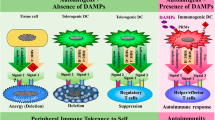
Abstract
Although autoimmune diseases by definition imply adaptive immune system pathologies, growing evidence points to the relevance of innate receptors in modulating the initiation and progression of the autoreactive response. Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterised by central nervous system (CNS) demyelination, inflammation and axonal damage, in which the role of several pathogens such as herpes viruses have long been described as potential triggers. Encounters of these pathogens with altered innate receptors in susceptible individuals might drive pathological autoreactivity and inflammation, overcoming tolerance and causing subsequent CNS damage. In particular, functional and genetic studies reveal that Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 and the Nod-like receptor (NLR) P3 could be involved in MS pathogenesis, whereas TLR3, the triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells (TREM)-2 and the C-type lectin receptors (CLRs) MBL and MASP-3 would have a putative protective role. A better understanding of these interactions will provide important insights into the aetiopathogenesis of MS and could help design potential targets for novel therapies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Piccinini AM, Midwood KS (2011) DAMPening inflammation by modulating TLR signalling. Mediators Inflamm 2010
Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R, Flavell RA (2001) Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 413(6857):732–738
Hemmi H, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Kaisho T, Sato S, Sanjo H, Matsumoto M, Hoshino K et al (2000) A Toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature 408(6813):740–745
Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Sanjo H, Copeland NG, Gilbert DJ, Jenkins NA, Takeda K, Akira S (1999) TLR6: a novel member of an expanding toll-like receptor family. Gene 231(1–2):59–65
Wang T, Town T, Alexopoulou L, Anderson JF, Fikrig E, Flavell RA (2004) Toll-like receptor 3 mediates West Nile virus entry into the brain causing lethal encephalitis. Nat Med 10(12):1366–1373
Akira S, Sato S (2003) Toll-like receptors and their signaling mechanisms. Scand J Infect Dis 35(9):555–562
Galdiero M, Galdiero M, Finamore E, Rossano F, Gambuzza M, Catania MR, Teti G, Midiri A et al (2004) Haemophilus influenzae porin induces Toll-like receptor 2-mediated cytokine production in human monocytes and mouse macrophages. Infect Immun 72(2):1204–1209
WHO (2008) Atlas: multiple sclerosis resources in the world 2008
Milo R, Kahana E (2010) Multiple sclerosis: geoepidemiology, genetics and the environment. Autoimmun Rev 9(5):A387–A394
Schmidt H, Williamson D, Ashley-Koch A (2007) HLA-DR15 haplotype and multiple sclerosis: a HuGE review. Am J Epidemiol 165(10):1097–1109
Ascherio A (2013) Environmental factors in multiple sclerosis. Expert Rev Neurother 13(12 Suppl):3–9
Rahal EA, Hajjar H, Rajeh M, Yamout B, Abdelnoor AM (2015) Epstein-Barr virus and human herpes virus 6 type a DNA enhance IL-17 production in mice. Viral Immunol 28(5):297–302
Sharma S, Rajasagi NK, Veiga-Parga T, Rouse BT (2014) Herpes virus entry mediator (HVEM) modulates proliferation and activation of regulatory T cells following HSV-1 infection. Microbes Infect 16(8):648–660
Ascherio A, Munger KL, Lennette ET, Spiegelman D, Hernan MA, Olek MJ, Hankinson SE, Hunter DJ (2001) Epstein-Barr virus antibodies and risk of multiple sclerosis: a prospective study. JAMA 286(24):3083–3088
Levin LI, Munger KL, Rubertone MV, Peck CA, Lennette ET, Spiegelman D, Ascherio A (2005) Temporal relationship between elevation of Epstein-Barr virus antibody titers and initial onset of neurological symptoms in multiple sclerosis. JAMA 293(20):2496–2500
Lunemann JD, Edwards N, Muraro PA, Hayashi S, Cohen JI, Munz C, Martin R (2006) Increased frequency and broadened specificity of latent EBV nuclear antigen-1-specific T cells in multiple sclerosis. Brain 129(Pt 6):1493–1506
