Abstract
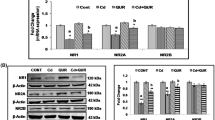
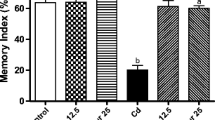
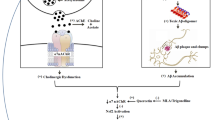
With the increasing evidences of cadmium-induced cognitive deficits associated with brain cholinergic dysfunctions, the present study aimed to decipher molecular mechanisms involved in the neuroprotective efficacy of quercetin in rats. A decrease in the binding of cholinergic–muscarinic receptors and mRNA expression of cholinergic receptor genes (M1, M2, and M4) was observed in the frontal cortex and hippocampus on exposure of rats to cadmium (5.0 mg/kg body weight, p.o.) for 28 days compared to controls. Cadmium exposure resulted to decrease mRNA and protein expressions of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and enhance reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation associated with mitochondrial dysfunctions, ultrastructural changes, and learning deficits. Enhanced apoptosis, as evidenced by alterations in key proteins involved in the pro- and anti-apoptotic pathway and mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase signaling, was evident on cadmium exposure. Simultaneous treatment with quercetin (25 mg/kg body weight, p.o.) resulted to protect cadmium-induced alterations in cholinergic–muscarinic receptors, mRNA expression of genes (M1, M2, and M4), and expression of ChAT and AChE. The protective effect on brain cholinergic targets was attributed to the antioxidant potential of quercetin, which reduced ROS generation and protected mitochondrial integrity by modulating proteins involved in apoptosis and MAP kinase signaling. The results exhibit that quercetin may modulate molecular targets involved in brain cholinergic signaling and attenuate cadmium neurotoxicity.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernhoft RA (2013) Cadmium toxicity and treatment. Sci World J 2013:7
Schoeters G, HOND ED, Zuurbier M, Naginiene R, HAZEL P, Stilianakis N, Ronchetti R, Koppe JG (2006) Cadmium and children: exposure and health effects. Acta Paediatr 95(s453):50–54
Satarug S, Garrett SH, Sens MA, Sens DA (2011) Cadmium, environmental exposure, and health outcomes. Ciencia Saude Coletiva 16(5):2587–2602
Méndez-Armenta M, Ríos C (2007) Cadmium neurotoxicity. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 23(3):350–358
Wang B, Du Y (2013) Cadmium and its neurotoxic effects. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2013:12
Khade SW, Adholeya A (2009) Arbuscular mycorrhizal association in plants growing on metal-contaminated and noncontaminated soils adjoining Kanpur tanneries, Uttar Pradesh, India. Water Air Soil Pollut 202(1–4):45–56
Radha RV, Kumutha K, Marimuthu P (2014) Assessment of cadmium contamination of soils in sewage disposal areas of Coimbatore district, Tamil Nadu, India. Curr World Environ 9(2):379–386
Borah K, Bhuyan B, Sarma H (2009) Heavy metal contamination of groundwater in the Tea Garden Belt of Darrang District, Assam, India. J Chem 6(S1):S501–S507
Simmons R, Pongsakul P, Saiyasitpanich D, Klinphoklap S (2005) Elevated levels of cadmium and zinc in paddy soils and elevated levels of cadmium in rice grain downstream of a zinc mineralized area in Thailand: implications for public health. Environ Geochem Health 27(5–6):501–511
Wang Y, Björn LO (2014) Heavy metal pollution in Guangdong Province, China, and the strategies to manage the situation. Front Environ Sci 2(9):1–12
Cai S, Yue L, Shang Q, Nordberg G (1995) Cadmium exposure among residents in an area contaminated by irrigation water in China. Bull World Health Organ 73(3):359–367
