Abstract
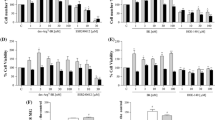
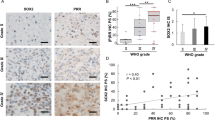
This study investigated the role of kinins and their receptors in malignant brain tumors. As a first approach, GL-261 glioma cells were injected (2 × 105 cells in 2 μl/2 min) into the right striatum of adult C57/BL6 wild-type, kinin B1 and B2 receptor knockout (KOB1R and KOB2R) and B1 and B2 receptor double knockout mice (KOB1B2R). The animals received the selective B1R (SSR240612) and/or B2R (HOE-140) antagonists by intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) route at 5, 10, and 15 days. The tumor size quantification, mitotic index, western blot analysis, quantitative autoradiography, immunofluorescence, and confocal microscopy were carried out in brain tumor samples, 20 days after tumor induction. Our results revealed an uncontrolled tumor growing in KOB1R or SSR240612-treated mice, which was blunted by B2R blockade with HOE-140, suggesting a crosstalk between B1R and B2R in tumor growing. Combined treatment with B1R and B2R antagonists normalized the upregulation of tumor B1R and decreased the tumor size and the mitotic index, as was seen in double KOB1B2R. The B1R was detected on astrocytes in the tumor, indicating a close relationship between this receptor and astroglial cells. Noteworthy, an immunohistochemistry analysis of tumor samples from 16 patients with glioma diagnosis revealed a marked B1R immunopositivity in low-grade gliomas or in older glioblastoma individuals. Furthermore, the clinical data revealed a significantly higher immunopositivity for B1R, when compared to a lower B2R immunolabeling. Taken together, our results show that blocking simultaneously both kinin receptors or alternatively stimulating B1R may be of therapeutic value in the treatment of brain glioblastoma growth and malignancy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wen PY, Kesari S (2008) Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med 359(5):492–507. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0708126
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW, Kleihues P (2007) The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 114(2):97–109. doi:10.1007/s00401-007-0243-4
Omuro A, DeAngelis LM (2013) Glioblastoma and other malignant gliomas: a clinical review. JAMA 310(17):1842–1850. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.280319
Agarwal S, Sane R, Oberoi R, Ohlfest JR, Elmquist WF (2011) Delivery of molecularly targeted therapy to malignant glioma, a disease of the whole brain. Expert Rev Mol Med 13:e17. doi:10.1017/S1462399411001888
Leeb-Lundberg LM, Marceau F, Muller-Esterl W, Pettibone DJ, Zuraw BL (2005) International union of pharmacology. XLV. Classification of the kinin receptor family: from molecular mechanisms to pathophysiological consequences. Pharmacol Rev 57(1):27–77. doi:10.1124/pr.57.1.2
Regoli D, Plante GE, Gobeil F Jr (2012) Impact of kinins in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Pharmacol Ther 135(1):94–111 doi: 1016/j.pharmthera.2012.04.002
Couture R, Blaes N, Girolami JP (2014) Kinin receptors in vascular biology and pathology. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 12(2):223–248 doi:CVP-EPUB-59365
Couture R, Lindsey CJ (2000) Brain kallikrein-kinin system: from receptors to neuronal pathways and physiological functions. In: Quirion R, Bjorklund A, Hokfelt T (eds) Handbook of chemical neuroanatomy, vol 16. Elsevier Science, Oxford, pp. 241–300
Cote J, Bovenzi V, Savard M, Dubuc C, Fortier A, Neugebauer W, Tremblay L, Muller-Esterl W et al (2012) Induction of selective blood-tumor barrier permeability and macromolecular transport by a biostable kinin B1 receptor agonist in a glioma rat model. PLoS One 7(5):e37485. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0037485PONE-D-12-05042
Liu LB, Xue YX, Liu YH (2010) Bradykinin increases the permeability of the blood-tumor barrier by the caveolae-mediated transcellular pathway. J Neuro-Oncol 99(2):187–194. doi:10.1007/s11060-010-0124-x
Cote J, Savard M, Bovenzi V, Dubuc C, Tremblay L, Tsanaclis AM, Fortin D, Lepage M et al (2010) Selective tumor blood-brain barrier opening with the kinin B2 receptor agonist [Phe(8)psi(CH(2)NH)Arg(9)]-BK in a F98 glioma rat model: an MRI study. Neuropeptides 44(2):177–185. doi:10.1016/j.npep.2009.12.009 24
