suppurative otitis media. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 90(3 Pt 3):58–62
Kenna MA (1988) Etiology and pathogenesis of chronic suppurative otitis media. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 97(2-suppl):16–17
Arguedas A, Loaiza C, Herrera JF, Mohs E (1994) Antimicrobial therapy for children with chronic suppurative otitis media without cholesteatoma. Pediatr Infect Dis J 13(10):878–882
Attallah MS (2000) Microbiology of chronic suppurative otitis media with cholesteatoma. Saudi Med J 21(10):924–927
Fliss DM, Meidan N, Dagan R, Leiberman A (1992) Aerobic bass cteriology of chronic suppurative otitis media without cholesteatoma in children. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 101(10):866–869
Anifasi WB, Tumushime-Buturo CG (1989) Bacteriology and drug sensitivity of chronic suppurative otitis media at a central hospital in Zimbabwe. Cent Afr J Med 35(9):481–483
Kumar H, Seth S (2012) Bacterial and fungal study of 100 cases of chronic suppurative otitis media. J Clin Diagn Res. 1(5):1224–1227
Rout MR, Mohanty D, Vijaylaxmi Y, Kamalesh B, Chakradhar M (2012) Prevalence of cholesteatoma in chronic suppurative otitis media with central perforation. Indian J Otol 18(1):7
Smith JA, Danner CJ (2006) Complications of chronic otitis media and cholesteatoma. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 39(6):1237–1255
Adoga A, Nimkur T, Silas O (2010) Chronic suppurative otitis media: socio-economic implications in a tertiary hospital in Northern Nigeria. Pan Afr Med J 26(4):3
Yeo SG, Park DC, Hong SM, Cha CI, Kim MG (2007) Bacteriology of chronic suppurative otitis media–a multicenter study. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 127(10):1062–1067
Madana J, Yolmo D, Kalaiarasi R, Gopalakrishnan S, Sujatha S (2011) Microbiological profile with antibiotic sensitivity pattern of cholesteatomatous chronic suppurative otitis media among children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 75(9):1104–1108
Collee J, Fraser A, Marnion B, Simmons A (1996) Mackie and McCartney practical medical microbiology, 14th edn. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburg, pp 131–150
World Medical Association (1989) Declaration of Helsinki, vol 79. Bulletin of World Health Organisation, Hong Kong
Lakshmi K, Prakash M, Anuradha S, Swathi G (2013) Bacteriological profile and their antibiotic susceptibility pattern of cases of chronic suppurative otitis media. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 6(7):210–212
Shrestha BL, Amatya RCM, Shrestha I, Ghosh I (2012) Microbiological profile of chronic supurative otitis media. Nepal J ENT Head Neck Surg 2(2):6–7
Teele DW, Klein JO, Rosner B (1989) Epidemiology of otitis media during the first seven years of life in children in greater Boston: a prospective, cohort study. J Infect Dis 160(1):83–94
Agrawal A, Kumar D, Goyal A, Goyal S, Singh N, Khandelwal G (2013) Microbiological profile and their antimicrobial sensitivity pattern in patients of otitis media with ear discharge. Indian J Otol 19(1):5
Shyamala R, Reddy PS (2012) The study of becteriologigal agents of chronic suppurative otitis media: aerobic culture and evaluation. J Microbiol Biotech Res 2:152–162
Gulati J, Tondon PL, Singh W, Bias AS (1969) Study of bacterial Flora in chronic suppurative otitis media. Indian. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 21:198
Malkappa SK, Kondapaneni S, Surpam RB, Chakraverti TK (2012) Study of aerobic bacterial isolates and their antibiotic susceptibility pattern in chronic suppurative otitis media. Indian J Otol 18(3):136
Taneja M (1995) C.S.O.M: a bacteriological study. Indian J Otol 1(2):24–27
Shaheen MM, Raquib A, Ahmad SM (2012) Chronic suppurative otitis media and its association with socio-econonic factors among rural primary school children of Bangladesh. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 64(1):36–41
Saraswati J, Venkatesh R, Jeya M (2013) Study of aerobic bacterial and fungal etiology of chronic suppurative otitis media in tertiary care hospital in out skirts of Chennai, India. Int J Res Health Sci 1(3):199–203
Ahmad S (2013) Antibiotics in chronic suppurative otitis media: a bacteriologic study. Egypt J Ear Nose Throat Allied Sci 14(3):191–194
Rangaiah ST, Dudda R, Prasad MH, Balaji NK, Sumangala B, Gudikote MM (2017) Bacteriological profile of chronic suppurative otitis media in a tertiary care hospital. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 3(3):601–605