Satarug S, Moore MR (2004) Adverse health effects of chronic exposure to low-level cadmium in foodstuffs and cigarette smoke. Environ Health Perspect 112(10):1099–1103
Hayashi C, Koizumi N, Nishio H, Koizumi N, Ikeda M (2012) Cadmium and other metal levels in autopsy samples from a cadmium-polluted area and non-polluted control areas in Japan. Biol Trace Elem Res 145(1):10–22
Y-f C, J-f W, J-f C, Xiao-Ying W, Yang L, Guo Y-d (2012) An investigation and pathological analysis of two fatal cases of cadmium poisoning. Forensic Sci Int 220(1):e5–e8
Mari M, Nadal M, Schuhmacher M, Barbería E, García F, Domingo JL (2014) Human exposure to metals: levels in autopsy tissues of individuals living near a hazardous waste incinerator. Biol Trace Elem Res 159(1–3):15–21
Waalkes MP, Coogan TP, Barter RA (1992) Toxicological principles of metal carcinogenesis with special emphasis on cadmium. Crit Rev Toxicol 22(3–4):175–201
Wong K-L, Klaassen CD (1982) Neurotoxic effects of cadmium in young rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 63(3):330–337
Järup L, Berglund M, Elinder CG, Nordberg G, Vanter M (1998) Health effects of cadmium exposure—a review of the literature and a risk estimate. Scand J Work Environ Health 24:1–51
Pihl R, Parkes M (1977) Hair element content in learning disabled children. Science 198(4313):204–206
Thatcher R, Lester M, McAlaster R, Horst R (1982) Effects of low levels of cadmium and lead on cognitive functioning in children. Arch Environ Health: Int J 37(3):159–166
Marlowe M, Errera J, Jacobs J (1983) Increased lead and cadmium burdens among mentally retarded children and children with borderline intelligence. Am J Ment Defic 87(5):477–483
Okuda B, Iwamoto Y, Tachibana H, Sugita M (1998) Parkinsonism after acute cadmium poisoning. Occup Health Ind Med 5(38):232–265
Viaene M, Masschelein R, Leenders J, De Groof M, Swerts L, Roels H (2000) Neurobehavioural effects of occupational exposure to cadmium: a cross sectional epidemiological study. Occup Environ Med 57(1):19–27
Viaene M, Roels H, Leenders J, De Groof M, Swerts L, Lison D, Masschelein R (1999) Cadmium: a possible etiological factor in peripheral polyneuropathy. Neurotoxicology 20(1):7–16
Choudhuri S, Liu WL, Berman NE, Klaassen CD (1996) Cadmium accumulation and metallothionein expression in brain of mice at different stages of development. Toxicol Lett 84(3):127–133
Shukla A, Shukla GS, Srimal R (1996) Cadmium-induced alterations in blood–brain barrier permeability and its possible correlation with decreased microvessel antioxidant potential in rat. Hum Exp Toxicol 15(5):400–405
Gonçalves JF, Fiorenza AM, Spanevello RM, Mazzanti CM, Bochi GV, Antes FG, Stefanello N, Rubin MA, Dressler VL, Morsch VM (2010) N-acetylcysteine prevents memory deficits, the decrease in acetylcholinesterase activity and oxidative stress in rats exposed to cadmium. Chem Biol Interact 186(1):53–60
Zalups RK, Ahmad S (2003) Molecular handling of cadmium in transporting epithelia. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 186(3):163–188
Attia A, Ibrahim F, EL-Latif NAA, Aziz SW (2014) Antioxidant effects of curcumin against cadmium chloride-induced oxidative stress in the blood of rats. J Pharmacogn Phytother 6(3):33–40
Shagirtha K, Muthumani M, Prabu SM (2011) Melatonin abrogates cadmium induced oxidative stress related neurotoxicity in rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 15(9):1039–1050
Nemmiche S, Chabane-Sari D, Guiraud P (2007) Role of α-tocopherol in cadmium-induced oxidative stress in Wistar rat’s blood, liver and brain. Chem Biol Interact 170(3):221–230