Borlongan CV, Emerich DF (2003) Facilitation of drug entry into the CNS via transient permeation of blood brain barrier: laboratory and preliminary clinical evidence from bradykinin receptor agonist, Cereport. Brain Res Bull 60(3):297–306 doi:S0361923003000431
Zhao Y, Xue Y, Liu Y, Fu W, Jiang N, An P, Wang P, Yang Z et al (2005) Study of correlation between expression of bradykinin B2 receptor and pathological grade in human gliomas. Br J Neurosurg 19(4):322–326. doi:10.1080/02688690500305555
Watkins S, Sontheimer H (2012) Unique biology of gliomas: challenges and opportunities. Trends Neurosci 35(9):546–556. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2012.05.001
Montana V, Sontheimer H (2011) Bradykinin promotes the chemotactic invasion of primary brain tumors. J Neurosci 31(13):4858–4867. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3825-10.2011
Hsieh HL, Wu CY, Yang CM (2008) Bradykinin induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and cell migration through a PKC-delta-dependent ERK/elk-1 pathway in astrocytes. Glia 56(6):619–632. doi:10.1002/glia.20637
Ifuku M, Farber K, Okuno Y, Yamakawa Y, Miyamoto T, Nolte C, Merrino VF, Kita S et al (2007) Bradykinin-induced microglial migration mediated by B1- bradykinin receptors depends on Ca2+ influx via reverse-mode activity of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. J Neurosci 27(48):13065–13073. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3467- 07.2007
Nicoletti NF, Erig TC, Zanin RF, Pereira TC, Bogo MR, Campos MM, Morrone FB (2014) Mechanisms involved in kinin-induced glioma cells proliferation: the role of ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt pathways. J Neuro-Oncol 120(2):235–244. doi:10.1007/s11060-014-1549-4
Andreansky S, He B, van Cott J, McGhee J, Markert JM, Gillespie GY, Roizman B, Whitley RJ (1998) Treatment of intracranial gliomas in immunocompetent mice using herpes simplex viruses that express murine interleukins. Gene Ther 5(1):121–130. doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3300550
Aulwurm S, Wischhusen J, Friese M, Borst J, Weller M (2006) Immune stimulatory effects of CD70 override CD70-mediated immune cell apoptosis in rodent glioma models and confer long-lasting antiglioma immunity in vivo. Int J Cancer 118(7):1728–1735. doi:10.1002/ijc.21544
Schleicher SM, Thotala DK, Linkous AG, Hu R, Leahy KM, Yazlovitskaya EM, Hallahan DE (2011) Autotaxin and LPA receptors represent potential molecular targets for the radiosensitization of murine glioma through effects on tumor vasculature. PLoS One 6(7):e22182. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022182
Gehring MP, Kipper F, Nicoletti NF, Sperotto ND, Zanin R, Tamajusuku AS, Flores DG, Meurer L et al (2015) P2X7 receptor as predictor gene for glioma radiosensitivity and median survival. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 68:92–100. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2015.09.001
Szatmari T, Lumniczky K, Desaknai S, Trajcevski S, Hidvegi EJ, Hamada H, Safrany G (2006) Detailed characterization of the mouse glioma 261 tumor model for experimental glioblastoma therapy. Cancer Sci 97(6):546–553. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00208.x
Dias JP, Gariépy Hde B, Ongali B, Couture R (2015) Brain kinin B1 receptor is upregulated by the oxidative stress and its activation leads to stereotypic nociceptive behavior in insulin resistant rats. Peptides 69:118–126. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2015.04.022
Quintao NL, Passos GF, Medeiros R, Paszcuk AF, Motta FL, Pesquero JB, Campos MM, Calixto JB (2008) Neuropathic pain-like behavior after brachial plexus avulsion in mice: the relevance of kinin B1 and B2 receptors. J Neurosci 28(11):2856–2863. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4389-07.2008
Costa R, Motta EM, Dutra RC, Manjavachi MN, Bento AF, Malinsky FR, Pesquero JB, Calixto JB (2011) Anti-nociceptive effect of kinin B(1) and B(2) receptor antagonists on peripheral neuropathy induced by paclitaxel in mice. Br J Pharmacol 164(2b):681–693. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01408.x
