Abstract
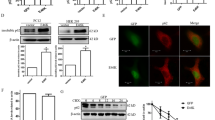
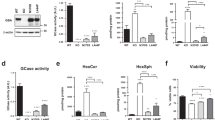
Misfolding and aggregation of α-Synuclein (α-Syn), which are hallmark pathological features of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s disease (PD) and dementia with Lewy Bodies, continue to be significant areas of research. Among the diverse forms of α-Syn – monomer, oligomer, and fibril, the oligomer is considered the most toxic. However, the mechanisms governing α-Syn oligomerization are not yet fully understood. In this study, we utilized genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 loss-of-function screening in human HEK293 cells to identify negative regulators of α-Syn oligomerization. We found that tetraspanin 3 (TSPAN3), a presumptive four-pass transmembrane protein, but not its homolog TSPAN7, significantly modulates α-Syn oligomer levels. TSPAN3 was observed to interact with α-Syn oligomers, regulate the amount of α-Syn oligomers on the cell membrane, and promote their degradation via the clathrin-AP2 mediated endo-lysosome pathway. Our findings highlight TSPAN3 as a potential regulator of α-Syn oligomers, presenting a promising target for future PD prevention and treatment strategies.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw sequencing data have been deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA: SRR14660095).
References
Uncategorized References
Maroteaux L, Campanelli JT, Scheller RH (1988) Synuclein: a neuron-specific protein localized to the nucleus and presynaptic nerve terminal. J Neurosci 8(8):2804–2815
Spillantini MG, Crowther RA, Jakes R, Cairns NJ, Lantos PL, Goedert M (1998) Filamentous alpha-synuclein inclusions link multiple system atrophy with Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurosci Lett 251(3):205–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3940(98)00504-7
Spillantini MG, Crowther RA, Jakes R, Hasegawa M, Goedert M (1998) alpha-Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(11):6469–6473. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.11.6469
Dettmer U, Selkoe D, Bartels T (2016) New insights into cellular alpha-synuclein homeostasis in health and disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol 36:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2015.07.007
Burre J (2015) The synaptic function of alpha-synuclein. J Parkinsons Dis 5(4):699–713. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-150642
Ding TT, Lee SJ, Rochet JC, Lansbury PT Jr (2002) Annular alpha-synuclein protofibrils are produced when spherical protofibrils are incubated in solution or bound to brain-derived membranes. Biochemistry 41(32):10209–10217. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi020139h
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H et al (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276(5321):2045–2047. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.276.5321.2045
Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J, Singleton A, Hague S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Peuralinna T et al (2003) alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science 302(5646):841. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1090278
Hellstrand E, Grey M, Ainalem ML, Ankner J, Forsyth VT, Fragneto G, Haertlein M, Dauvergne MT et al (2013) Adsorption of alpha-synuclein to supported lipid bilayers: positioning and role of electrostatics. ACS Chem Neurosci 4(10):1339–1351. https://doi.org/10.1021/cn400066t
Grozdanov V, Bousset L, Hoffmeister M, Bliederhaeuser C, Meier C, Madiona K, Pieri L, Kiechle M et al (2019) Increased immune activation by pathologic alpha-Synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25557
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388(6645):839–840. https://doi.org/10.1038/42166
Braak H, Sandmann-Keil D, Gai W, Braak E (1999) Extensive axonal Lewy neurites in Parkinson’s disease: a novel pathological feature revealed by alpha-synuclein immunocytochemistry. Neurosci Lett 265(1):67–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3940(99)00208-6
Outeiro TF, Lindquist S (2003) Yeast cells provide insight into alpha-synuclein biology and pathobiology. Science 302(5651):1772–1775. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1090439
Tardiff DF, Jui NT, Khurana V, Tambe MA, Thompson ML, Chung CY, Kamadurai HB, Kim HT et al (2013) Yeast reveal a “druggable” Rsp5/Nedd4 network that ameliorates alpha-synuclein toxicity in neurons. Science 342(6161):979–983. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1245321
Hamamichi S, Rivas RN, Knight AL, Cao S, Caldwell KA, Caldwell GA (2008) Hypothesis-based RNAi screening identifies neuroprotective genes in a Parkinson’s disease model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(2):728–733. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0711018105