Lopez E, Arce C, Oset-Gasque M, Canadas S, Gonzalez M (2006) Cadmium induces reactive oxygen species generation and lipid peroxidation in cortical neurons in culture. Free Radic Biol Med 40(6):940–951
Monroe RK, Halvorsen SW (2006) Cadmium blocks receptor-mediated Jak/STAT signaling in neurons by oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 41(3):493–502
Méndez-Armenta M, Villeda-Hernández J, Barroso-Moguel R, Nava-Ruı́ C, Jiménez-Capdeville ME, Rı́ C (2003) Brain regional lipid peroxidation and metallothionein levels of developing rats exposed to cadmium and dexamethasone. Toxicol Lett 144(2):151–157
Hidalgo J, Aschner M, Zatta P, Vašák M (2001) Roles of the metallothionein family of proteins in the central nervous system. Brain Res Bull 55(2):133–145
Nishimura N, Nishimura H, Ghaffar A, Tohyama C (1992) Localization of metallothionein in the brain of rat and mouse. J Histochem Cytochem 40(2):309–315
Antonio M, Corpas I, Leret M (1999) Neurochemical changes in newborn rat’s brain after gestational cadmium and lead exposure. Toxicol Lett 104(1):1–9
Antonio MT, Corredor L, Leret ML (2003) Study of the activity of several brain enzymes like markers of the neurotoxicity induced by perinatal exposure to lead and/or cadmium. Toxicol Lett 143(3):331–340
Minami A, Takeda A, Nishibaba D, Takefuta S, Oku N (2001) Cadmium toxicity in synaptic neurotransmission in the brain. Brain Res 894(2):336–339
Andersson H, Petersson-Grawe K, Lindqvist E, Luthman J, Oskarsson A, Olson L (1997) Low-level cadmium exposure of lactating rats causes alterations in brain serotonin levels in the offspring. Neurotoxicol Teratol 19(2):105–115
Lafuente A, Fenàndez-Rey E, Seara R, Pérez-Lorenzo M, Esquifino A (2001) Alternate cadmium exposure differentially affects amino acid metabolism within the hypothalamus, median eminence, striatum and prefrontal cortex of male rats. Neurochem Int 39(3):187–192
Lafuente A, Gonzalez-Carracedo A, Romero A, Esquifino A (2003) Effect of cadmium on 24-h variations in hypothalamic dopamine and serotonin metabolism in adult male rats. Exp Brain Res 149(2):200–206
Ashok A, Rai NK, Tripathi S, Bandyopadhyay S (2015) Exposure to As-, Cd-, and Pb-mixture induces Aβ, amyloidogenic APP processing and cognitive impairments via oxidative stress-dependent neuroinflammation in young rats. Toxicol Sci 143:64–80
Abdalla FH, Schmatz R, Cardoso AM, Carvalho FB, Baldissarelli J, de Oliveira JS, Rosa MM, Nunes MAG, Rubin MA, da Cruz IB (2014) Quercetin protects the impairment of memory and anxiogenic-like behavior in rats exposed to cadmium: possible involvement of the acetylcholinesterase and Na+, K+-ATPase activities. Physiol Behav 135:152–167
Carageorgiou H, Tzotzes V, Pantos C, Mourouzis C, Zarros A, Tsakiris S (2004) In vivo and in vitro effects of cadmium on adult rat brain total antioxidant status, acetylcholinesterase, (Na+, K+)‐ATPase and Mg2+-ATPase activities: protection by L‐cysteine. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 94(3):112–118
Belyaeva EA, Sokolova TV, Emelyanova LV, Zakharova IO (2012) Mitochondrial electron transport chain in heavy metal-induced neurotoxicity: effects of cadmium, mercury, and copper. Sci World J 2012:14
Chang K-C, Hsu C-C, Liu S-H, Su C-C, Yen C-C, Lee M-J, Chen K-L, Ho T-J, Hung D-Z, Wu C-C (2013) Cadmium induces apoptosis in pancreatic β-cells through a mitochondria-dependent pathway: the role of oxidative stress-mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation. PLoS One 8(2), e54374
Beal MF (1996) Mitochondria, free radicals, and neurodegeneration. Curr Opin Neurobiol 6(5):661–666
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu B-e, Karandikar M, Berman K, Cobb MH (2001) Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions 1. Endocr Rev 22(2):153–183