Poorey VK, lyer A (2002) Study of bacterial flora in csom and its clinical significance. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 54(2):91–95
Kumar S, Sharma R, Saxena A, Pandey A, Gautam P, Taneja V (2012) Bacterial flora of infected unsafe CSOM. Indian J Otol 18(4):208
Ettehad Gh, Refahi S, Nemmati A, Pirzadeh A, Daryani A (2006) Microbial and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns from patients with chronic otitis media in ardebil. Int J Trop Med 1(2):62–65
Al-Marzoqi AH, Al-Janabi HSO, Hussein HJ, Taee ZMA, Yheea SK (2013) Otitis media; etiology and antibiotics susceptibility among children under ten years old in Hillah city, Iraq. J Nat Sci Res 3(3):1–7
Ghosh A, Rana A, Prasad S (2015) Risk factors and microbiology of chronic suppurative otitits media and its clinical signififcane in a tertiary care setup in Western Uttar Pradesh, India. Int J Curr Med Appl Sci 6(3):177–183
Elmanama AA, Tayyem NEA, Allah SAN (2014) The bacterial etiology of otitis media and their antibiogram among children in Gaza Strip, Palestine. Egypt J Ear Nose Throat Allied Sci 15(2):87–91
Melaku A, Lulseged S (1999) Chronic suppurative otitis media in a children’s hospital in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Ethiop Med J. 37(4):237–246
Tessema G (2001) Otitis media seen in Yekatit 12 hospital. Ethiop Med J 28:41–44
Tobih JE, Taiwo SS, Olowe OA, Olaosun OA, Adejumao SD (2006) Clinical and microbiological profiles of ear infections in Osogbo, Nigeria. Trop Dr 36(3):165–166
Wariso BA, Ibe SN (2006) Bacteriology of chronic discharging ears in Port Harcourt, Nigeria. West Afr J Med 25(3):219–222
Bardanis J, Batzakakis D, Mamatas S (2003) Types and causes of otorrhea. Auris Nasus Larynx 30(3):253–257
Aslam MA, Ahmed Z, Azim R (2004) Microbiology and drug sensitivity patterns of chronic suppurative otitis media. J Coll Physicians Surg-Pak 14(8):459–461
Gül HC, Kurnaz A, Turhan V, Oncül O, Pahsa A (2006) Microorganisms isolated from middle ear cultures and their antibacterial susceptibility in patients with chronic suppurative otitis media. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg KBB J Ear Nose Throat 16(4):164–168
Sharma S, Rehan HS, Goyal A, Jha AK, Upadhyaya S, Mishra SC (2004) Bacteriological profile in chronic suppurative otitis media in Eastern Nepal. Trop Dr 34(2):102–104
Indudaran R, Haq JA, Aiyar S (1999) Antibiotics in chronic suppurative titis media: a bacteriologic study. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 108:440–445
Mukassabi K (2007) Bacteriology of discharging ears. Ir Med J 100(2):379–380
Arshad M, Khan NU, Ali N, Afridi NM (2004) Sensitivity and spectrum of bacterial isolates in infectious otitis externa. J Coll Physicians Surg-Pak 14(3):146–149
Prakash R, Juyal D, Negi V, Pal S, Adekhandi S, Sharma M et al (2013) Microbiology of chronic suppurative otitis media in a tertiary care setup of Uttarakhand state, India. North Am J Med Sci 5(4):282–287
Rao BN, Reddy MS (1994) Chronic suppurative otitis media—a prospective study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 46(2):72–77
Singh AH, Basu R, Venkatesh A (2012) Aerobic bacteriology of chronic suppurative otitis media in Rajahmundry, Andhra Pradesh, India. Biol Med 1(4):73–79
Arvind N, Pavan C, Vishrutha KV (2014) Microbiological profile of chronic suppurative otitis media. Int J Biomed Res 5:204–206
Gaur RS, Mathew J, Varghese AM, Mathew GA, Chandrasekharan R, Anandan S (2013) Microbiological pattern of ear swabs in chronically discharging ears in a Tertiary Care Hospital in India. Indian J Otol 19:51–54
Shetty AK, Shetty A (2014) Aerobic bacteriological profile and their antibiotic susceptibility in chronic suppurative otitis media in patients from Mangalore, Karnataka State. J Acad Clin Microbiol 16(1):3
Ayson PN, Lopez JE, Erasmo Gonzalo DV (2006) Chronic suppurative otitis media : bacterioloy and drug sensitivity patterns at the Quirino Memorial Medical Centre (2004–2005): a preliminary study. Philipp J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 21:20–23
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahajan, T., Dass, A., Gupta, N. et al. Bacteriological Profile in Attico-antral type of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 71 (Suppl 2), 1412–1421 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1486-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1486-1