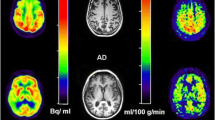
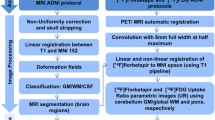
Abstract
We investigated the association between amyloid-β deposition and white matter (WM) integrity as a determinant of brain glucose hypometabolism across the Alzheimer’s disease (AD) spectrum. We assessed ninety-six subjects (27 cognitively normal, 49 mild cognitive impairment, and 20 AD dementia) who underwent [18F]FDG and [18F]Florbetapir positron emission tomography (PET) as well as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with diffusion tensor imaging. Among the regions with reduced fractional anisotropy (FA) in the AD group, we selected a voxel of interest in the angular bundle bilaterally for subsequent analyses. Using voxel-based interaction models at voxel level, we tested whether the regional hypometabolism is associated with FA in the angular bundle and regional amyloid-β deposition. In the AD patients, [18F]FDG hypometabolism in the striatum, mesiobasal temporal, orbitofrontal, precuneus, and cingulate cortices were associated with the interaction between high levels of [18F]Florbetapir standard uptake value ratios (SUVR) in these regions and low FA in the angular bundle. We found that the interaction between, rather than the independent effects of, high levels of amyloid-β deposition and WM integrity disruption determined limbic hypometabolism in patients with AD. This finding highlights a more integrative model for AD, where the interaction between partially independent processes determines the glucose hypometabolism.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- ADNI:
-
Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative
- CDR:
-
clinical dementia rating
- CN:
-
cognitive normal
- FA:
-
fractional anisotropy
- LAB:
-
left angular bundle
- [18F]FDG:
-
[18F]fluorodeoxyglucose
- MCI:
-
mild cognitive impairment
- MMSE:
-
mini-mental state examination
- MRI:
-
magnetic resonance imaging
- RAB:
-
right angular bundle
- SD:
-
standard deviation
- SUVR:
-
standardized uptake value ratio
- VOI:
-
voxel of interest; WM white matter
References
Alzheimer's A (2016) 2016 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 12(4):459–509
Hardy J, Selkoe DJ (2002) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297(5580):353–356. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1072994
Jack CR Jr, Knopman DS, Jagust WJ, Petersen RC, Weiner MW, Aisen PS, Shaw LM, Vemuri P et al (2013) Tracking pathophysiological processes in Alzheimer’s disease: an updated hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers. Lancet Neurol 12(2):207–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70291-0
Sperling RA, Aisen PS, Beckett LA, Bennett DA, Craft S, Fagan AM, Iwatsubo T, Jack CR Jr et al (2011) Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 7(3):280–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.003
Altmann A, Ng B, Landau SM, Jagust WJ, Greicius MD, Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging I (2015) Regional brain hypometabolism is unrelated to regional amyloid plaque burden. Brain 138(Pt 12):3734–3746. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awv278
Pascoal TA, Mathotaarachchi S, Mohades S, Benedet AL, Chung CO, Shin M, Wang S, Beaudry T et al (2016) Amyloid-beta and hyperphosphorylated tau synergy drives metabolic decline in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Psychiatry 22:306–311. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.37
Cipriani G, Dolciotti C, Picchi L, Bonuccelli U (2011) Alzheimer and his disease: a brief history. Neurol Sci 32(2):275–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-010-0454-7
Hardy JA, Higgins GA (1992) Alzheimer’s disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science 256(5054):184–185
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82(4):239–259
