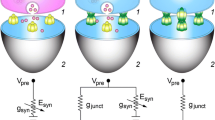
Abstract
Our brain and nervous system coordinate all activities of our body and its interaction with the environment. Our brain is made up of a large number of cells called neurons that form specialised points of contacts with other neurons. These contacts are called synapses. The development and functioning of these synapses are clearly vital for nervous system function. A set of molecules call Cell AdhesionMolecules (CAMs) have been shown to be required for the development and maintenance of synapses. More recent work with CAMs indicates that these molecules are also required for signalling and hence normal functioning of synapses. Here, I discuss how CAMs function both in normal synapse development and in signalling at the synapse.
Similar content being viewed by others
Suggested Reading
J M Pearce, Sir Charles Scott Sherrington (1857–1952) and the synapse, JNeurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, Vol.75, p.544, 2004.
M Hortsch, The Sticky Synapse Cell Adhesion Molecules and Their Role in Synapse Formation and Maintenance, 1 edn (Springer), 2009.
K Gerrow and A El-Husseini, Cell adhesion molecules at the synapse, Front Biosci, Vol.11, pp.2400–2419, 2006.
D D Krueger, L P Tuffy, T Papadopoulos and N Brose, The role of neurexins and neuroligins in the formation, maturation, and function of vertebrate synapses, Curr Opin Neurobiol., Vol.22, pp.412–422, 2012.
X J Tong, E J Lopez-Soto, L Li, H Liu, D Nedelcu, D Lipscombe, Z Hu and J M Kaplan, Retrograde synaptic inhibition is mediated by alpha-neurexin binding to the alpha2delta subunits of N-Type calcium channels, Neuron, Vol.95, pp.326–340, p.e325, 2017.
V Sytnyk, I Leshchyns’ka and M Schachner, Neural cell adhesion molecules of the immunoglobulin superfamily regulate synapse formation, maintenance, and function, Trends Neurosci, Vol.40, pp.295–308, 2017.
K Babu, Z Hu, S C Chien, G Garriga and J M Kaplan, The immunoglobulin super family protein RIG-3 prevents synaptic potentiation and regulates Wnt signaling, Neuron, Vol.71, pp.103–116, 2011.
P Pandey, A Bhardwaj and K Babu, Regulation of WNT signaling at the neuromuscular junction by the immunoglobulin superfamily protein RIG-3 in Caenorhabditis elegans, Genetics, Vol.206, pp.1521–1534, 2017.
E Seong, L Yuan and J Arikkath, Cadherins and catenins in dendrite and synapse morphogenesis, Cell Adh Migr., Vol.9, pp.202–213, 2015.
S Thapliyal and K Babu, C. elegans locomotion: finding balance in imbalance, Adv Exp Med Biol., Vol.1112, pp.185–196, 2018.
S Thapliyal, S Ravindranath and K Babu, Regulation of glutamate signaling in the sensorimotor circuit by CASY-1A/Calsyntenin in Caenorhabditis elegans, Genetics, Vol.208, pp.1553–1564, 2018a.
S Thapliyal, A Vasudevan, Y Dong, J Bai, S P Koushika and K Babu, The Cterminal of CASY-1/Calsyntenin regulates GABAergic synaptic transmission at the Caenorhabditis elegans neuromuscular junction, PLoS genetics, Vol.14, p.e1007263, 2018b.
I Leshchyns’ka and V Sytnyk, Synaptic cell adhesion molecules in Alzheimer’s disease, Neural Plast., 6427537, 2016.
X Cao and K Tabuchi, Functions of synapse adhesion molecules neurexin/neuroligins and neurodevelopmental disorders, Neurosci Res, Vol.116, pp.3–9, 2017.
L K Jacobsen, M R Picciotto, C J Heath, W E Mencl and J Gelernter, Allelic variation of calsyntenin 2 (CLSTN2) modulates the impact of developmental tobacco smoke exposure on mnemonic processing in adolescents, Biol Psychiatry, Vol.65, pp.671–679, 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Kavita Babu holds a PhD in developmental biology from The National University of Singapore. She has worked on Caenorhabditis elegans at Massachusetts General Hospital for her postdoctoral research. Kavita headed her lab at IISER Mohali for close to eight years before moving to the Centre for Neuroscience, IISc in the middle of 2019. Kavita continues to be fascinated by the mind of the worm and her lab is largely interested in understanding how cell adhesion molecules signal at the synapse.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babu, K. Sticking and Signalling at the Synapse. Reson 25, 419–429 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12045-020-0954-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12045-020-0954-6