Abstract
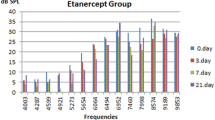
Ototoxicity is a common side effect of cisplatin chemotherapy. The aim of this study was to investigate the potential protective effect of chrysin against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Thirty-four adult female Wistar albino rats were separated into four groups: a cisplatin group (Group A), with cisplatin administered to ten rats once daily for three consecutive days at doses of 8 mg/kg body weight intraperitoneally (i.p.); a cisplatin plus chrysin group (Group B), with 8 mg/kg of cisplatin administered i.p. daily to ten rats for three consecutive days and 25 mg/kg of chrysin administered via oral gavage in a corn oil for 5 days: a chrysin group (Group C), with 25 mg/kg of chrysin administered via oral gavage in corn oil for 5 days to seven rats; and a control group (Group D), with 5 ml/kg of corn oil administered to seven rats via oral gavage for 5 days. Distortion product otoacoustic emission measurements were performed in the same ear of the rats under general anesthesia at baseline and on the first and fifth days after drug administration. No significant differences were noted between the measurements either in the chrysin group or in the control group. In the cisplatin group, there was a significant worsening of hearing compared to baseline and the measurements on the fifth day at all frequencies. In the statistical analysis, a statistically significant difference was observed at 5039, 6351, 8003, and 10078 Hz frequencies between the measurements on the first and fifth days. In the cisplatin plus chrysin group, there were statistically significant differences at frequencies of 2,003 and 5,039 Hz between the measurements at baseline and on the fifth day, at 3,175 and 5,039 Hz between the measurements on the first and fifth days, and at 8,003 and 100,078 Hz between the measurements at baseline and on the first day. According to these results, this study demonstrates that cisplatin-related ototoxicity can be prevented in rats by the administration of chrysin.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rybak LP, Mukherjea D, Jajoo S, Ramkumar V (2009) Cisplatin ototoxicity and protection: clinical and experimental studies. Tohoku J Exp Med 219(3):177–186
Rybak LP, Ramkumar V (2007) Ototoxicity. Kidney Int 72(8):931–935
Clerici WJ, Hensley K, DiMartino DL, Butterfield DA (1996) Direct detection of ototoxicant-induced reactive oxygen species generation in cochlear explants. Hear Res 98(1–2):116–124
Yumusakhuylu AC, Yazici M, Sari M, Binnetoglu A, Kosemihal E, Akdas F, Sirvanci S, Yuksel M, Uneri C, Tutkun A (2012) Protective role of resveratrol against cisplatin induced ototoxicity in guinea pigs. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 76(3):404–408
Kizilay A, Kalcioglu MT, Ozerol E, Iraz M, Gulec M, Akyol O, Ozturan O (2004) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester ameliorated ototoxicity induced by cisplatin inrats. J Chemother 16(4):381–387
Korver KD, Rybak LP, Whitworth C, Campbell KM (2002) Round window application of d-methionine provides complete cisplatin otoprotection. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126(6):683–689
Daldal A, Odabasi O, Serbetcioglu B (2007) The protective effect of intratympanic dexamethasone on cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in guinea pigs. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 137(5):747–752
Chen X, Frisina RD, Bowers WJ, Frisina DR, Federoff HJ (2001) HSV amplicon-mediated neurotrophin-3 expression protects murine spiral ganglion neurons from cisplatin-induced damage. Mol Ther 3(6):958–963
So HS, Park C, Kim HJ, Lee JH, Park SY, Lee JH, Lee ZW, Kim HM, Kalinec F, Lim DJ, Park R (2005) Protective effect of T-type calcium channel blocker flunarizine on cisplatin-induced death of auditory cells. Hear Res 204(1–2):127–139
Church MW, Blakley BW, Burgio DL, Gupta AK (2004) WR-2721 (Amifostine) ameliorates cisplatin-induced hearing loss but causes neurotoxicity in hamsters: dose-dependent effects. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 5(3):227–237
Choe WT, Chinosornvatana N, Chang KW (2004) Prevention of cisplatin ototoxicity using transtympanic N-acetylcysteine and lactate. Otol Neurotol 25(6):910–915
Yoo J, Hamilton SJ, Angel D, Fung K, Franklin J, Parnes LS, Lewis D, Venkatesan V, Winquist E (2013) Cisplatin otoprotection using transtympanic l-N-acetylcysteine: a pilot randomized study in head and neck cancer patients. Laryngoscope. doi:10.1002/lary.24360
Kalcioglu MT, Kizilay A, Gulec M, Karatas E, Iraz M, Akyol O, Egri M, Ozturan O (2005) The protective effect of erdosteine against ototoxicity induced by cisplatin in rats. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 262(10):856–863
Hyppolito MA, de Oliveira JA, Rossato M (2006) Cisplatin ototoxicity and otoprotection with sodium salicylate. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 263(9):798–803
Huang X, Whitworth CA, Rybak LP (2007) Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) protects against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in rats. Otol Neurotol 28(6):828–833
Lynch ED, Gu R, Pierce C, Kil J (2005) Reduction of acute cisplatin ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats by oral administration of allopurinol and ebselen. Hear Res 201(1–2):81–89