Kyriakis JM, Avruch J (2001) Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev 81(2):807–869
Chen L, Liu L, Luo Y, Huang S (2008) MAPK and mTOR pathways are involved in cadmium‐induced neuronal apoptosis. J Neurochem 105(1):251–261
Chen L, Liu L, Huang S (2008) Cadmium activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway via induction of reactive oxygen species and inhibition of protein phosphatases 2A and 5. Free Radic Biol Med 45(7):1035–1044
Leuner K, Hauptmann S, Abdel-Kader R, Scherping I, Keil U, Strosznajder JB, Eckert A, Müller WE (2007) Mitochondrial dysfunction: the first domino in brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease? Antioxid Redox Signal 9(10):1659–1676
De Sarno P, Shestopal SA, King TD, Zmijewska A, Song L, Jope RS (2003) Muscarinic receptor activation protects cells from apoptotic effects of DNA damage, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial inhibition. J Biol Chem 278(13):11086–11093
Li X, Lv Y, Yu S, Zhao H, Yao L (2012) The effect of cadmium on Aβ levels in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Exp Ther Med 4(1):125–130
Panayi A, Spyrou N, Iversen B, White M, Part P (2002) Determination of cadmium and zinc in Alzheimer’s brain tissue using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J Neurol Sci 195(1):1–10
Johnson S (2001) Gradual micronutrient accumulation and depletion in Alzheimer’s disease. Med Hypotheses 56(6):595–597
Dajas F, Rivera-Megret F, Blasina F, Arredondo F, Abin-Carriquiry J, Costa G, Echeverry C, Lafon L, Heizen H, Ferreira M (2003) Neuroprotection by flavonoids. Braz J Med Biol Res 36(12):1613–1620
Havsteen BH (2002) The biochemistry and medical significance of the flavonoids. Pharmacol Ther 96(2):67–202
Larson AJ, Symons JD, Jalili T (2010) Quercetin: a treatment for hypertension?—A review of efficacy and mechanisms. Pharmaceuticals 3(1):237–250
Sandhir R, Mehrotra A (2013) Quercetin supplementation is effective in improving mitochondrial dysfunctions induced by 3-nitropropionic acid: implications in Huntington’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Mol Basis Dis 1832(3):421–430
Yang T, Kong B, Gu J-W, Kuang Y-Q, Cheng L, Yang W-T, Xia X, Shu H-F (2014) Anti-apoptotic and anti-oxidative roles of quercetin after traumatic brain injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol 34(6):797–804
Haleagrahara N, Siew CJ, Mitra NK, Kumari M (2011) Neuroprotective effect of bioflavonoid quercetin in 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative stress biomarkers in the rat striatum. Neurosci Lett 500(2):139–143
Abdalla FH, Cardoso AM, Pereira LB, Schmatz R, Gonçalves JF, Stefanello N, Fiorenza AM, Gutierres JM, da Silva Serres JD, Zanini D (2013) Neuroprotective effect of quercetin in ectoenzymes and acetylcholinesterase activities in cerebral cortex synaptosomes of cadmium-exposed rats. Mol Cell Biochem 381(1–2):1–8
Glowinski J, Iversen LL (1966) Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain—I. J Neurochem 13(8):655–669
Wang W, Li S, Dong H-p, Lv S, Y-y T (2009) Differential impairment of spatial and nonspatial cognition in a mouse model of brain aging. Life Sci 85(3):127–135
Yamada K, Noda Y, Hasegawa T, Komori Y, Nikai T, Sugihara H, Nabeshima T (1996) The role of nitric oxide in dizocilpine-induced impairment of spontaneous alternation behavior in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 276(2):460–466
Yadav RS, Chandravanshi LP, Shukla RK, Sankhwar ML, Ansari RW, Shukla PK, Pant AB, Khanna VK (2011) Neuroprotective efficacy of curcumin in arsenic induced cholinergic dysfunctions in rats. Neurotoxicology 32(6):760–768