Ablashi DV, Balachandran N, Josephs SF, Hung CL, Krueger GR, Kramarsky B, Salahuddin SZ, Gallo RC (1991) Genomic polymorphism, growth properties, and immunologic variations in human herpesvirus-6 isolates. Virology 184(2):545–552
Ablashi DV, Lapps W, Kaplan M, Whitman JE, Richert JR, Pearson GR (1998) Human Herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6) infection in multiple sclerosis: a preliminary report. Mult Scler 4(6):490–496
Ablashi DV, Marsh S, Kaplan M, Whitman JE Jr, Pearson GR (1998) HHV-6 infection in HIV-infected asymptomatic and AIDS patients. Intervirology 41(1):1–9
Braun DK, Dominguez G, Pellett PE (1997) Human herpesvirus 6. Clin Microbiol Rev 10(3):521–567
Challoner PB, Smith KT, Parker JD, MacLeod DL, Coulter SN, Rose TM, Schultz ER, Bennett JL et al (1995) Plaque-associated expression of human herpesvirus 6 in multiple sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92(16):7440–7444
Yamanishi K (1992) Human herpesvirus 6. Microbiol Immunol 36(6):551–561
Alvarez-Lafuente R, De las Heras V, Bartolome M, Picazo JJ, Arroyo R (2004) Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis and human herpesvirus 6 active infection. Arch Neurol 61(10):1523–1527
Babbe H, Roers A, Waisman A, Lassmann H, Goebels N, Hohlfeld R, Friese M, Schroder R et al (2000) Clonal expansions of CD8(+) T cells dominate the T cell infiltrate in active multiple sclerosis lesions as shown by micromanipulation and single cell polymerase chain reaction. J Exp Med 192(3):393–404
Jacobsen M, Cepok S, Quak E, Happel M, Gaber R, Ziegler A, Schock S, Oertel WH et al (2002) Oligoclonal expansion of memory CD8+ T cells in cerebrospinal fluid from multiple sclerosis patients. Brain 125(Pt 3):538–550
Simpson S Jr, Taylor B, Dwyer DE, Taylor J, Blizzard L, Ponsonby AL, Pittas F, Dwyer T et al (2012) Anti-HHV-6 IgG titer significantly predicts subsequent relapse risk in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 18(6):799–806
Soldan SS, Berti R, Salem N, Secchiero P, Flamand L, Calabresi PA, Brennan MB, Maloni HW et al (1997) Association of human herpes virus 6 (HHV-6) with multiple sclerosis: increased IgM response to HHV-6 early antigen and detection of serum HHV-6 DNA. Nat Med 3(12):1394–1397
Murakami Y, Tanimoto K, Fujiwara H, An J, Suemori K, Ochi T, Hasegawa H, Yasukawa M (2010) Human herpesvirus 6 infection impairs Toll-like receptor signaling. Virol J 7:91
Sotelo J, Corona T (2011) Varicella zoster virus and relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Int 2011:214763
Ordonez G, Martinez-Palomo A, Corona T, Pineda B, Flores-Rivera J, Gonzalez A, Chavez-Munguia B, Sotelo J (2010) Varicella zoster virus in progressive forms of multiple sclerosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 112(8):653–657
Pucci E, Taus C, Cartechini E, Morelli M, Giuliani G, Clementi M, Menzo S (2000) Lack of Chlamydia infection of the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 48(3):399–400
Sriram S, Stratton CW, Yao S, Tharp A, Ding L, Bannan JD, Mitchell WM (1999) Chlamydia pneumoniae infection of the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 46(1):6–14
Correale J, Farez M (2007) Monocyte-derived dendritic cells in multiple sclerosis: the effect of bacterial infection. J Neuroimmunol 190(1–2):177–189
Herrmann I, Kellert M, Spreer A, Gerber J, Eiffert H, Prinz M, Nau R (2007) Minocycline delays but does not attenuate the course of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in Streptococcus pneumoniae-infected mice. J Antimicrob Chemother 59(1):74–79
Smits HH, Everts B, Hartgers FC, Yazdanbakhsh M (2010) Chronic helminth infections protect against allergic diseases by active regulatory processes. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 10(1):3–12
Lunemann JD, Jelcic I, Roberts S, Lutterotti A, Tackenberg B, Martin R, Munz C (2008) EBNA1-specific T cells from patients with multiple sclerosis cross react with myelin antigens and co-produce IFN-gamma and IL-2. J Exp Med 205(8):1763–1773
Serafini B, Rosicarelli B, Franciotta D, Magliozzi R, Reynolds R, Cinque P, Andreoni L, Trivedi P et al (2007) Dysregulated Epstein-Barr virus infection in the multiple sclerosis brain. J Exp Med 204(12):2899–2912