Lin JC, Talbot S, Lahjouji K, Roy JP, Senecal J, Couture R, Morin A (2010) Mechanism of cigarette smoke-induced kinin B(1) receptor expression in rat airways. Peptides 31(10):1940–1945. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2010.07.008
Ongali B, Campos MM, Bregola G, Rodi D, Regoli D, Thibault G, Simonato M, Couture R (2003) Autoradiographic analysis of rat brain kinin B1 and B2 receptors: normal distribution and alterations induced by epilepsy. J Comp Neurol 461(4):506–519. doi:10.1002/cne.10706
Campos MM, Ongali B, Thibault G, Neugebauer W, Couture R (2005) Autoradiographic distribution and alterations of kinin B(2) receptors in the brain and spinal cord of streptozotocin diabetic rats. Synapse 58(3):184–192. doi:10.1002/syn.20196
Lacoste B, Tong XK, Lahjouji K, Couture R, Hamel E (2013) Cognitive and cerebrovascular improvements following kinin B1 receptor blockade in Alzheimer’s disease mice. J Neuroinflammation 10:57. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-10-57
Gougat, J, Ferrari, B, Sarran, L, Planchenault, C, Poncelet, M, Maruani, J, Alonso, R, Cudennec, A, Croci, T, Guagnini, F, Urban-Szabo, K, Martinolle, JP, Soubrie, P, Finance, O, Le Fur, G (2004) SSR240612 [(2R)-2-[((3R)-3-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-3-[[(6-methoxy-2-naphthyl)sulfonyl]amino]propanoyl)amino]-3-(4-[[2R,6S)-2,6-dimethylpiperidinyl]methyl]phenyl)-N-isopropyl-N-methylpropanamide hydrochloride], a new nonpeptide antagonist of the bradykinin B1 receptor: biochemical and pharmacological characterization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 309 (2):661–669. doi: 10.1124/jpet.103.059527jpet.103.05952726
Gobeil F, Neugebauer W, Filteau C, Jukic D, Allogho SN, Pheng LH, Nguyen-Le XK, Blouin D et al (1996) Structure-activity studies of B1 receptor-related peptides. Antagonists Hypertension 28(5):833–839
Figueroa CD, Ehrenfeld P, Bhoola KD (2012) Kinin receptors as targets for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets 16(3):299–312. doi:10.1517/14728222.2012.662957
Huang Z, Cheng L, Guryanova OA, Wu Q, Bao S (2010) Cancer stem cells in glioblastoma—molecular signaling and therapeutic targeting. Protein Cell 1(7):638–655. doi:10.1007/s13238-010-0078-y
Sarin H, Kanevsky AS, Fung SH, Butman JA, Cox RW, Glen D, Reynolds R, Auh S (2009) Metabolically stable bradykinin B2 receptor agonists enhance transvascular drug delivery into malignant brain tumors by increasing drug half-life. J Transl Med 7:33. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-7-33
Cote J, Savard M, Neugebauer W, Fortin D, Lepage M, Gobeil F (2013) Dual kinin B1 and B2 receptor activation provides enhanced blood-brain barrier permeability and anticancer drug delivery into brain tumors. Cancer Biol Ther 14(9):806–811. doi:10.4161/cbt.25327
Mathieu D, Fortin D (2006) The role of chemotherapy in the treatment of malignant astrocytomas. Can J Neurol Sci 33(2):127–140
Nieder C, Mehta MP, Jalali R (2009) Combined radio- and chemotherapy of brain tumours in adult patients. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 21(7):515–524. doi:10.1016/j.clon.2009.05.003
Thornton E, Ziebell JM, Leonard AV, Vink R (2010) Kinin receptor antagonists as potential neuroprotective agents in central nervous system injury. Molecules 15(9):6598–6618. doi:10.3390/molecules15096598
Austinat M, Braeuninger S, Pesquero JB, Brede M, Bader M, Stoll G, Renne T, Kleinschnitz C (2009) Blockade of bradykinin receptor B1 but not bradykinin receptor B2 provides protection from cerebral infarction and brain edema. Stroke 40(1):285–293. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.526673
Avdieiev S, Gera L, Havrylyuk D, Hodges RS, Lesyk R, Ribrag V, Vassetzky Y, Kavsan V (2014) Bradykinin antagonists and thiazolidinone derivatives as new potential anti-cancer compounds. Bioorg Med Chem 22(15):3815–3823. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2014.06.046
Marceau F, Regoli D (2004) Bradykinin receptor ligands: therapeutic perspectives. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3(10):845–852. doi:10.1038/nrd1522nrd1522