Rose SE, Chen F, Chalk JB, Zelaya FO, Strugnell WE, Benson M, Semple J, Doddrell DM (2000) Loss of connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease: an evaluation of white matter tract integrity with colour coded MR diffusion tensor imaging. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 69(4):528–530
Bozzali M, Falini A, Franceschi M, Cercignani M, Zuffi M, Scotti G, Comi G, Filippi M (2002) White matter damage in Alzheimer’s disease assessed in vivo using diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 72(6):742–746
de la Monte SM (1989) Quantitation of cerebral atrophy in preclinical and end-stage Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 25(5):450–459. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410250506
Medina D, DeToledo-Morrell L, Urresta F, Gabrieli JD, Moseley M, Fleischman D, Bennett DA, Leurgans S et al (2006) White matter changes in mild cognitive impairment and AD: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Neurobiol Aging 27(5):663–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.03.026
Zhang Y, Schuff N, Jahng GH, Bayne W, Mori S, Schad L, Mueller S, Du AT et al (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging of cingulum fibers in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease. Neurology 68(1):13–19. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000250326.77323.01
Nowrangi MA, Lyketsos CG, Leoutsakos JM, Oishi K, Albert M, Mori S, Mielke MM (2013) Longitudinal, region-specific course of diffusion tensor imaging measures in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement 9(5):519–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2012.05.2186
Pierpaoli C, Basser PJ (1996) Toward a quantitative assessment of diffusion anisotropy. Magn Reson Med 36(6):893–906
Le Bihan D, Mangin JF, Poupon C, Clark CA, Pappata S, Molko N, Chabriat H (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging: concepts and applications. J Magn Reson Imaging 13(4):534–546
Chua TC, Wen W, Slavin MJ, Sachdev PS (2008) Diffusion tensor imaging in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: a review. Curr Opin Neurol 21(1):83–92. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0b013e3282f4594b
Bartzokis G, Cummings JL, Sultzer D, Henderson VW, Nuechterlein KH, Mintz J (2003) White matter structural integrity in healthy aging adults and patients with Alzheimer disease: a magnetic resonance imaging study. Arch Neurol 60(3):393–398
Fellgiebel A, Muller MJ, Wille P, Dellani PR, Scheurich A, Schmidt LG, Stoeter P (2005) Color-coded diffusion-tensor-imaging of posterior cingulate fiber tracts in mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging 26(8):1193–1198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.11.006
Reisberg B, Franssen EH, Hasan SM, Monteiro I, Boksay I, Souren LE, Kenowsky S, Auer SR et al (1999) Retrogenesis: clinical, physiologic, and pathologic mechanisms in brain aging, Alzheimer’s and other dementing processes. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 249(Suppl 3):28–36
Brun A, Gustafson L, Englund E (1990) Subcortical pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Adv Neurol 51:73–77
Schilling LP, Leuzy A, Zimmer ER, Gauthier S, Rosa-Neto P (2014) Nonamyloid PET biomarkers and Alzheimer ’ s disease : current and future perspectives. Future Neurol 9(6):597–613
Schilling LP, Zimmer ER, Shin M, Leuzy A, Pascoal TA, Benedet AL, Borelli WV, Palmini A et al (2016) Imaging Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology with PET. Dement Neuropsychol 10(2):79–90
Meguro K, Blaizot X, Kondoh Y, Le Mestric C, Baron JC, Chavoix C (1999) Neocortical and hippocampal glucose hypometabolism following neurotoxic lesions of the entorhinal and perirhinal cortices in the non-human primate as shown by PET. Implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 122(Pt 8):1519–1531
Forster S, Grimmer T, Miederer I, Henriksen G, Yousefi BH, Graner P, Wester HJ, Forstl H et al (2012) Regional expansion of hypometabolism in Alzheimer’s disease follows amyloid deposition with temporal delay. Biol Psychiatry 71(9):792–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.04.023