Erdem T, Bayindir T, Filiz A, Iraz M, Selimoglu E (2012) The effect of resveratrol on the prevention of cisplatin ototoxicity. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269(10):2185–2188
Sagit M, Korkmaz F, Akcadag A, Somdas MA (2013) Protective effect of thymoquinone against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270(8):2231–2237
Bayindir T, Iraz M, Kelles M, Kaya S, Tan M, Filiz A, Toplu Y, Kalcioglu MT (2013) The effect of betaglucan on cisplatin ototoxicity. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. doi:10.1007/s12070-013-0623-0
Cicek MT, Kalcioglu MT, Bayindir T, Toplu Y, Iraz M (2013) The effect of lycopene on the ototoxicity induced by cisplatin. Turk J Med Sci. doi:10.3906/sag-1304-66
Rapta P, Misík V, Stasko A, Vrábel I (1995) Redox intermediates of flavonoids and caffeic acid esters from propolis: an EPR spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry study. Free Radic Biol Med. 18(5):901–908
Williams CA, Harborne JB, Newman M, Greenham J, Eagles J (1997) Chrysin and other leaf exudate flavonoids in the genus Pelargonium. Phytochemistry 46(8):1349–1353
Hecker M, Preiss C, Klemm P, Busse R (1996) Inhibition by antioxidants of nitric oxide synthase expression in murine macrophages: role of nuclear factor kappa B and interferon regulatory factor 1. Br J Pharmacol 118(8):2178–2184
Cho H, Yun CW, Park WK, Kong JY, Kim KS, Park Y, Lee S, Kim BK (2004) Modulation of the activity of pro-inflammatory enzymes, COX-2 and iNOS, by chrysin derivatives. Pharmacol Res 49(1):37–43
Pearce FL, Befus AD, Bienenstock J (1984) Mucosal mast cells. III. Effect of quercetin and other flavonoids on antigen-induced histamine secretion from rat intestinal mast cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol 73(6):819–823
Cárdenas M, Marder M, Blank VC, Roguin LP (2006) Antitumor activity of some natural flavonoids and synthetic derivatives on various human and murine cancer cell lines. Bioorg Med Chem 14(9):2966–2971
Wolfman C, Viola H, Paladini A, Dajas F, Medina JH (1994) Possible anxiolytic effects of chrysin, a central benzodiazepine receptor ligand isolated from Passiflora coerulea. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 47(1):1–4
Kao YC, Zhou C, Sherman M, Laughton CA, Chen S (1998) Molecular basis of the inhibition of human aromatase (estrogen synthetase) by flavone and isoflavone phytoestrogens: a site-directed mutagenesis study. Environ Health Perspect 106(2):85–92
Tsukasaki N, Whitworth CA, Rybak LP (2000) Acute changes in cochlear potentials due to cisplatin. Hear Res 149(1–2):189–198
van Ruijven MW, de Groot JC, Klis SF, Smoorenburg GF (2005) The cochlear targets of cisplatin: an electrophysiological and morphological time-sequence study. Hear Res 205(1–2):241–248
Rybak LP, Whitworth CA, Mukherjea D, Ramkumar V (2007) Mechanisms of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity and prevention. Hear Res 226(1–2):157–167
Dehne N, Lautermann J, Petrat F, Rauen U, de Groot H (2001) Cisplatin ototoxicity:involvement of iron and enhanced formation of superoxide anion radicals. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 174(1):27–34
Waissbluth S, Salehi P, He X, Daniel SJ (2013) Systemic dexamethasone for the prevention of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270(5):1597–1605
Hyppolito MA, de Oliveira JA, Rossato M (2006) Cisplatin ototoxicity and otoprotection with sodium salicylate. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 263(9):798–803
Riga MG, Chelis L, Kakolyris S, Papadopoulos S, Stathakidou S, Chamalidou E, Xenidis N, Amarantidis K, Dimopoulos P, Danielides V (2013) Transtympanic injections of N-acetylcysteine for the prevention of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: a feasible method with promising efficacy. Am J Clin Oncol 36(1):1–6
Duval M, Daniel SJ (2012) Meta-analysis of the efficacy of amifostine in the prevention of cisplatin ototoxicity. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 41(5):309–315
Li X, Huang Q, Ong CN, Yang XF, Shen HM (2010) Chrysin sensitizes tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis in human tumor cells via suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB. Cancer Lett 293(1):109–116
Sultana S, Verma K, Khan R (2012) Nephroprotective efficacy of chrysin against cisplatin-induced toxicity via attenuation of oxidative stress. J Pharm Pharmacol 64(6):872–881
Khan R, Khan AQ, Qamar W, Lateef A, Tahir M, Rehman MU, Ali F, Sultana S (2012) Chrysin protects against cisplatin-induced colon. toxicity via amelioration of oxidative stress and apoptosis: probable role of p38MAPK and p53. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 258(3):315–329
Khan R, Khan AQ, Qamar W, Lateef A, Ali F, Rehman MU, Tahir M, Sharma S, Sultana S (2012) Chrysin abrogates cisplatin-induced oxidative stress, p53 expression, goblet cell disintegration and apoptotic responses in the jejunum of Wistar rats. Br J Nutr 108(9):1574–1585
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kelles, M., Tan, M., Kalcioglu, M.T. et al. The Protective Effect of Chrysin Against Cisplatin İnduced Ototoxicity in Rats. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 66, 369–374 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-013-0695-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-013-0695-x