Khanna VK, Husain R, Seth PK (1994) Effect of protein malnutrition on the neurobehavioural toxicity of styrene in young rats. J Appl Toxicol 14(5):351–356
Singh A, Mudawal A, Shukla RK, Yadav S, Khanna VK, Sethumadhavan R, Parmar D (2014) Effect of gestational exposure of cypermethrin on postnatal development of brain cytochrome P450 2D1 and 3A1 and neurotransmitter receptors. Mol Neurobiol 52(1):741–756
Morley BJ, Warr WB, Rodriguez–Sierra J (2004) Transient expression of acetylcholinesterase in the posterior ventral cochlear nucleus of rat brain. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 5(4):391–403
Madziar B, Shah S, Brock M, Burke R, Lopez‐Coviella I, Nickel AC, Cakal EB, Blusztajn JK, Berse B (2008) Nerve growth factor regulates the expression of the cholinergic locus and the high‐affinity choline transporter via the Akt/PKB signaling pathway. J Neurochem 107(5):1284–1293
Borges MO, Abreu ML, Porto CS, Avellar MCW (2001) Characterization of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in rat Sertoli cells. Endocrinology 142(11):4701–4710
Bagh MB, Maiti AK, Jana S, Banerjee K, Roy A, Chakrabarti S (2008) Quinone and oxyradical scavenging properties of N-acetylcysteine prevent dopamine mediated inhibition of Na+, K+-ATPase and mitochondrial electron transport chain activity in rat brain: implications in the neuroprotective therapy of Parkinson’s disease. Free Radic Res 42(6):574–581
Hatefi Y (1978) Preparation and properties of NADH: ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I), EC 1.6. 5.3. Methods Enzymol 53:11–16
Clark J, Bates T, Boakye P, Kuimov A, Land J (1997) Investigation of mitochondrial defects in brain and skeletal muscle. In: Turner AJ, Bachelard HS (eds) Neurochemistry: a practical approach. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 151–174
Wharton DC (1967) Cytochrome oxidase from beef heart mitochondria. Methods Enzymol 10:245–250
Rush JW, Quadrilatero J, Levy AS, Ford RJ (2007) Chronic resveratrol enhances endothelium-dependent relaxation but does not alter eNOS levels in aorta of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Exp Biol Med 232(6):814–822
Kane CJ, Chang JY, Roberson PK, Garg TK, Han L (2008) Ethanol exposure of neonatal rats does not increase biomarkers of oxidative stress in isolated cerebellar granule neurons. Alcohol 42(1):29–36
Jamal M, Ameno K, Ameno S, Morishita J, Wang W, Kumihashi M, Ikuo U, Miki T, Ijiri I (2007) Changes in cholinergic function in the frontal cortex and hippocampus of rat exposed to ethanol and acetaldehyde. Neuroscience 144(1):232–238
Veena J, Srikumar B, Mahati K, Raju T, Rao BS (2011) Oxotremorine treatment restores hippocampal neurogenesis and ameliorates depression-like behaviour in chronically stressed rats. Psychopharmacology 217(2):239–253
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Kim W, Kim DW, Yoo DY, Jung HY, Nam SM, Kim JW, Hong S-M, Kim D-W, Choi JH, Moon SM (2014) Dendropanax morbifera Léveille extract facilitates cadmium excretion and prevents oxidative damage in the hippocampus by increasing antioxidant levels in cadmium-exposed rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 14(1):428
El-Demerdash FM, Yousef MI, Kedwany FS, Baghdadi HH (2004) Cadmium-induced changes in lipid peroxidation, blood hematology, biochemical parameters and semen quality of male rats: protective role of vitamin E and β-carotene. Food Chem Toxicol 42(10):1563–1571
Haider S, Anis L, Batool Z, Sajid I, Naqvi F, Khaliq S, Ahmed S (2015) Short term cadmium administration dose dependently elicits immediate biochemical, neurochemical and neurobehavioral dysfunction in male rats. Metab Brain Dis 30(1):83–92
