Abstract
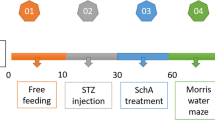
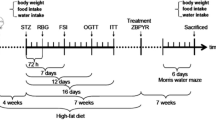
Accumulating clinical and epidemiological studies indicate that learning and memory impairment is more prevalent among people with diabetes mellitus (DM). PTP1B is a member of protein tyrosine phosphatase family and participates in a variety of pathophysiological effects including inflammatory, insulin signaling pathway, and learning and memory. This study was aimed to investigate the effects of CA, a specific inhibitor of PTP1B, on spatial learning and memory impairment in diabetic mice caused by high-fat diet and injection of streptozotocin. We found that the protein expressions of PTP1B increased in hippocampal CA1, CA3, and PFC regions of diabetic mice. Network pharmacology results showed that PTP1B might be one of the key targets between diabetes and cognitive dysfunction, and CA might alleviate DM-induced cognitive dysfunction. Animal experiments showed that CA ameliorated DM-induced spatial learning and memory impairment, and improved glucose and lipid metabolic disorders. Moreover, administration of CA alleviated hippocampal structure damage and enhanced the expressions of synaptic proteins, including PSD-95, SYN-1, and SYP in diabetic mice. Furthermore, CA treatment not only significantly down-regulated the expressions of PTP1B and NLRP3 inflammatory related proteins (NLRP3, ASC, Caspase-1, COX-2, IL-1β, and TNF-α), but also significantly up-regulated the expressions of insulin signaling pathway–related proteins (p-IRS1, p-PI3K, p-AKT, and p-GSK-3β) in diabetic mice. Taken together, these results suggested that PTP1B might be a targeted strategy to rescue learning and memory deficits in DM, possibly through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome and regulation of insulin signaling pathway.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CA:
-
Claramine
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- AD:
-
Alzheimer disease
- HFD:
-
High-fat diet
- FBG:
-
Fasting blood glucose
- STZ:
-
Streptozotocin
- MWM:
-
Morris water maze
- PTP1B:
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B
- IRS1:
-
Insulin receptor substrates 1
- AKT:
-
Protein kinase B
- PI3K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- GSK-3β:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3β
- NLRP3:
-
Recombinant NLR family, pyrin domain containing protein 3
- ASC:
-
Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD
- Caspase-1:
-
Cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase-1
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- IL-18:
-
Interleukin-18
- PSD-95:
-
Postsynaptic density protein-95
- SYN-1:
-
Synapsin-1
- SYP:
-
Synaptophysin
References
Leslie RD, Evans-Molina C, Freund-Brown J, Buzzetti R, Dabelea D, Gillespie KM, Goland R, Jones AG et al (2021) Adult-onset type 1 diabetes: current understanding and challenges. Diabetes Care 44(11):2449–2456. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc21-0770
Shaw JE (2021) Paul Zimmet: a voice for diabetes. Diabetes Care 44(11):2460–2463. https://doi.org/10.2337/dci21-0040
Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, Stein C, Basit A et al (2022) IDF Diabetes Atlas: global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 183:109119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119
Jiao F, Fung CS, Wan YF, McGhee SM, Wong CK, Dai D, Kwok R, Lam CL (2016) Effectiveness of the multidisciplinary Risk Assessment and Management Program for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus (RAMP-DM) for diabetic microvascular complications: a population-based cohort study. Diabetes Metab 42(6):424–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabet.2016.07.030
Maccari R, Del Corso A, Paoli P, Adornato I, Lori G, Balestri F, Cappiello M, Nass A et al (2018) An investigation on 4-thiazolidinone derivatives as dual inhibitors of aldose reductase and protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B, in the search for potential agents for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 28(23–24):3712–3720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.10.024
