Abstract
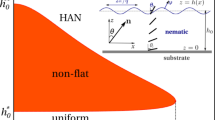
One discusses phenomenologically the statics and dynamics of surface anchoring of nematic liquid crystals. In statics, for symmetrical situations, one can induce, under the action of an external field, a surface breaking with a bifurcation between two opposite orientations of the director. In dynamics, one shows that the surface director relaxation is intrinsically fast, and accompanied by a transient surface shear flow. In thin cells with planar anchorings, filled by cyanobiphenyl materials which orient normal to the plates under a strong electric field, there are now two effects which couple the relaxation of the surface director: a static one, which favors parallel orientation and a uniform cell texture, and a transient dynamical coupling from the surface flow, which forces π-twisted texture. With suitable electric signals, one can control the surface bifurcations to give at will one of these two bistable textures. Results are presented which show that these mechanisms could lead to a new class of surface controlled, fast nematic bistable displays.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G D Boyd, J Cheng and P D T Ngo, Appl. Phys. Lett. 36, 556 (1980)
D W Berreman and W R Heffner, Appl. Phys. Lett. 37, 109 (1980)
N A Clark and S T Lagerwall, Appl. Phys. Lett. 36, 899 (1980)
R Barberi, M Giocondo and G Durand, Appl. Phys. Lett. 60, 1085 (1992)
G Durand, Proc. SPIE, 2949, 2 (1996)
I Dozov, M Nobili and G Durand, Appl. Phys. Lett. 70, 1179 (1997)
I Dozov, Ph. Martinot-Lagarde, E Polossat, I Lelidis, M Giocondo and G Durnad, Proc. SPIE, 3015, 61 (1997)
Ph. Martinot-Lagarde, I Dozov, E Polossat, M Giocondo, I Lelidis, G Durand, J Angele, B Pecout and A Boissier, SID ’97 Digest, 41 (1997)
G Durand, presented at the VIIth International Topical Meeting on Optics of Liquid Crystals, Heppenheim, to be submitted for publication (1997)
A Gharbi, F R Fekih and G Durand, Liq. Cryst. 12, 515 (1992)
G Barbero and R Barberi, J. Phys. (Paris) 44, 609 (1983)
R Barberi and G Durnad, Appl. Phys. Lett. 58, 2907 (1991)
R Barberi, M Giocondo, J Li, R Bartolino, I Dozov and G Durand, Proc SPIE, 3013, 229 (1997)
E Virga and G Durand, presented at the 17th International Liquid Crystal Conference (Strasbourg, 1998)
T Tanaka, I Sato, A Inoue, Y Momose, H Nomura and S Lino, Proceedings of Asia Display ’95 (Tokyo, 1995) p. 259.
E Wood and G P Bryan-Brown et al, presented at the Network Meeting Liquid Crystals: Surface Properties from Basic to Application (Moena, 1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Reproduced from ‘Liquid Crystals Today’ (Vol. 8, p. 1–7, 1998) by permission from Taylor and Francis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dozov, I., Durand, G. Surface controlled nematic bistability. Pramana - J Phys 53, 25–35 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-999-0138-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-999-0138-0