Abstract
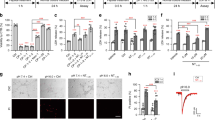
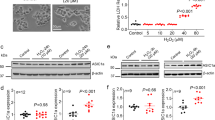
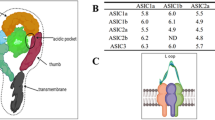
Tissue acidosis is a common feature in many pathological conditions. Activation of acid-sensing ion channel 1a (ASIC1a) plays a key role in acidosis-mediated neurotoxicity. Protein kinase C (PKC) activity has been proved to be associated with many physiological processes and pathological conditions; however, whether PKC activation regulates ASIC1a protein expression and channel function remains ill defined. In this study, we demonstrated that treatment with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA, a PKC activator) for 6 h significantly increased ASIC1a protein expression and ASIC currents in NS20Y cells, a neuronal cell line, and in primary cultured mouse cortical neurons. In contrast, treatment with Calphostin C (a nonselective PKC inhibitor) for 6 h or longer decreased ASIC1a protein expression and ASIC currents. Similar to Calphostin C, PKC α and βI inhibitor Go6976 exposure also reduced ASIC1a protein expression. The reduction in ASIC1a protein expression by PKC inhibition involves a change in ASIC1a protein degradation, which is mediated by ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS)-dependent degradation pathway. In addition, we showed that PKC regulation of ASIC1a protein expression involves NF-κB signaling pathway. Consistent with their effects on ASIC1a protein expression and channel function, PKC inhibition protected NS20Y cells against acidosis-induced cytotoxicity, while PKC activation potentiated acidosis-induced cells injury. Together, these results indicate that ASIC1a protein expression and channel function are closely regulated by the activity of protein kinase C and its downstream signaling pathway(s).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Verri WA Jr, Chiu IM (2017) Nociceptor sensory neuron-immune interactions in pain and inflammation. Trends Immunol 38(1):5–19
Pignataro G, Simon RP, Xiong ZG (2007) Prolonged activation of ASIC1a and the time window for neuroprotection in cerebral ischaemia. Brain 130(Pt 1):151–158
Kim EK, Park JM, Lim S, Choi JW, Kim HS, Seok H, Seo JK, Oh K et al (2011) Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase is essential for lysophosphatidic acid-induced cell migration in ovarian cancer cells. J Biol Chem 286(27):24036–24045
Suetrong B, Walley KR (2016) Lactic acidosis in sepsis: it’s not all anaerobic: implications for diagnosis and management. Chest 149(1):252–261
Nedergaard M, Kraig RP, Tanabe J, Pulsinelli WA (1991) Dynamics of interstitial and intracellular pH in evolving brain infarct. Am J Phys 260(3 Pt 2):R581–R588
Rehncrona S (1985) Brain acidosis. Ann Emerg Med 14(8):770–776
Siesjo BK, Katsura KI, Kristian T, Li PA, Siesjo P (1996) Molecular mechanisms of acidosis-mediated damage. Acta Neurochir Suppl 66:8–14
Bianchi L, Driscoll M (2002) Protons at the gate: DEG/ENaC ion channels help us feel and remember. Neuron 34(3):337–340
Xiong ZG, Zhu XM, Chu XP, Minami M, Hey J, Wei WL, MacDonald JF, Wemmie JA et al (2004) Neuroprotection in ischemia: blocking calcium-permeable acid-sensing ion channels. Cell 118(6):687–698
Lingueglia E (2007) Acid-sensing ion channels in sensory perception. J Biol Chem 282(24):17325–17329
Wemmie JA, Coryell MW, Askwith CC, Lamani E, Leonard AS, Sigmund CD, Welsh MJ (2004) Overexpression of acid-sensing ion channel 1a in transgenic mice increases acquired fear-related behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101(10):3621–3626
Gao J, Duan B, Wang DG, Deng XH, Zhang GY, Xu L, Xu TL (2005) Coupling between NMDA receptor and acid-sensing ion channel contributes to ischemic neuronal death. Neuron 48(4):635–646
Sherwood TW, Askwith CC (2009) Dynorphin opioid peptides enhance acid-sensing ion channel 1a activity and acidosis-induced neuronal death. J Neurosci 29(45):14371–14380
Ardito F, Giuliani M, Perrone D, Troiano G, Lo Muzio L (2017) The crucial role of protein phosphorylation in cell signaling and its use as targeted therapy (review). Int J Mol Med 40(2):271–280