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA work group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 34(7):939–944
Mathotaarachchi S, Wang S, Shin M, Pascoal TA, Benedet AL, Kang MS, Beaudry T, Fonov VS et al (2016) VoxelStats: a MATLAB package for multi-modal voxel-wise brain image analysis. Front Neuroinform 10:20. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2016.00020
Hachinski VC, Iliff LD, Zilhka E, Du Boulay GH, McAllister VL, Marshall J, Russell RW, Symon L (1975) Cerebral blood flow in dementia. Arch Neurol 32(9):632–637
Benjamini; Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B 57(1):289–300
Duyckaerts C (2011) Tau pathology in children and young adults: can you still be unconditionally baptist? Acta Neuropathol 121(2):145–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-010-0794-7
Mesulam MM (1999) Neuroplasticity failure in Alzheimer’s disease: bridging the gap between plaques and tangles. Neuron 24(3):521–529
Small SA, Duff K (2008) Linking Abeta and tau in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease: a dual pathway hypothesis. Neuron 60(4):534–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.11.007
Mielke MM, Kozauer NA, Chan KC, George M, Toroney J, Zerrate M, Bandeen-Roche K, Wang MC et al (2009) Regionally-specific diffusion tensor imaging in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage 46(1):47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.01.054
Agosta F, Pievani M, Sala S, Geroldi C, Galluzzi S, Frisoni GB, Filippi M (2011) White matter damage in Alzheimer disease and its relationship to gray matter atrophy. Radiology 258(3):853–863. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.10101284
Rowley J, Fonov V, Wu O, Eskildsen SF, Schoemaker D, Wu L, Mohades S, Shin M et al (2013) White matter abnormalities and structural hippocampal disconnections in amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 8(9):e74776. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0074776
Salat DH, Tuch DS, van der Kouwe AJ, Greve DN, Pappu V, Lee SY, Hevelone ND, Zaleta AK et al (2010) White matter pathology isolates the hippocampal formation in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 31(2):244–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.03.013
Kochunov P, Ramage AE, Lancaster JL, Robin DA, Narayana S, Coyle T, Royall DR, Fox P (2009) Loss of cerebral white matter structural integrity tracks the gray matter metabolic decline in normal aging. NeuroImage 45(1):17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.11.010
Bozoki AC, Korolev IO, Davis NC, Hoisington LA, Berger KL (2012) Disruption of limbic white matter pathways in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: a DTI/FDG-PET study. Hum Brain Mapp 33(8):1792–1802. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.21320
Kantarci K, Schwarz CG, Reid RI, Przybelski SA, Lesnick TG, Zuk SM, Senjem ML, Gunter JL et al (2014) White matter integrity determined with diffusion tensor imaging in older adults without dementia: influence of amyloid load and neurodegeneration. JAMA Neurol 71(12):1547–1554. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.1482
Yakushev I, Schreckenberger M, Muller MJ, Schermuly I, Cumming P, Stoeter P, Gerhard A, Fellgiebel A (2011) Functional implications of hippocampal degeneration in early Alzheimer’s disease: a combined DTI and PET study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38(12):2219–2227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-011-1882-1
Villain N, Desgranges B, Viader F, de la Sayette V, Mezenge F, Landeau B, Baron JC, Eustache F et al (2008) Relationships between hippocampal atrophy, white matter disruption, and gray matter hypometabolism in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 28(24):6174–6181. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1392-08.2008