Rom S, Zuluaga-Ramirez V, Gajghate S, Seliga A, Winfield M, Heldt NA, Kolpakov MA, Bashkirova YV et al (2019) Hyperglycemia-driven neuroinflammation compromises BBB leading to memory loss in both diabetes mellitus (DM) type 1 and type 2 mouse models. Mol Neurobiol 56(3):1883–1896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1195-5
Dove A, Shang Y, Xu W, Grande G, Laukka EJ, Fratiglioni L, Marseglia A (2021) The impact of diabetes on cognitive impairment and its progression to dementia. Alzheimers Dement 17(11):1769–1778. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.12482
Gong J, Harris K, Hackett M, Peters SAE, Brodaty H, Cooper M, Hamet P, Harrap S et al (2021) Sex differences in risk factors for cognitive decline and dementia, including death as a competing risk, in individuals with diabetes: results from the ADVANCE trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 23(8):1775–1785. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.14391
Jacobson AM, Ryan CM, Braffett BH, Gubitosi-Klug RA, Lorenzi GM, Luchsinger JA, Trapani VR, Bebu I et al (2021) Cognitive performance declines in older adults with type 1 diabetes: results from 32 years of follow-up in the DCCT and EDIC Study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 9(7):436–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-8587(21)00086-3
Akimoto H, Negishi A, Oshima S, Wakiyama H, Okita M, Horii N, Inoue N, Ohshima S et al (2020) Antidiabetic drugs for the risk of Alzheimer disease in patients with type 2 DM using FAERS. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen 35:1533317519899546. https://doi.org/10.1177/1533317519899546
He Z, Han S, Zhu H, Hu X, Li X, Hou C, Wu C, Xie Q et al (2020) The protective effect of vanadium on cognitive impairment and the neuropathology of Alzheimer’s disease in APPSwe/PS1dE9 mice. Front Mol Neurosci 13:21. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2020.00021
Park S, Kim DS, Kang S, Moon NR (2013) beta-Amyloid-induced cognitive dysfunction impairs glucose homeostasis by increasing insulin resistance and decreasing beta-cell mass in non-diabetic and diabetic rats. Metabolism 62(12):1749–1760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2013.08.007
Datusalia AK, Sharma SS (2014) Amelioration of diabetes-induced cognitive deficits by GSK-3beta inhibition is attributed to modulation of neurotransmitters and neuroinflammation. Mol Neurobiol 50(2):390–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8632-x
Xu T, Liu J, Li XR, Yu Y, Luo X, Zheng X, Cheng Y, Yu PQ et al (2021) The mTOR/NF-kappaB pathway mediates neuroinflammation and synaptic plasticity in diabetic encephalopathy. Mol Neurobiol 58(8):3848–3862. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02390-1
Feng H, Zhu X, Tang Y, Fu S, Kong B, Liu X (2021) Astragaloside IV ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome‑mediated inflammation. Int J Mol Med 48(2). https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2021.4996
Oh S, Yang J, Park C, Son K, Byun K (2021) Dieckol attenuated glucocorticoid-induced muscle atrophy by decreasing NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis. Int J Mol Sci 22(15). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158057
Hu T, Lu XY, Shi JJ, Liu XQ, Chen QB, Wang Q, Chen YB, Zhang SJ (2020) Quercetin protects against diabetic encephalopathy via SIRT1/NLRP3 pathway in db/db mice. J Cell Mol Med 24(6):3449–3459. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15026
Liu P, Li H, Wang Y, Su X, Li Y, Yan M, Ma L, Che H (2020) Harmine ameliorates cognitive impairment by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and enhancing the BDNF/TrkB signaling pathway in STZ-induced diabetic rats. Front Pharmacol 11:535. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00535
Ye T, Meng X, Wang R, Zhang C, He S, Sun G, Sun X (2018) Gastrodin alleviates cognitive dysfunction and depressive-like behaviors by inhibiting ER stress and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in db/db mice. Int J Mol Sci 19(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123977
Kuwar R, Rolfe A, Di L, Blevins H, Xu Y, Sun X, Bloom GS, Zhang S et al (2021) A novel inhibitor targeting NLRP3 inflammasome reduces neuropathology and improves cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice. J Alzheimers Dis 82(4):1769–1783. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-210400