Lin Y, Jover-Mengual T, Wong J, Bennett MV, Zukin RS (2006) PSD-95 and PKC converge in regulating NMDA receptor trafficking and gating. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103(52):19902–19907
Kobayashi H, Shiraishi S, Yanagita T, Yokoo H, Yamamoto R, Minami S, Saitoh T, Wada A (2002) Regulation of voltage-dependent sodium channel expression in adrenal chromaffin cells: involvement of multiple calcium signaling pathways. Ann N Y Acad Sci 971:127–134
Bashari E, Qadri YJ, Zhou ZH, Kapoor N, Anderson SJ, Meltzer RH, Fuller CM, Benos DJ (2009) Two PKC consensus sites on human acid-sensing ion channel 1b differentially regulate its function. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 296(2):C372–C384
Ogiwara T, Negishi T, Chik CL, Ho AK (1998) Differential effects of two protein kinase C inhibitors, calphostin C and Go6976, on pineal cyclic nucleotide accumulation. J Neurochem 71(4):1405–1412
Berdiev BK, Xia J, Jovov B, Markert JM, Mapstone TB, Gillespie GY, Fuller CM, Bubien JK et al (2002) Protein kinase C isoform antagonism controls BNaC2 (ASIC1) function. J Biol Chem 277(48):45734–45740
Leonard AS, Yermolaieva O, Hruska-Hageman A, Askwith CC, Price MP, Wemmie JA, Welsh MJ (2003) cAMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation of the acid-sensing ion channel-1 regulates its binding to the protein interacting with C-kinase-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100(4):2029–2034
Chai S, Li M, Lan J, Xiong ZG, Saugstad JA, Simon RP (2007) A kinase-anchoring protein 150 and calcineurin are involved in regulation of acid-sensing ion channels ASIC1a and ASIC2a. J Biol Chem 282(31):22668–22677
Inoue K, Branigan D, Xiong ZG (2010) Zinc-induced neurotoxicity mediated by transient receptor potential melastatin 7 channels. J Biol Chem 285(10):7430–7439
Leng TD, Si HF, Li J, Yang T, Zhu M, Wang B, Simon RP, Xiong ZG (2016) Amiloride analogs as ASIC1a inhibitors. CNS Neurosci Ther 22(6):468–476
Grouse LD, Schrier BK, Letendre CH, Zubairi MY, Nelson PG (1980) Neuroblastoma differentiation involves both the disappearance of old and the appearance of new poly(A)+ messenger RNA sequences in polyribosomes. J Biol Chem 255(9):3871–3877
O'Bryant Z, Leng T, Liu M, Inoue K, Vann KT, Xiong ZG (2016) Acid sensing ion channels (ASICs) in NS20Y cells - potential role in neuronal differentiation. Mol Brain 9(1):68
Li MH, Leng TD, Feng XC, Yang T, Simon RP, Xiong ZG (2016) Modulation of acid-sensing ion channel 1a by intracellular pH and its role in ischemic stroke. J Biol Chem 291(35):18370–18383
Leng TD, Lin J, Sun HW, Zeng Z, O'Bryant Z, Inoue K, Xiong ZG (2015) Local anesthetic lidocaine inhibits TRPM7 current and TRPM7-mediated zinc toxicity. CNS Neurosci Ther 21(1):32–39
Inoue K, Leng T, Yang T, Zeng Z, Ueki T, Xiong ZG (2016) Role of serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinases in stroke. J Neurochem 138(2):354–361
Zhou RP, Leng TD, Yang T, Chen FH, Xiong ZG (2019) Acute ethanol exposure promotes autophagy-lysosome pathway-dependent ASIC1a protein degradation and protects against acidosis-induced neurotoxicity. Mol Neurobiol 56(5):3326–3340
Jin W, Shen C, Jing L, Zha XM, Xia J (2010) PICK1 regulates the trafficking of ASIC1a and acidotoxicity in a BAR domain lipid binding-dependent manner. Mol Brain 3:39
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9(7):671–675
Nakamura J (2008) Protein kinase CbetaI interacts with the beta1-adrenergic signaling pathway to attenuate lipolysis in rat adipocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1781(5):277–281
Leithe E, Cruciani V, Sanner T, Mikalsen SO, Rivedal E (2003) Recovery of gap junctional intercellular communication after phorbol ester treatment requires proteasomal degradation of protein kinase C. Carcinogenesis 24(7):1239–1245
Steinberg SF (2008) Structural basis of protein kinase C isoform function. Physiol Rev 88(4):1341–1378
Reyland ME (2009) Protein kinase C isoforms: multi-functional regulators of cell life and death. Front Biosci 14:2386–2399.