Kuwahara T, Koyama A, Koyama S, Yoshina S, Ren CH, Kato T, Mitani S et al (2008) A systematic RNAi screen reveals involvement of endocytic pathway in neuronal dysfunction in alpha-synuclein transgenic C. elegans. Hum Mol Genet 17(19):2997–3009. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddn198
Auluck PK, Chan HY, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Bonini NM (2002) Chaperone suppression of alpha-synuclein toxicity in a Drosophila model for Parkinson’s disease. Science 295(5556):865–868. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1067389
Harrington AJ, Yacoubian TA, Slone SR, Caldwell KA, Caldwell GA (2012) Functional analysis of VPS41-mediated neuroprotection in Caenorhabditis elegans and mammalian models of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 32(6):2142–2153. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2606-11.2012
Moree B, Yin G, Lazaro DF, Munari F, Strohaker T, Giller K, Becker S, Outeiro TF et al (2015) Small molecules detected by second-harmonic generation modulate the conformation of monomeric alpha-synuclein and reduce its aggregation in cells. J Biol Chem 290(46):27582–27593. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.636027
Wagner J, Ryazanov S, Leonov A, Levin J, Shi S, Schmidt F, Prix C, Pan-Montojo F et al (2013) Anle138b: a novel oligomer modulator for disease-modifying therapy of neurodegenerative diseases such as prion and Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 125(6):795–813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1114-9
Pujols J, Pena-Diaz S, Lazaro DF, Peccati F, Pinheiro F, Gonzalez D, Carija A, Navarro S et al (2018) Small molecule inhibits alpha-synuclein aggregation, disrupts amyloid fibrils, and prevents degeneration of dopaminergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(41):10481–10486. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1804198115
Hollerhage M, Moebius C, Melms J, Chiu WH, Goebel JN, Chakroun T, Koeglsperger T, Oertel WH et al (2017) Protective efficacy of phosphodiesterase-1 inhibition against alpha-synuclein toxicity revealed by compound screening in LUHMES cells. Sci Rep 7(1):11469. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11664-5
Kerppola TK (2006) Design and implementation of bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays for the visualization of protein interactions in living cells. Nat Protoc 1(3):1278–1286. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.201
Outeiro TF, Putcha P, Tetzlaff JE, Spoelgen R, Koker M, Carvalho F, Hyman BT, McLean PJ (2008) Formation of toxic oligomeric alpha-synuclein species in living cells. PLoS One 3(4):e1867. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001867
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y, He QY (2012) clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 16(5):284–287. https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2011.0118
Dettmer U, Newman AJ, Luth ES, Bartels T, Selkoe D (2013) In vivo cross-linking reveals principally oligomeric forms of alpha-synuclein and beta-synuclein in neurons and non-neural cells. J Biol Chem 288(9):6371–6385. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.403311
Seipold L, Damme M, Prox J, Rabe B, Kasparek P, Sedlacek R, Altmeppen H, Willem M et al (2017) Tetraspanin 3: a central endocytic membrane component regulating the expression of ADAM10, presenilin and the amyloid precursor protein. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1864(1):217–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.11.003
Kozik P, Francis RW, Seaman MN, Robinson MS (2010) A screen for endocytic motifs. Traffic 11(6):843–855. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01056.x
Webb JL, Ravikumar B, Atkins J, Skepper JN, Rubinsztein DC (2003) Alpha-Synuclein is degraded by both autophagy and the proteasome. J Biol Chem 278(27):25009–25013. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M300227200
Fusco G, Chen SW, Williamson PTF, Cascella R, Perni M, Jarvis JA, Cecchi C, Vendruscolo M et al (2017) Structural basis of membrane disruption and cellular toxicity by alpha-synuclein oligomers. Science 358(6369):1440–1443. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aan6160
Thiede-Stan NK, Tews B, Albrecht D, Ristic Z, Ewers H, Schwab ME (2015) Tetraspanin-3 is an organizer of the multi-subunit Nogo-A signaling complex. J Cell Sci 128(19):3583–3596. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.167981
Masaracchia C, Hnida M, Gerhardt E, Lopes da Fonseca T, Villar-Pique A, Branco T, Stahlberg MA, Dean C et al (2018) Membrane binding, internalization, and sorting of alpha-synuclein in the cell. Acta Neuropathol Commun 6(1):79. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-018-0578-1
Mettlen M, Chen PH, Srinivasan S, Danuser G, Schmid SL (2018) Regulation of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem 87:871–896. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-062917-012644