Blander JM, Torchinsky MB, Campisi L (2012) Revisiting the old link between infection and autoimmune disease with commensals and T helper 17 cells. Immunol Res 54(1–3):50–68
Fujinami RS, Oldstone MB, Wroblewska Z, Frankel ME, Koprowski H (1983) Molecular mimicry in virus infection: crossreaction of measles virus phosphoprotein or of herpes simplex virus protein with human intermediate filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 80(8):2346–2350
Fujinami RS, von Herrath MG, Christen U, Whitton JL (2006) Molecular mimicry, bystander activation, or viral persistence: infections and autoimmune disease. Clin Microbiol Rev 19(1):80–94
Oldstone MB (1987) Molecular mimicry and autoimmune disease. Cell 50(6):819–820
Vanderlugt CJ, Miller SD (1996) Epitope spreading. Curr Opin Immunol 8(6):831–836
Pender MP (2003) Infection of autoreactive B lymphocytes with EBV, causing chronic autoimmune diseases. Trends Immunol 24(11):584–588
Peltier DC, Simms A, Farmer JR, Miller DJ (2010) Human neuronal cells possess functional cytoplasmic and TLR-mediated innate immune pathways influenced by phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase signaling. J Immunol 184(12):7010–7021
Bsibsi M, Persoon-Deen C, Verwer RW, Meeuwsen S, Ravid R, Van Noort JM (2006) Toll-like receptor 3 on adult human astrocytes triggers production of neuroprotective mediators. Glia 53(7):688–695
Kim H, Yang E, Lee J, Kim SH, Shin JS, Park JY, Choi SJ, Kim SJ et al (2008) Double-stranded RNA mediates interferon regulatory factor 3 activation and interleukin-6 production by engaging Toll-like receptor 3 in human brain astrocytes. Immunology 124(4):480–488
McCarthy DP, Richards MH, Miller SD (2012) Mouse models of multiple sclerosis: experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and Theiler’s virus-induced demyelinating disease. Methods Mol Biol 900:381–401
Cook SD, Dowling PC (1980) Multiple sclerosis and viruses: an overview. Neurology 30(7 Pt 2):80–91
Touil T, Fitzgerald D, Zhang GX, Rostami A, Gran B (2006) Cutting Edge: TLR3 stimulation suppresses experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inducing endogenous IFN-beta. J Immunol 177(11):7505–7509
Ellestad KK, Tsutsui S, Noorbakhsh F, Warren KG, Yong VW, Pittman QJ, Power C (2009) Early life exposure to lipopolysaccharide suppresses experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by promoting tolerogenic dendritic cells and regulatory T cells. J Immunol 183(1):298–309
Marta M, Andersson A, Isaksson M, Kampe O, Lobell A (2008) Unexpected regulatory roles of TLR4 and TLR9 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol 38(2):565–575
Hamerman JA, Jarjoura JR, Humphrey MB, Nakamura MC, Seaman WE, Lanier LL (2006) Cutting edge: inhibition of TLR and FcR responses in macrophages by triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells (TREM)-2 and DAP12. J Immunol 177(4):2051–2055
Piccio L, Buonsanti C, Mariani M, Cella M, Gilfillan S, Cross AH, Colonna M, Panina-Bordignon P (2007) Blockade of TREM-2 exacerbates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol 37(5):1290–1301
Takahashi K, Rochford CD, Neumann H (2005) Clearance of apoptotic neurons without inflammation by microglial triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-2. J Exp Med 201(4):647–657
Turnbull IR, Gilfillan S, Cella M, Aoshi T, Miller M, Piccio L, Hernandez M, Colonna M (2006) Cutting edge: TREM-2 attenuates macrophage activation. J Immunol 177(6):3520–3524
Back SA, Tuohy TM, Chen H, Wallingford N, Craig A, Struve J, Luo NL, Banine F et al (2005) Hyaluronan accumulates in demyelinated lesions and inhibits oligodendrocyte progenitor maturation. Nat Med 11(9):966–972
Hanafy KA, Sloane JA (2011) Regulation of remyelination in multiple sclerosis. FEBS Lett 585(23):3821–3828
Sloane JA, Batt C, Ma Y, Harris ZM, Trapp B, Vartanian T (2010) Hyaluronan blocks oligodendrocyte progenitor maturation and remyelination through TLR2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(25):11555–11560
Soulika AM, Lee E, McCauley E, Miers L, Bannerman P, Pleasure D (2009) Initiation and progression of axonopathy in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neurosci 29(47):14965–14979