Nguyen DT, To DC, Tran TT, Tran MH, Nguyen PH (2021) PTP1B and alpha-glucosidase inhibitors from Selaginella rolandi-principis and their glucose uptake stimulation. J Nat Med 75(1):186–193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-020-01448-z
Byeon HJ, Kim JY, Ko J, Lee EJ, Don K, Yoon JS (2020) Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B as a therapeutic target for Graves’ orbitopathy in an in vitro model. PLoS ONE 15(8):e0237015. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0237015
Lee S, Kim S, Kang HY, Lim HR, Kwon Y, Jo M, Jeon YM, Kim SR et al (2020) The overexpression of TDP-43 in astrocytes causes neurodegeneration via a PTP1B-mediated inflammatory response. J Neuroinflammation 17(1):299. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-020-01963-6
Song GJ, Jung M, Kim JH, Park H, Rahman MH, Zhang S, Zhang ZY, Park DH et al (2016) A novel role for protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B as a positive regulator of neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation 13(1):86. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-016-0545-3
Mendes NF, Castro G, Guadagnini D, Tobar N, Cognuck SQ, Elias LL, Boer PA, Prada PO (2017) Knocking down amygdalar PTP1B in diet-induced obese rats improves insulin signaling/action, decreases adiposity and may alter anxiety behavior. Metabolism 70:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2017.01.029
Wang H, Sun X, Zhang N, Ji Z, Ma Z, Fu Q, Qu R, Ma S (2017) Ferulic acid attenuates diabetes-induced cognitive impairment in rats via regulation of PTP1B and insulin signaling pathway. Physiol Behav 182:93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2017.10.001
Ha MT, Shrestha S, Tran TH, Kim JA, Woo MH, Choi JS, Min BS (2020) Inhibition of PTP1B by farnesylated 2-arylbenzofurans isolated from Morus alba root bark: unraveling the mechanism of inhibition based on in vitro and in silico studies. Arch Pharm Res 43(9):961–975. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-020-01269-4
Bansal S, Mahendiratta S, Agrawal M, Kumar S, Sharma AR, Garg N, Joshi R, Sarma P et al (2021) Role of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitor in central insulin resistance and associated cognitive deficits. Brain Res Bull 171:113–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2021.02.026
Yang JB, Ye F, Tian JY, Song YF, Gao HY, Liu Y, Wang Q, Wang Y et al (2020) Multiflorumisides HK, stilbene glucosides isolated from Polygonum multiflorum and their in vitro PTP1B inhibitory activities. Fitoterapia 146:104703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2020.104703
Qin Z, Pandey NR, Zhou X, Stewart CA, Hari A, Huang H, Stewart AF, Brunel JM et al (2015) Functional properties of claramine: a novel PTP1B inhibitor and insulin-mimetic compound. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 458(1):21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.01.040
Zhang R, Liao W, Wu K, Hua L, Wu M, Li C, Cai F (2022) Matrine alleviates spatial learning and memory impairment in diabetic mice by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and through modulation of PK2/PKRs pathway. Neurochem Int 154:105289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2022.105289
Dodd GT, Xirouchaki CE, Eramo M, Mitchell CA, Andrews ZB, Henry BA, Cowley MA, Tiganis T (2019) Intranasal targeting of hypothalamic PTP1B and TCPTP reinstates leptin and insulin sensitivity and promotes weight loss in obesity. Cell Rep 28(11):2905-2922.e2905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.08.019
Denver P, Gault VA, McClean PL (2018) Sustained high-fat diet modulates inflammation, insulin signalling and cognition in mice and a modified xenin peptide ameliorates neuropathology in a chronic high-fat model. Diabetes Obes Metab 20(5):1166–1175. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.13210
Maugard M, Doux C, Bonvento G (2019) A new statistical method to analyze Morris Water Maze data using Dirichlet distribution. F1000Res 8:1601. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.20072.2
Zhou T, Liu L, Wang Q, Gao Y (2020) Naringenin alleviates cognition deficits in high-fat diet-fed SAMP8 mice. J Food Biochem 44(9):e13375. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.13375