Winiarska-Mieczan A (2015) The potential protective effect of green, black, red and white tea infusions against adverse effect of cadmium and lead during chronic exposure—a rat model study. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 73(2):521–529
Gong D, Liu B, Tan X (2015) Genistein prevents cadmium-induced neurotoxic effects through its antioxidant mechanisms. Drug Res 65(2):65–69
Karaca S, Eraslan G (2013) The effects of flaxseed oil on cadmium-induced oxidative stress in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 155(3):423–430
Halder S, Kar R, Mehta AK, Bhattacharya SK, Mediratta PK, Banerjee BD (2016) Quercetin modulates the effects of chromium exposure on learning, memory and antioxidant enzyme activity in F1 generation mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 171:391–398
Bavithra S, Selvakumar K, Kumari RP, Krishnamoorthy G, Venkataraman P, Arunakaran J (2012) Polychlorinated biphenyl (PCBs)-induced oxidative stress plays a critical role on cerebellar dopaminergic receptor expression: ameliorative role of quercetin. Neurotox Res 21(2):149–159
Sharma DR, Wani WY, Sunkaria A, Kandimalla RJ, Verma D, Cameotra SS, Gill KD (2013) Quercetin protects against chronic aluminum-induced oxidative stress and ensuing biochemical, cholinergic, and neurobehavioral impairments in rats. Neurotox Res 23(4):336–357
Tota S, Awasthi H, Kamat PK, Nath C, Hanif K (2010) Protective effect of quercetin against intracerebral streptozotocin induced reduction in cerebral blood flow and impairment of memory in mice. Behav Brain Res 209(1):73–79
Joseph KD (2015) Combined oral supplementation of fish oil and quercetin enhances neuroprotection in a chronic rotenone rat model: relevance to Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Res 40(5):894–905
Davis JM, Murphy EA, Carmichael MD, Davis B (2009) Quercetin increases brain and muscle mitochondrial biogenesis and exercise tolerance. Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Phys 296(4):R1071–R1077
Chakraborty J, Singh R, Dutta D, Naskar A, Rajamma U, Mohanakumar KP (2014) Quercetin improves behavioral deficiencies, restores astrocytes and microglia, and reduces serotonin metabolism in 3‐nitropropionic acid‐induced rat model of Huntington’s disease. CNS Neurosci Ther 20(1):10–19
Carageorgiou H, Tzotzes V, Sideris A, Zarros A, Tsakiris S (2005) Cadmium effects on brain acetylcholinesterase activity and antioxidant status of adult rats: modulation by zinc, calcium and L‐cysteine co‐administration. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 97(5):320–324
Gkanti V, Stolakis V, Kalafatakis K, Liapi C, Zissis KM, Zarros A, Tsakiris S (2014) Postnuclear supernatants of rat brain regions as substrates for the in vitro assessment of cadmium-induced neurotoxicity on acetylcholinesterase activity. Biol Trace Elem Res 158(1):87–89
Zarros A, Kalopita K, Tsakiris S, Baillie GS (2013) Can acetylcholinesterase activity be considered as a reliable biomarker for the assessment of cadmium-induced neurotoxicity? Food Chem Toxicol 56:406–410
Casalino E, Sblano C, Landriscina C (1997) Enzyme activity alteration by cadmium administration to rats: the possibility of iron involvement in lipid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 346(2):171–179
Dwivedi C (1983) Cadmium-induced sterility: possible involvement of the cholinergic system. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 12(2):151–156