Olson JK, Miller SD (2004) Microglia initiate central nervous system innate and adaptive immune responses through multiple TLRs. J Immunol 173(6):3916–3924
Clatch RJ, Miller SD, Metzner R, Dal Canto MC, Lipton HL (1990) Monocytes/macrophages isolated from the mouse central nervous system contain infectious Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus (TMEV). Virology 176(1):244–254
Dal Canto MC, Lipton HL (1975) Primary demyelination in Theiler’s virus infection. An ultrastructural study. Lab Invest 33(6):626–637
Olson JK (2014) Effect of the innate immune response on development of Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus-induced demyelinating disease. J Neurovirol 20(5):427–436
Singh MK, Scott TF, LaFramboise WA, Hu FZ, Post JC, Ehrlich GD (2007) Gene expression changes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from multiple sclerosis patients undergoing beta-interferon therapy. J Neurol Sci 258(1–2):52–59
Wolf NA, Amouzegar TK, Swanborg RH (2007) Synergistic interaction between Toll-like receptor agonists is required for induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats. J Neuroimmunol 185(1–2):115–122
Bsibsi M, Ravid R, Gveric D, van Noort JM (2002) Broad expression of Toll-like receptors in the human central nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61(11):1013–1021
Saresella M, Gatti A, Tortorella P, Marventano I, Piancone F, La Rosa F, Caputo D, Rovaris M et al (2014) Toll-like receptor 3 differently modulates inflammation in progressive or benign multiple sclerosis. Clin Immunol 150(1):109–120
Derkow K, Bauer JM, Hecker M, Paap BK, Thamilarasan M, Koczan D, Schott E, Deuschle K et al (2013) Multiple sclerosis: modulation of toll-like receptor (TLR) expression by interferon-beta includes upregulation of TLR7 in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. PLoS One 8(8), e70626
Johnson TP, Tyagi R, Patel K, Schiess N, Calabresi PA, Nath A (2013) Impaired toll-like receptor 8 signaling in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroinflammation 10:74
Wandstrat A, Wakeland E (2001) The genetics of complex autoimmune diseases: non-MHC susceptibility genes. Nat Immunol 2(9):802–809
Christensen T, Petersen T, Thiel S, Brudek T, Ellermann-Eriksen S, Moller-Larsen A (2007) Gene-environment interactions in multiple sclerosis: innate and adaptive immune responses to human endogenous retrovirus and herpesvirus antigens and the lectin complement activation pathway. J Neuroimmunol 183(1–2):175–188
Piccio L, Buonsanti C, Cella M, Tassi I, Schmidt RE, Fenoglio C, Rinker J 2nd, Naismith RT et al (2008) Identification of soluble TREM-2 in the cerebrospinal fluid and its association with multiple sclerosis and CNS inflammation. Brain 131(Pt 11):3081–3091
Blasius AL, Cella M, Maldonado J, Takai T, Colonna M (2006) Siglec-H is an IPC-specific receptor that modulates type I IFN secretion through DAP12. Blood 107(6):2474–2476
Watarai H, Sekine E, Inoue S, Nakagawa R, Kaisho T, Taniguchi M (2008) PDC-TREM, a plasmacytoid dendritic cell-specific receptor, is responsible for augmented production of type I interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(8):2993–2998
Hayward JH, Lee SJ (2014) A decade of research on TLR2 discovering its pivotal role in glial activation and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Exp Neurobiol 23(2):138–147
Rajbhandari L, Tegenge MA, Shrestha S, Ganesh Kumar N, Malik A, Mithal A, Hosmane S, Venkatesan A (2014) Toll-like receptor 4 deficiency impairs microglial phagocytosis of degenerating axons. Glia 62(12):1982–1991
Andersson A, Covacu R, Sunnemark D, Danilov AI, Dal Bianco A, Khademi M, Wallstrom E, Lobell A et al (2008) Pivotal advance: HMGB1 expression in active lesions of human and experimental multiple sclerosis. J Leukoc Biol 84(5):1248–1255
Swanberg M, Lidman O, Padyukov L, Eriksson P, Akesson E, Jagodic M, Lobell A, Khademi M et al (2005) MHC2TA is associated with differential MHC molecule expression and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and myocardial infarction. Nat Genet 37(5):486–494