Song Y, Zhang F, Ying C, Kumar KA, Zhou X (2017) Inhibition of NF-kappaB activity by aminoguanidine alleviates neuroinflammation induced by hyperglycemia. Metab Brain Dis 32(5):1627–1637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0013-5
Lees EK, Krol E, Shearer K, Mody N, Gettys TW, Delibegovic M (2015) Effects of hepatic protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B and methionine restriction on hepatic and whole-body glucose and lipid metabolism in mice. Metabolism 64(2):305–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2014.10.038
Dos Santos MM, Rodrigues GCS, de Sousa NF, Scotti MT, Scotti L, Mendonça-Junior FJB (2020) Identification of new targets and the virtual screening of lignans against Alzheimer’s disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020:3098673. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3098673
Vieira MN, Silva Lyra E, NM, Ferreira ST, De Felice FG, (2017) Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B (PTP1B): a potential target for alzheimer’s therapy? Front Aging Neurosci 9:7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2017.00007
Xu K-K, Pan B-Y, Wang Y-Y, Ren Q-Q, Li C (2020) Roles of the PTP61F gene in regulating energy metabolism of Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Front Physiol 11:1071. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.01071
Bourebaba L, Kornicka-Garbowska K, Al Naem M, Rocken M, Lyczko J, Marycz K (2021) MSI-1436 improves EMS adipose derived progenitor stem cells in the course of adipogenic differentiation through modulation of ER stress, apoptosis, and oxidative stress. Stem Cell Res Ther 12(1):97. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-02102-x
Nasseri B, Zareian P, Alizade H (2020) Apelin attenuates streptozotocin-induced learning and memory impairment by modulating necroptosis signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 84:106546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106546
Tian H, Ding N, Guo M, Wang S, Wang Z, Liu H, Yang J, Li Y, et al (2019) Analysis of learning and memory ability in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model using the Morris water maze. J Vis Exp (152). https://doi.org/10.3791/60055
Maan HB, Meo SA, Rouq FA, Meo IMU (2021) Impact of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) on cognitive functions in type 2 diabetic patients. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 25(19):5978–5985. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202110_26875
Liu T, Bai Y, Ma L, Ma X, Wei W, Zhang J, Roberts N, Wang M (2020) Altered effective connectivity of bilateral hippocampus in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front Neurosci 14:657. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.00657
Thomas J, Garg ML, Smith DW (2013) Altered expression of histone and synaptic plasticity associated genes in the hippocampus of streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Metab Brain Dis 28(4):613–618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9418-y
Alkan I, Altunkaynak BZ, Gultekin GI, Baycu C (2021) Hippocampal neural cell loss in high-fat diet-induced obese rats-exploring the protein networks, ultrastructure, biochemical and bioinformatical markers. J Chem Neuroanat 114:101947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchemneu.2021.101947
Zhang X, Zhu Y, Zhou Y, Fei B (2020) Activation of Nrf2 signaling by apelin attenuates renal ischemia reperfusion injury in diabetic rats. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 13:2169–2177. https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S246743
Bliss TV, Collingridge GL (1993) A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361(6407):31–39. https://doi.org/10.1038/361031a0
Xiang Q, Zhang J, Li CY, Wang Y, Zeng MJ, Cai ZX, Tian RB, Jia W et al (2015) Insulin resistance-induced hyperglycemia decreased the activation of Akt/CREB in hippocampus neurons: molecular evidence for mechanism of diabetes-induced cognitive dysfunction. Neuropeptides 54:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npep.2015.08.009
Hull C, Dekeryte R, Buchanan H, Kamli-Salino S, Robertson A, Delibegovic M, Platt B (2020) NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition with MCC950 improves insulin sensitivity and inflammation in a mouse model of frontotemporal dementia. Neuropharmacology 180:108305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108305