Del Pino J, Zeballos G, Anadon MJ, Capo MA, Díaz MJ, García J, Frejo MT (2014) Higher sensitivity to cadmium induced cell death of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons: a cholinesterase dependent mechanism. Toxicology 325:151–159
Hayashi H, Takayama K (1978) Inhibitory effects of cadmium on the release of acetylcholine from cardiac nerve terminals. Jpn J Physiol 28(3):333–345
Alberts P, Ögren V, Sellström Å (1985) Cadmium inhibition of [3H]acetylcholine secretion in guinea‐pig ileum myenteric plexus. Acta Physiol Scand 124(2):313–316
Abrams P, Andersson KE, Buccafusco JJ, Chapple C, Groat WC, Fryer AD, Kay G, Laties A, Nathanson NM, Pasricha PJ (2006) Muscarinic receptors: their distribution and function in body systems, and the implications for treating overactive bladder. Br J Pharmacol 148(5):565–578
Hedlund B, Gamarra M, Bartfai T (1979) Inhibition of striatal muscarinic receptors in vivo by cadmium. Brain Res 168(1):216–218
Levey AI (1996) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor expression in memory circuits: implications for treatment of Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93(24):13541–13546
Nyakas C, Granic I, Halmy LG, Banerjee P, Luiten PG (2011) The basal forebrain cholinergic system in aging and dementia. Rescuing cholinergic neurons from neurotoxic amyloid-β42 with memantine. Behav Brain Res 221(2):594–603
O’Reilly RC, Rudy JW (2001) Conjunctive representations in learning and memory: principles of cortical and hippocampal function. Psychol Rev 108(2):311
Schliebs R, Arendt T (2011) The cholinergic system in aging and neuronal degeneration. Behav Brain Res 221(2):555–563
Whishaw IQ (1989) Dissociating performance and learning deficits on spatial navigation tasks in rats subjected to cholinergic muscarinic blockade. Brain Res Bull 23(4–5):347–358
Jarrard LE (1993) On the role of the hippocampus in learning and memory in the rat. Behav Neural Biol 60(1):9–26
Van der Zee E, Luiten P (1999) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in the hippocampus, neocortex and amygdala: a review of immunocytochemical localization in relation to learning and memory. Prog Neurobiol 58(5):409–471
Bank B, DeWeer A, Kuzirian AM, Rasmussen H, Alkon DL (1988) Classical conditioning induces long-term translocation of protein kinase C in rabbit hippocampal CA1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 85(6):1988–1992
Alkon DL, Sun M-K, Nelson TJ (2007) PKC signaling deficits: a mechanistic hypothesis for the origins of Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 28(2):51–60
Abeliovich A, Chen C, Goda Y, Silva AJ, Stevens CF, Tonegawa S (1993) Modified hippocampal long-term potentiation in PKCγ-mutant mice. Cell 75(7):1253–1262
Weeber EJ, Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Varga AW, Mirnikjoo B, Paylor R, Leitges M, Sweatt JD (2000) A role for the β isoform of protein kinase C in fear conditioning. J Neurosci 20(16):5906–5914
Wu J, Song T-B, Li Y-J, He K-S, Ge L, Wang L-R (2007) Prenatal restraint stress impairs learning and memory and hippocampal PKCbeta1 expression and translocation in offspring rats. Brain Res 1141:205–213
Paratcha G, Furman M, Bevilaqua L, Cammarota M, Vianna M, de Stein ML, Izquierdo I, Medina JH (2000) Involvement of hippocampal PKCβI isoform in the early phase of memory formation of an inhibitory avoidance learning. Brain Res 855(2):199–205
Shukla RK, Gupta R, Srivastava P, Dhuriya YK, Singh A, Chandravanshi LP, Kumar A, Siddiqui MH, Parmar D, Pant AB (2015) Brain cholinergic alterations in rats subjected to repeated immobilization or forced swim stress on lambda-cyhalothrin exposure. Neurochem Int 0186(15):30081–30084