Martiny-Baron G, Kazanietz MG, Mischak H, Blumberg PM, Kochs G, Hug H, Marme D, Schachtele C (1993) Selective inhibition of protein kinase C isozymes by the indolocarbazole Go 6976. J Biol Chem 268(13):9194–9197
Koivunen J, Aaltonen V, Koskela S, Lehenkari P, Laato M, Peltonen J (2004) Protein kinase C alpha/beta inhibitor Go6976 promotes formation of cell junctions and inhibits invasion of urinary bladder carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 64(16):5693–5701
Li M, Inoue K, Branigan D, Kratzer E, Hansen JC, Chen JW, Simon RP, Xiong ZG (2010) Acid-sensing ion channels in acidosis-induced injury of human brain neurons. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 30(6):1247–1260
Rai Y, Pathak R, Kumari N, Sah DK, Pandey S, Kalra N, Soni R, Dwarakanath BS et al (2018) Mitochondrial biogenesis and metabolic hyperactivation limits the application of MTT assay in the estimation of radiation induced growth inhibition. Sci Rep 8(1):1531.
Wang YZ, Wang JJ, Huang Y, Liu F, Zeng WZ, Li Y, Xiong ZG, Zhu MX et al (2015) Tissue acidosis induces neuronal necroptosis via ASIC1a channel independent of its ionic conduction. eLife 4:e05682
Eskelinen EL, Saftig P (2009) Autophagy: a lysosomal degradation pathway with a central role in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1793(4):664–673
Ciechanover A (2017) Intracellular protein degradation:from a vague idea thru the lysosome and the ubiquitin-proteasome system and onto human diseases and drug targeting. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 30(4):341–355
Pan T, Kondo S, Le W, Jankovic J (2008) The role of autophagy-lysosome pathway in neurodegeneration associated with Parkinson’s disease. Brain 131(Pt 8):1969–1978
Teng AC, Miyake T, Yokoe S, Zhang L, Rezende LM Jr, Sharma P, MacLennan DH, Liu PP et al (2015) Metformin increases degradation of phospholamban via autophagy in cardiomyocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112(23):7165–7170
Mut M, Amos S, Hussaini IM (2010) PKC alpha phosphorylates cytosolic NF-kappaB/p65 and PKC delta delays nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB/p65 in U1242 glioblastoma cells. Turk Neurosurg 20(3):277–285
Xia J, Matsuhashi S, Hamajima H, Iwane S, Takahashi H, Eguchi Y, Mizuta T, Fujimoto K et al (2012) The role of PKC isoforms in the inhibition of NF-kappaB activation by vitamin K2 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Nutr Biochem 23(12):1668–1675
Moscat J, Diaz-Meco MT, Rennert P (2003) NF-kappaB activation by protein kinase C isoforms and B-cell function. EMBO Rep 4(1):31–36
Pfeifhofer C, Kofler K, Gruber T, Tabrizi NG, Lutz C, Maly K, Leitges M, Baier G (2003) Protein kinase C theta affects Ca2+ mobilization and NFAT cell activation in primary mouse T cells. J Exp Med 197(11):1525–1535
Krishtal O (2003) The ASICs: signaling molecules? Modulators? Trends Neurosci 26(9):477–483
Wemmie JA, Price MP, Welsh MJ (2006) Acid-sensing ion channels: advances, questions and therapeutic opportunities. Trends Neurosci 29(10):578–586.
Waldmann R, Bassilana F, de Weille J, Champigny G, Heurteaux C, Lazdunski M (1997) Molecular cloning of a non-inactivating proton-gated Na+ channel specific for sensory neurons. J Biol Chem 272(34):20975–20978
Waldmann R, Champigny G, Bassilana F, Heurteaux C, Lazdunski M (1997) A proton-gated cation channel involved in acid-sensing. Nature 386(6621):173–177
Yermolaieva O, Leonard AS, Schnizler MK, Abboud FM, Welsh MJ (2004) Extracellular acidosis increases neuronal cell calcium by activating acid-sensing ion channel 1a. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101(17):6752–6757
Walder RY, Rasmussen LA, Rainier JD, Light AR, Wemmie JA, Sluka KA (2010) ASIC1 and ASIC3 play different roles in the development of hyperalgesia after inflammatory muscle injury. J pain 11(3):210–218
Mazzuca M, Heurteaux C, Alloui A, Diochot S, Baron A, Voilley N, Blondeau N, Escoubas P et al (2007) A tarantula peptide against pain via ASIC1a channels and opioid mechanisms. Nat Neurosci 10(8):943–945.