Li Q, Leng K, Liu Y, Sun H, Gao J, Ren Q, Zhou T, Dong J et al (2020) The impact of hyperglycaemia on PKM2-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome/stress granule signalling in macrophages and its correlation with plaque vulnerability: an in vivo and in vitro study. Metabolism: Clin Exp 107:154231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154231
Wu XL, Deng MZ, Gao ZJ, Dang YY, Li YC, Li CW (2020) Neferine alleviates memory and cognitive dysfunction in diabetic mice through modulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway and alleviation of endoplasmic-reticulum stress. Int Immunopharmacol 84:106559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106559
Li CW, Deng MZ, Gao ZJ, Dang YY, Zheng GD, Yang XJ, Chao YX, Cai YF et al (2020) Effects of compound K, a metabolite of ginsenosides, on memory and cognitive dysfunction in db/db mice involve the inhibition of ER stress and the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Food Funct 11(5):4416–4427. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9fo02602a
Cai W, Zhang X, Batista TM, Garcia-Martin R, Softic S, Wang G, Ramirez AK, Konishi M et al (2021) Peripheral insulin regulates a broad network of gene expression in hypothalamus, hippocampus, and nucleus accumbens. Diabetes 70(8):1857–1873. https://doi.org/10.2337/db20-1119
Wang S, Zhou SL, Min FY, Ma JJ, Shi XJ, Bereczki E, Wu J (2014) mTOR-mediated hyperphosphorylation of tau in the hippocampus is involved in cognitive deficits in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Metab Brain Dis 29(3):729–736. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9528-1
Barone E, Di Domenico F, Perluigi M, Butterfield DA (2021) The interplay among oxidative stress, brain insulin resistance and AMPK dysfunction contribute to neurodegeneration in type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer disease. Free Radic Biol Med 176:16–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.09.006
Rahmati M, Keshvari M, Mirnasouri R, Chehelcheraghi F (2021) Exercise and Urtica dioica extract ameliorate hippocampal insulin signaling, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and cognitive function in STZ-induced diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother 139:111577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111577
Wang Q, Hu J, Liu Y, Li J, Liu B, Li M, Lou S (2019) Aerobic exercise improves synaptic-related proteins of diabetic rats by inhibiting FOXO1/NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammatory signaling pathway and ameliorating PI3K/Akt insulin signaling pathway. J Mol Neurosci 69(1):28–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01302-2
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81870576) to FC, Hubei University of Science and Technology (2021WG01) to FC, and Department of Education of Hubei Province (T201921, B2021225) to FC and WL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MW: writing original draft, methodology, formal analysis. WL: methodology, formal analysis, funding acquisition. RZ: formal analysis, project administration. YG: methodology, performed immunofluorescence examination. TC: performed immunofluorescence examination. LH: performed Morris water maze test. FC: project administration, writing original draft, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Hubei University of Science and Technology (Approval No: 2018–03-019).
Consent for Publication
The consent to publish this manuscript has been obtained from all authors.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• The protein expressions of PTP1B increased in hippocampal CA1, CA3, and PFC regions of diabetic mice.
• PTP1B inhibitor claramine alleviated DM-induced spatial learning and memory impairment in mice.
• Inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome and regulation of insulin signaling pathway were involved in the neuroprotective molecular mechanism of claramine.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, M., Liao, W., Zhang, R. et al. PTP1B Inhibitor Claramine Rescues Diabetes-Induced Spatial Learning and Memory Impairment in Mice. Mol Neurobiol 60, 524–544 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-03079-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-03079-9