Emmanouilidou E, Melachroinou K, Roumeliotis T, Garbis SD, Ntzouni M, Margaritis LH, Stefanis L, Vekrellis K (2010) Cell-produced alpha-synuclein is secreted in a calcium-dependent manner by exosomes and impacts neuronal survival. J Neurosci 30(20):6838–6851. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5699-09.2010
Huotari J, Helenius A (2011) Endosome maturation. EMBO J 30(17):3481–3500. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2011.286
Sung JY, Kim J, Paik SR, Park JH, Ahn YS, Chung KC (2001) Induction of neuronal cell death by Rab5A-dependent endocytosis of alpha-synuclein. J Biol Chem 276(29):27441–27448. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M101318200
Eisbach SE, Outeiro TF (2013) Alpha-synuclein and intracellular trafficking: impact on the spreading of Parkinson’s disease pathology. J Mol Med (Berl) 91(6):693–703. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-013-1038-9
Dalfo E, Gomez-Isla T, Rosa JL, Nieto Bodelon M, Cuadrado Tejedor M, Barrachina M, Ambrosio S, Ferrer I (2004) Abnormal alpha-synuclein interactions with Rab proteins in alpha-synuclein A30P transgenic mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63(4):302–313. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnen/63.4.302
Shi MM, Shi CH, Xu YM (2017) Rab GTPases: the key players in the molecular pathway of Parkinson’s disease. Front Cell Neurosci 11:81. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2017.00081
Smith WW, Margolis RL, Li X, Troncoso JC, Lee MK, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Iwatsubo T et al (2005) Alpha-synuclein phosphorylation enhances eosinophilic cytoplasmic inclusion formation in SH-SY5Y cells. J Neurosci 25(23):5544–5552. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0482-05.2005
Neumann M, Kahle PJ, Giasson BI, Ozmen L, Borroni E, Spooren W, Muller V, Odoy S et al (2002) Misfolded proteinase K-resistant hyperphosphorylated alpha-synuclein in aged transgenic mice with locomotor deterioration and in human alpha-synucleinopathies. J Clin Invest 110(10):1429–1439. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI15777
Lee HJ, Khoshaghideh F, Patel S, Lee SJ (2004) Clearance of alpha-synuclein oligomeric intermediates via the lysosomal degradation pathway. J Neurosci 24(8):1888–1896. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3809-03.2004
Karpinar DP, Balija MB, Kugler S, Opazo F, Rezaei-Ghaleh N, Wender N, Kim HY, Taschenberger G et al (2009) Pre-fibrillar alpha-synuclein variants with impaired beta-structure increase neurotoxicity in Parkinson’s disease models. EMBO J 28(20):3256–3268. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2009.257
Winner B, Jappelli R, Maji SK, Desplats PA, Boyer L, Aigner S, Hetzer C, Loher T et al (2011) In vivo demonstration that alpha-synuclein oligomers are toxic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(10):4194–4199. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1100976108
Lashuel HA, Petre BM, Wall J, Simon M, Nowak RJ, Walz T, Lansbury PT Jr (2002) Alpha-synuclein, especially the Parkinson’s disease-associated mutants, forms pore-like annular and tubular protofibrils. J Mol Biol 322(5):1089–1102. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00735-0
Cooper AA, Gitler AD, Cashikar A, Haynes CM, Hill KJ, Bhullar B, Liu K, Xu K et al (2006) Alpha-synuclein blocks ER-Golgi traffic and Rab1 rescues neuron loss in Parkinson’s models. Science 313(5785):324–328. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1129462
Paillusson S, Gomez-Suaga P, Stoica R, Little D, Gissen P, Devine MJ, Noble W, Hanger DP et al (2017) alpha-Synuclein binds to the ER-mitochondria tethering protein VAPB to disrupt Ca(2+) homeostasis and mitochondrial ATP production. Acta Neuropathol 134(1):129–149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-017-1704-z
Chung JY, Lee SJ, Lee SH, Jung YS, Ha NC, Seol W, Park BJ (2011) Direct interaction of alpha-synuclein and AKT regulates IGF-1 signaling: implication of Parkinson disease. Neurosignals 19(2):86–96. https://doi.org/10.1159/000325028
Currais A, Hortobagyi T, Soriano S (2009) The neuronal cell cycle as a mechanism of pathogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Aging (Albany NY) 1(4):363–371. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.100045
Kao SY (2009) Rescue of alpha-synuclein cytotoxicity by insulin-like growth factors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 385(3):434–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.05.089
Tiwari-Woodruff SK, Kaplan R, Kornblum HI, Bronstein JM (2004) Developmental expression of OAP-1/Tspan-3, a member of the tetraspanin superfamily. J Neurosci Res 77(2):166–173. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.20141
Pols MS, Klumperman J (2009) Trafficking and function of the tetraspanin CD63. Exp Cell Res 315(9):1584–1592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.09.020