Villain N, Fouquet M, Baron JC, Mezenge F, Landeau B, de La Sayette V, Viader F, Eustache F et al (2010) Sequential relationships between grey matter and white matter atrophy and brain metabolic abnormalities in early Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 133(11):3301–3314. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq203
Gold BT, Zhu Z, Brown CA, Andersen AH, LaDu MJ, Tai L, Jicha GA, Kryscio RJ et al (2014) White matter integrity is associated with cerebrospinal fluid markers of Alzheimer’s disease in normal adults. Neurobiol Aging 35(10):2263–2271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.04.030
Stenset V, Bjornerud A, Fjell AM, Walhovd KB, Hofoss D, Due-Tonnessen P, Gjerstad L, Fladby T (2011) Cingulum fiber diffusivity and CSF T-tau in patients with subjective and mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging 32(4):581–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2009.04.014
Li X, Li TQ, Andreasen N, Wiberg MK, Westman E, Wahlund LO (2014) The association between biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid and structural changes in the brain in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Intern Med 275(4):418–427. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12164
Zhang Y, Schuff N, Du AT, Rosen HJ, Kramer JH, Gorno-Tempini ML, Miller BL, Weiner MW (2009) White matter damage in frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease measured by diffusion MRI. Brain 132(Pt 9):2579–2592. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awp071
Kantarci K, Avula R, Senjem ML, Samikoglu AR, Zhang B, Weigand SD, Przybelski SA, Edmonson HA et al (2010) Dementia with Lewy bodies and Alzheimer disease: neurodegenerative patterns characterized by DTI. Neurology 74(22):1814–1821. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181e0f7cf
Racine AM, Adluru N, Alexander AL, Christian BT, Okonkwo OC, Oh J, Cleary CA, Birdsill A et al (2014) Associations between white matter microstructure and amyloid burden in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease: a multimodal imaging investigation. Neuroimage Clin 4:604–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2014.02.001
Wirth M, Madison CM, Rabinovici GD, Oh H, Landau SM, Jagust WJ (2013) Alzheimer’s disease neurodegenerative biomarkers are associated with decreased cognitive function but not beta-amyloid in cognitively normal older individuals. J Neurosci 33(13):5553–5563. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4409-12.2013
Hansson O, Zetterberg H, Buchhave P, Londos E, Blennow K, Minthon L (2006) Association between CSF biomarkers and incipient Alzheimer’s disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment: a follow-up study. Lancet Neurol 5(3):228–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70355-6
Okello A, Koivunen J, Edison P, Archer HA, Turkheimer FE, Nagren K, Bullock R, Walker Z et al (2009) Conversion of amyloid positive and negative MCI to AD over 3 years: an 11C-PIB PET study. Neurology 73(10):754–760. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181b23564
Buchhave P, Minthon L, Zetterberg H, Wallin AK, Blennow K, Hansson O (2012) Cerebrospinal fluid levels of beta-amyloid 1-42, but not of tau, are fully changed already 5 to 10 years before the onset of Alzheimer dementia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 69(1):98–106. https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.155
Acknowledgments
Consortia
Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative Group:
Michael W. Weiner5, Paul Aisen6, Ronald Petersen7, Clifford R. Jack, Jr.8, William Jagust9, John Q. Trojanowki10, Arthur W. Toga11, Laurel Beckett12, Robert C. Green13, Andrew J. Saykin14, John Morris15, Leslie M. Shaw15, Jeffrey Kaye16, Joseph Quinn16, Lisa Silbert16, Betty Lind16, Raina Carter16, Sara Dolen16, Lon S. Schneider11, Sonia Pawluczyk11, Mauricio Beccera11, Liberty Teodoro11, Bryan M. Spann11, James Brewer17, Helen Vanderswag17, Adam Fleisher17, Judith L. Heidebrink18, Joanne L. Lord18, Sara S. Mason8, Colleen S. Albers8, David Knopman8, Kris Johnson8, Rachelle S. Doody19, Javier Villanueva-Meyer19, Munir Chowdhury19, Susan Rountree19, Mimi Dang19, Yaakov Stern20, Lawrence S. Honig20, Karen L. Bell20, Beau Ances15, John C. Morris15, Maria Carroll15, Mary L. Creech15, Erin Franklin15, Mark A. Mintun15, Stacy Schneider15, Angela Oliver15, Daniel Marson21, Randall Griffith21, David Clark21, David Geldmacher21, John Brockington21, Erik Roberson21, Marissa Natelson Love21, Hillel Grossman22, Effie Mitsis22, Raj C. Shah23, Leyla deToledo-Morrell23, Ranjan Duara24, Daniel Varon24, Maria T. Greig24, Peggy Roberts24, Marilyn Albert25, Chiadi Onyike25, Daniel D’Agostino25, Stephanie Kielb25, James E. Galvin26, Brittany Cerbone26, Christina A. Michel26, Dana M. Pogorelec26, Henry Rusinek26, Mony J de Leon26, Lidia Glodzik26, Susan De Santi26, P. Murali Doraiswamy27, Jeffrey R. Petrella27, Salvador Borges-Neto27, Terence Z. Wong27, Edward Coleman27, Charles D. Smith28, Greg Jicha28, Peter Hardy28, Partha Sinha28, Elizabeth Oates28, Gary Conrad28, Anton P. Porsteinsson29, Bonnie S. Goldstein29, Kim Martin29, Kelly M. Makino29, M. Saleem Ismail29, Connie Brand29, Ruth A. Mulnard30, Gaby Thai30, Catherine Mc-Adams-Ortiz30, Kyle Womack31, Dana Mathews31, Mary Quiceno31, Allan I. Levey32, James J. Lah32, Janet S. Cellar32, Jeffrey M. Burns33, Russell H. Swerdlow33, William M. Brooks33, Liana Apostolova34, Kathleen Tingus34, Ellen Woo34, Daniel H.S. Silverman34, Po H. Lu34, George Bartzokis34, Neill R Graff-Radford35, Francine Parfitt35, Tracy Kendall35, Heather Johnson35, Martin R. Farlow14, Ann Marie Hake14, Brandy R. Matthews14, Jared R. Brosch14, Scott Herring14, Cynthia Hunt14, Christopher H. van Dyck36, Richard E. Carson36, Martha G. MacAvoy36, Pradeep Varma36, Howard Chertkow37, Howard Bergman37, Chris Hosein37, Sandra Black38, Bojana Stefanovic38, Curtis Caldwell38, Ging-Yuek Robin Hsiung39, Howard Feldman39, Benita Mudge39, Michele Assaly39, Elizabeth Finger40, Stephen Pasternack40, Irina Rachisky40, Dick Trost40, Andrew Kertesz40, Charles Bernick41, Donna Munic41, Marek-Marsel Mesulam42, Kristine Lipowski42, Sandra Weintraub42, Borna Bonakdarpour42, Diana Kerwin42, Chuang-Kuo Wu42, Nancy Johnson42, Carl Sadowsky43, Teresa Villena43, Raymond Scott Turner44, Kathleen Johnson44, Brigid Reynolds44, Reisa A. Sperling45, Keith A. Johnson45, Gad Marshall45, Jerome Yesavage46, Joy L. Taylor46, Barton Lane46, Allyson Rosen46, Jared Tinklenberg46, Marwan N. Sabbagh47, Christine M. Belden47, Sandra A. Jacobson47, Sherye A. Sirrel47, Neil Kowall48, Ronald Killiany48, Andrew E. Budson48, Alexander Norbash48, Patricia Lynn Johnson48, Thomas O. Obisesan49, Saba Wolday49, Joanne Allard49, Alan Lerner50, Paula Ogrocki50, Curtis Tatsuoka50, Parianne Fatica50, Evan Fletcher51, Pauline Maillard51, John Olichney51, Charles DeCarli51, Owen Carmichael51, Smita Kittur52, Michael Borrie53, T-Y Lee53, Rob Bartha53, Sterling Johnson54, Sanjay Asthana54, Cynthia M. Carlsson54, Steven G. Potkin55, Adrian Preda55, Dana Nguyen55, Pierre Tariot56, Anna Burke56, Nadira Trncic56, Adam Fleisher56, Stephanie Reeder56, Vernice Bates57, Horacio Capote57, Michelle Rainka57, Douglas W. Scharre58, Maria Kataki58, Anahita Adeli58, Earl A. Zimmerman59, Dzintra Celmins59, Alice D. Brown59, Godfrey D. Pearlson60, Karen Blank60, Karen Anderson60, Laura A. Flashman61, Marc Seltzer61, Mary L. Hynes61, Robert B. Santulli61, Kaycee M. Sink62, Leslie Gordineer62, Jeff D. Williamson62, Pradeep Garg62, Franklin Watkins62, Brian R. Ott63, Henry Querfurth63, Geoffrey Tremont63, Stephen Salloway64, Paul Malloy64, Stephen Correia64, Howard J. Rosen65, Bruce L. Miller65, David Perry65, Jacobo Mintzer66, Kenneth Spicer66, David Bachman66, Nunzio Pomara67, Raymundo Hernando67, Antero Sarrael67, Norman Relkin67, Gloria Chaing68, Michael Lin68, Lisa Ravdin68, Amanda Smith69, Balebail Ashok Raj69, Kristin Fargher69.