Chandravanshi LP, Yadav RS, Shukla RK, Singh A, Sultana S, Pant AB, Parmar D, Khanna VK (2014) Reversibility of changes in brain cholinergic receptors and acetylcholinesterase activity in rats following early life arsenic exposure. Int J Dev Neurosci 34:60–75
Kumar R, Agarwal AK, Seth PK (1996) Oxidative stress-mediated neurotoxicity of cadmium. Toxicol Lett 89(1):65–69
Jing L, Anning L (2005) Role of JNK activation in apoptosis: a double-edged sword. Cell Res 15(1):36–42
Chen S, Gu C, Xu C, Zhang J, Xu Y, Ren Q, Guo M, Huang S, Chen L (2014) Celastrol prevents cadmium‐induced neuronal cell death via targeting JNK and PTEN‐Akt/mTOR network. J Neurochem 128(2):256–266
L-l L, J-l Z, Z-w Z, H-d Y, Sun G, Xu S-w (2014) Protective roles of selenium on nitric oxide-mediated apoptosis of immune organs induced by cadmium in chickens. Biol Trace Elem Res 159(1–3):199–209
Morikawa K, Nonaka M, Narahara M, Torii I, Kawaguchi K, Yoshikawa T, Kumazawa Y, Morikawa S (2003) Inhibitory effect of quercetin on carrageenan-induced inflammation in rats. Life Sci 74(6):709–721
Rivera L, Morón R, Sánchez M, Zarzuelo A, Galisteo M (2008) Quercetin ameliorates metabolic syndrome and improves the inflammatory status in obese Zucker rats. Obesity 16(9):2081–2087
Ansari MA, Abdul HM, Joshi G, Opii WO, Butterfield DA (2009) Protective effect of quercetin in primary neurons against Aβ(1–42): relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. J Nutr Biochem 20(4):269–275
Unsal C, Kanter M, Aktas C, Erboga M (2015) Role of quercetin in cadmium-induced oxidative stress, neuronal damage, and apoptosis in rats. Toxicol Ind Health 31:1106–1115. doi:10.1177/0748233713486960
Karuppagounder S, Madathil S, Pandey M, Haobam R, Rajamma U, Mohanakumar K (2013) Quercetin up-regulates mitochondrial complex-I activity to protect against programmed cell death in rotenone model of Parkinson’s disease in rats. Neuroscience 236:136–148
Yao R-Q, Qi D-S, Yu H-L, Liu J, Yang L-H, Wu X-X (2012) Quercetin attenuates cell apoptosis in focal cerebral ischemia rat brain via activation of BDNF–TrkB–PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Neurochem Res 37(12):2777–2786
Wang X-Q, Yao R-Q, Liu X, Huang J-J, Qi D-S, Yang L-H (2011) Quercetin protects oligodendrocyte precursor cells from oxygen/glucose deprivation injury in vitro via the activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Brain Res Bull 86(3):277–284
Sun SW, Yu HQ, Zhang H, Zheng YL, Wang JJ, Luo L (2007) Quercetin attenuates spontaneous behavior and spatial memory impairment in d-galactose-treated mice by increasing brain antioxidant capacity. Nutr Res 27(3):169–175
Richetti S, Blank M, Capiotti K, Piato A, Bogo M, Vianna M, Bonan C (2011) Quercetin and rutin prevent scopolamine-induced memory impairment in zebrafish. Behav Brain Res 217(1):10–15
Acknowledgments
The study has been carried out as a part of the INDEPTH programme of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi. Richa Gupta and Pranay Srivastava acknowledges the support of CSIR, New Delhi, for providing Research Fellowship. The authors thank the Director, CSIR–Indian Institute of Toxicology Research (CSIR-IITR), Lucknow, for his interest in the present study and providing necessary support. Technical assistance provided by Mr. B.S. Pandey is also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, R., Shukla, R.K., Chandravanshi, L.P. et al. Protective Role of Quercetin in Cadmium-Induced Cholinergic Dysfunctions in Rat Brain by Modulating Mitochondrial Integrity and MAP Kinase Signaling. Mol Neurobiol 54, 4560–4583 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9950-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9950-y