Charrin S, Jouannet S, Boucheix C, Rubinstein E (2014) Tetraspanins at a glance. J Cell Sci 127(Pt 17):3641–3648. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.154906
Fujita Y, Shirataki H, Sakisaka T, Asakura T, Ohya T, Kotani H, Yokoyama S, Nishioka H et al (1998) Tomosyn: a syntaxin-1-binding protein that forms a novel complex in the neurotransmitter release process. Neuron 20(5):905–915. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80472-9
Kerppola TK (2006) Visualization of molecular interactions by fluorescence complementation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7(6):449–456. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1929
Sanjana NE, Shalem O, Zhang F (2014) Improved vectors and genome-wide libraries for CRISPR screening. Nat Methods 11(8):783–784. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3047
Chen M, Amado N, Tan J, Reis A, Ge M, Abreu JG, He X (2020) TMEM79/MATTRIN defines a pathway for Frizzled regulation and is required for Xenopus embryogenesis. Elife 9. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.56793
Yuan NN, Cai CZ, Wu MY, Zhu Q, Su H, Li M, Ren J et al (2019) Canthin-6-one accelerates alpha-synuclein degradation by enhancing UPS activity: drug target identification by CRISPR-Cas9 whole genome-wide screening technology. Front Pharmacol 10:16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00016
Cai M, Li S, Shuai Y, Li J, Tan J, Zeng Q (2019) Genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 viability screen reveals genes involved in TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol 234(6):9184–9193. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27595
Shalem O, Sanjana NE, Hartenian E, Shi X, Scott DA, Mikkelson T, Heckl D, Ebert BL et al (2014) Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screening in human cells. Science 343(6166):84–87. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1247005
Li W, Xu H, Xiao T, Cong L, Love MI, Zhang F, Irizarry RA, Liu JS et al (2014) MAGeCK enables robust identification of essential genes from genome-scale CRISPR/Cas9 knockout screens. Genome Biol 15(12):554. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0554-4
Kim S, Yun SP, Lee S, Umanah GE, Bandaru VVR, Yin X, Rhee P, Karuppagounder SS et al (2018) GBA1 deficiency negatively affects physiological alpha-synuclein tetramers and related multimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(4):798–803. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1700465115
Imberdis T, Fanning S, Newman A, Ramalingam N, Dettmer U (2019) Studying alpha-Synuclein conformation by intact-cell cross-linking. Methods Mol Biol 1948:77–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9124-2_8
Zhang T, Xue L, Li L, Tang C, Wan Z, Wang R, Tan J, Tan Y et al (2016) BNIP3 protein suppresses PINK1 kinase proteolytic cleavage to promote mitophagy. J Biol Chem 291(41):21616–21629. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.733410
Zhang J, Lei H, Chen Y, Ma YT, Jiang F, Tan J, Zhang Y, Li JD (2017) Enzymatic O-GlcNAcylation of alpha-synuclein reduces aggregation and increases SDS-resistant soluble oligomers. Neurosci Lett 655:90–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.06.034
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Zhuohua Zhang, School of Life Sciences, Central South University, for the discussion and suggestions and Professor Jiada Li from the School of Life Sciences, Central South University, for his support in the purification of α-synuclein.
We are grateful for resources from the High Performance Computing Center of Central South University.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2021YFA0805200), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82171258), Changsha Science and Technology Foundation (Grant No. kq2004083), the Innovative Team Program 2019RS1010 from the Department of Science & Technology of Hunan Province, the Innovation-Driven Team Project 2020CX016 from Central South University, NHC Key Laboratory of Birth Defect for Research and Prevention, Hunan Provincial Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital, No. KF2021001. and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University (2022ZZTS0234, 2023ZZTS0254).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Designed the study: TJQ, HJJ, GJF. Performed experiments: HJJ, GXJ, XPQ. Analyzed the data: HJJ, TJQ. Drafted the manuscript: TJQ, HJJ. All authors critically revised the manuscript and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, J., Guan, X., Zhao, M. et al. Genome-wide CRISPR–Cas9 Knockout Screening Reveals a TSPAN3-mediated Endo-lysosome Pathway Regulating the Degradation of α-Synuclein Oligomers. Mol Neurobiol 60, 6731–6747 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03495-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03495-5