5Magnetic Resonance Unit at the VA Medical Center and Radiology, Medicine, Psychiatry and Neurology, University of California, San Francisco, USA. 6San Diego School of Medicine, University of California, California, USA. 7Mayo Clinic, Minnesota, USA. 8Mayo Clinic, Rochester, USA. 9University of California, Berkeley, USA. 10University of Pennsylvania, Pennsylvania, USA. 11University of Southern California, California, USA. 12University of California, Davis, California, USA. 13MPH Brigham and Women’s Hospital/Harvard Medical School; Massachusetts, USA.14Indiana University, Indiana, USA. 15Washington University St. Louis, Missouri, USA. 16Oregon Health and Science University, Oregon, USA. 17University of California--San Diego, California, USA. 18University of Michigan, Michigan, USA. 19Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, State of Texas, USA. 20Columbia University Medical Center, South Carolina, USA. 21University of Alabama – Birmingham, Alabama, USA. 22Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, USA. 23Rush University Medical Center, Rush University, Illinois, USA. 24Wien Center, Florida, USA. 25Johns.
Hopkins University, Maryland, USA. 26New York University, NY, USA. 27Duke University Medical Center, North Carolina, USA. 28University of Kentucky, Kentucky, USA. 29University of Rochester Medical Center, NY, USA. 30University of California, Irvine, California, USA. 31University of Texas Southwestern Medical School, Texas, USA. 32Emory University, Georgia, USA. 33University of Kansas, Medical Center, Kansas, USA. 34University of California, Los Angeles, California, USA. 35Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, USA. 36Yale University School of Medicine, Connecticut, USA. 37McGill University, Montreal-Jewish General Hospital, Canada. 38Sunnybrook Health Sciences, Ontario, USA. 39U.B.C. Clinic for AD & Related Disorders, Canada. 40Cognitive Neurology - St. Joseph’s, Ontario, USA. 41Cleveland Clinic Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health, Ohio, USA. 42Northwestern University, USA. 43Premiere Research Inst (Palm Beach Neurology), USA. 44Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington D.C, USA. 45Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Massachusetts, USA. 46Stanford University, California, USA. 47Banner Sun Health Research Institute, USA. 48Boston University, Massachusetts, USA.49Howard University, Washington D.C, USA. 50Case Western Reserve University, Ohio, USA. 51University of California, Davis – Sacramento, California, USA. 52Neurological Care of CNY, USA. 53Parkwood Hospital, Pennsylvania, USA. 54University of Wisconsin, Wisconsin, USA. 55University of California, Irvine – BIC, USA. 56Banner Alzheimer’s Institute, USA. 57Dent Neurologic Institute, NY, USA. 58Ohio State University, Ohio, USA. 59Albany Medical College, NY, USA. 60Hartford Hospital, Olin Neuropsychiatry Research Center, Connecticut, USA. 61Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, New Hampshire, USA. 62Wake Forest University Health Sciences, North Carolina, USA. 63Rhode Island Hospital, state of Rhode Island, USA. 64Butler Hospital, Providence, Rhode Island, USA. 65University of California, San Francisco, USA. 66Medical University South Carolina, USA. 67Nathan Kline Institute, Orangeburg, New York, USA. 68Cornell University, Ithaca, New York, USA. 69USF Health Byrd Alzheimer’s Institute, University of South Florida, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
L.P.S., T.A.P., C.R.M.R., S.G., A.P., and P.R-N. performed the conception of the study. L.P.S., T.A.P., E.R.Z., S.M., and M.S. performed the processing and the quality control of the image data. L.P.S., T.A.P., S.M., and P.R-N. analyzed and interpreted the data. L.P.S., T.A.P., E.R.Z., C.R.M.R., A.P., and P.R-N. prepared the figures, the table, and drafted the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 83 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
(DOCX 156 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schilling, L.P., Pascoal, T.A., Zimmer, E.R. et al. Regional Amyloid-β Load and White Matter Abnormalities Contribute to Hypometabolism in Alzheimer’s Dementia. Mol Neurobiol 56, 4916–4924 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1405-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1405-1