Calixto JB, Cabrini DA, Ferreira J, Campos MM (2000) Kinins in pain and inflammation. Pain 87(1):1–5 doi: S0304-3959(00)00335-3 27
da Costa PL, Sirois P, Tannock IF, Chammas R (2014) The role of kinin receptors in cancer and therapeutic opportunities. Cancer Lett 345(1):27–38. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2013.12.009
Fidler IJ, Balasubramanian K, Lin Q, Kim SW, Kim SJ (2010) The brain microenvironment and cancer metastasis. Mol Cells 30(2):93–98. doi:10.1007/s10059-010-0133-9
Duka A, Kintsurashvili E, Duka I, Ona D, Hopkins TA, Bader M, Gavras I, Gavras H (2008) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition after experimental myocardial infarct: role of the kinin B1 and B2 receptors. Hypertension 51(5):1352–1357. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.108506
Seguin T, Buleon M, Destrube M, Ranera MT, Couture R, Girolami JP, Tack I (2008) Hemodynamic and renal involvement of B1 and B2 kinin receptors during the acute phase of endotoxin shock in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 8(2):217–221 doi: 1016/j.intimp.2007.08.008
Rodi D, Buzzi A, Barbieri M, Zucchini S, Verlengia G, Binaschi A, Regoli D, Boschi A et al (2013) Bradykinin B2 receptors increase hippocampal excitability and susceptibility to seizures in mice. Neuroscience 248C:392–402. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.06.038
Marcon R, Claudino RF, Dutra RC, Bento AF, Schmidt EC, Bouzon ZL, Sordi R, Morais RL et al (2013) Exacerbation of DSS-induced colitis in mice lacking kinin B(1) receptors through compensatory up-regulation kinin B(2) receptors: the role of tight junctions and intestinal homeostasis. Br J Pharmacol 168(2):389–402. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02136.x
Schulze-Topphoff U, Prat A, Prozorovski T, Siffrin V, Paterka M, Herz J, Bendix I, Ifergan I et al (2009) Activation of kinin B1 limits encephalitogenic T lymphocyte recruitment to the central nervous system. Nat Med 15(7):788–793. doi:10.1038/nm.1980
Dillenburg-Pilla P, Maria AG, Reis RI, Floriano EM, Pereira CD, De Lucca FL, Ramos SG, Pesquero JB et al (2013) Activation of the kinin B1 receptor attenuates melanoma tumor growth and metastasis. PLoS One 8(5):e64453. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0064453PONE-D-12-25300
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P (2013) The definition of primary and secondary glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 19(4):764–772. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3002
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mr. Youssef Haddad for his excellent technical assistance in western blot analysis and Mrs. Julie Verner for her technical support in cell culture at the Université de Montréal. We recognize the expert technical assistance of Mrs. Janaína Silva in the immunohistochemistry analysis. We are grateful to Dr. Marcelo Paglioli Ferreira, Dr. Paulo Valdeci Worm, and Dr. Jorge Luiz Kraemer, from the Department of Neurosurgery, São José Hospital—ISCMPA (Brazil), for donating the human tissue specimens.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All the experimental procedures were in accord to the Principles of Laboratory Animal Care from NIH and approved by the Animal Ethical Committee of the Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil (protocol number 11/00258) and Université de Montréal, Canada (protocol number 13-040).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Financial Support
This study was supported by the FINEP research grant “Implantação, Modernização e Qualificação de Estrutura de Pesquisa da PUCRS” (PUCRSINFRA) no. 01.11.0014-00, CNPq, CAPES, and FAPERGS and by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research to RC (MOP-119329).
NFN was a PhD student in Cellular and Molecular Biology receiving a grant from CAPES (AUX-PE/Toxinologia), CAPES/PDSE, and PROBOLSAS/PUCRS.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nicoletti, N.F., Sénécal, J., da Silva, V.D. et al. Primary Role for Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors in Glioma Proliferation. Mol Neurobiol 54, 7869–7882 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0265-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0265-9