Pitt D, Werner P, Raine CS (2000) Glutamate excitotoxicity in a model of multiple sclerosis. Nat Med 6(1):67–70
Lossin C, Wang DW, Rhodes TH, Vanoye CG, George AL Jr (2002) Molecular basis of an inherited epilepsy. Neuron 34(6):877–884
Ziemann AE, Allen JE, Dahdaleh NS, Drebot II, Coryell MW, Wunsch AM, Lynch CM, Faraci FM et al (2009) The amygdala is a chemosensor that detects carbon dioxide and acidosis to elicit fear behavior. Cell 139(5):1012–1021
Rosse C, Linch M, Kermorgant S, Cameron AJ, Boeckeler K, Parker PJ (2010) PKC and the control of localized signal dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11(2):103–112
Dowling CM, Kiely PA (2015) Targeting protein kinase C downstream of growth factor and adhesion signalling. Cancers 7(3):1271–1291
Regala RP, Weems C, Jamieson L, Khoor A, Edell ES, Lohse CM, Fields AP (2005) Atypical protein kinase C iota is an oncogene in human non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 65(19):8905–8911
Tabit CE, Shenouda SM, Holbrook M, Fetterman JL, Kiani S, Frame AA, Kluge MA, Held A et al (2013) Protein kinase C-beta contributes to impaired endothelial insulin signaling in humans with diabetes mellitus. Circulation 127(1):86–95
Kim T, Hinton DJ, Choi DS (2011) Protein kinase C-regulated abeta production and clearance. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011:857368
Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T, Sudarsanam S (2002) The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science 298(5600):1912–1934
Kong R, Kang OH, Seo YS, Zhou T, Kim SA, Shin DW, Kwon DY (2018) MAPKs and NF‑κB pathway inhibitory effect of bisdemethoxycurcumin on phorbol‑12‑myristate‑13‑acetate and A23187‑induced inflammation in human mast cells. Mol Med Rep 17(1):630–635
Castagna M, Takai Y, Kaibuchi K, Sano K, Kikkawa U, Nishizuka Y (1982) Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem 257(13):7847–7851
Aley KO, Martin A, McMahon T, Mok J, Levine JD, Messing RO (2001) Nociceptor sensitization by extracellular signal-regulated kinases. J Neurosci 21(17):6933–6939
Perluigi M, Barone E, Di Domenico F, Butterfield DA (2016) Aberrant protein phosphorylation in Alzheimer disease brain disturbs pro-survival and cell death pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta 1862(10):1871–1882
Numann R, Catterall WA, Scheuer T (1991) Functional modulation of brain sodium channels by protein kinase C phosphorylation. Science 254(5028):115–118
Lo CF, Numann R (1999) PKC modulation of minK current involves multiple phosphorylation sites. Ann N Y Acad Sci 868:431–433
Hu ZL, Huang C, Fu H, Jin Y, Wu WN, Xiong QJ, Xie N, Long LH et al (2010) Disruption of PICK1 attenuates the function of ASICs and PKC regulation of ASICs. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 299(6):C1355–C1362
Baron A, Deval E, Salinas M, Lingueglia E, Voilley N, Lazdunski M (2002) Protein kinase C stimulates the acid-sensing ion channel ASIC2a via the PDZ domain-containing protein PICK1. J Biol Chem 277(52):50463–50468
Liu WS, Heckman CA (1998) The sevenfold way of PKC regulation. Cell Signal 10(8):529–542
Hug H, Sarre TF (1993) Protein kinase C isoenzymes: divergence in signal transduction? Biochem J 291(Pt 2):329–343
Liu M, Clarke CJ, Salama MF, Choi YJ, Obeid LM, Hannun YA (2017) Co-ordinated activation of classical and novel PKC isoforms is required for PMA-induced mTORC1 activation. PLoS One 12(9):e0184818
Campbell DS, Holt CE (2001) Chemotropic responses of retinal growth cones mediated by rapid local protein synthesis and degradation. Neuron 32(6):1013–1026
Eaton DC, Malik B, Bao HF, Yu L, Jain L (2010) Regulation of epithelial sodium channel trafficking by ubiquitination. Proc Am Thorac Soc 7(1):54–64
Baldwin AS Jr (1996) The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol 14:649–683
Durand JK, Baldwin AS (2017) Targeting IKK and NF-kappaB for therapy. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol 107:77–115
Luo JL, Kamata H, Karin M (2005) IKK/NF-kappaB signaling: balancing life and death--a new approach to cancer therapy. J Clin Invest 115(10):2625–2632
O'Neill LA, Kaltschmidt C (1997) NF-kappa B: a crucial transcription factor for glial and neuronal cell function. Trends in neurosciences 20(6):252–258
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ling Zhang, a visiting scholar, conducted most of the experiments, analyzed the results, and wrote the paper. Tao Yang performed culture of mouse cortical neurons. Zhi-Gang Xiong, Tian-Dong Leng, and Jun Li designed the experiments for the project. Zhi-Gang Xiong and Tian-Dong Leng wrote the paper with Ling Zhang.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 496 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Leng, TD., Yang, T. et al. Protein Kinase C Regulates ASIC1a Protein Expression and Channel Function via NF-kB Signaling Pathway. Mol Neurobiol 57, 4754–4766 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-020-02056-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-020-02056-4