Martinez A, Sanchez-Lopez M, Varade J, Mas A, Martin MC, de Las Heras V, Arroyo R, Mendoza JL et al (2007) Role of the MHC2TA gene in autoimmune diseases. Ann Rheum Dis 66(3):325–329
Willingham SB, Allen IC, Bergstralh DT, Brickey WJ, Huang MT, Taxman DJ, Duncan JA, Ting JP (2009) NLRP3 (NALP3, Cryopyrin) facilitates in vivo caspase-1 activation, necrosis, and HMGB1 release via inflammasome-dependent and -independent pathways. J Immunol 183(3):2008–2015
Guo B, Chang EY, Cheng G (2008) The type I IFN induction pathway constrains Th17-mediated autoimmune inflammation in mice. J Clin Invest 118(5):1680–1690
Dann A, Poeck H, Croxford AL, Gaupp S, Kierdorf K, Knust M, Pfeifer D, Maihoefer C et al (2011) Cytosolic RIG-I-like helicases act as negative regulators of sterile inflammation in the CNS. Nat Neurosci 15(1):98–106
Kalinke U, Prinz M (2012) Endogenous, or therapeutically induced, type I interferon responses differentially modulate Th1/Th17-mediated autoimmunity in the CNS. Immunol Cell Biol 90(5):505–509
Yan Y, Zhang GX, Gran B, Fallarino F, Yu S, Li H, Cullimore ML, Rostami A et al (2010) IDO upregulates regulatory T cells via tryptophan catabolite and suppresses encephalitogenic T cell responses in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 185(10):5953–5961
Herrmann I, Kellert M, Schmidt H, Mildner A, Hanisch UK, Bruck W, Prinz M, Nau R (2006) Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection aggravates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis via Toll-like receptor 2. Infect Immun 74(8):4841–4848
Visser L, Jan de Heer H, Boven LA, van Riel D, van Meurs M, Melief MJ, Zahringer U, van Strijp J et al (2005) Proinflammatory bacterial peptidoglycan as a cofactor for the development of central nervous system autoimmune disease. J Immunol 174(2):808–816
Aloisi F, Serafini B, Magliozzi R, Howell OW, Reynolds R (2010) Detection of Epstein-Barr virus and B-cell follicles in the multiple sclerosis brain: what you find depends on how and where you look. Brain 133(Pt 12), e157
Reynolds JM, Pappu BP, Peng J, Martinez GJ, Zhang Y, Chung Y, Ma L, Yang XO et al (2010) Toll-like receptor 2 signaling in CD4(+) T lymphocytes promotes T helper 17 responses and regulates the pathogenesis of autoimmune disease. Immunity 32(5):692–702
Reynolds JM, Martinez GJ, Chung Y, Dong C (2012) Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in T cells promotes autoimmune inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(32):13064–13069
Mellanby RJ, Cambrook H, Turner DG, O’Connor RA, Leech MD, Kurschus FC, MacDonald AS, Arnold B et al (2012) TLR-4 ligation of dendritic cells is sufficient to drive pathogenic T cell function in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroinflammation 9:248
Prinz M, Garbe F, Schmidt H, Mildner A, Gutcher I, Wolter K, Piesche M, Schroers R et al (2006) Innate immunity mediated by TLR9 modulates pathogenicity in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. J Clin Invest 116(2):456–464
Gris D, Ye Z, Iocca HA, Wen H, Craven RR, Gris P, Huang M, Schneider M et al (2010) NLRP3 plays a critical role in the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by mediating Th1 and Th17 responses. J Immunol 185(2):974–981
Inoue M, Williams KL, Gunn MD, Shinohara ML (2012) NLRP3 inflammasome induces chemotactic immune cell migration to the CNS in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(26):10480–10485
Furlan R, Martino G, Galbiati F, Poliani PL, Smiroldo S, Bergami A, Desina G, Comi G et al (1999) Caspase-1 regulates the inflammatory process leading to autoimmune demyelination. J Immunol 163(5):2403–2409
Jacobs CA, Baker PE, Roux ER, Picha KS, Toivola B, Waugh S, Kennedy MK (1991) Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis is exacerbated by IL-1 alpha and suppressed by soluble IL-1 receptor. J Immunol 146(9):2983–2989
Lampropoulou V, Hoehlig K, Roch T, Neves P, Calderon Gomez E, Sweenie CH, Hao Y, Freitas AA et al (2008) TLR-activated B cells suppress T cell-mediated autoimmunity. J Immunol 180(7):4763–4773
Bar-Or A, Fawaz L, Fan B, Darlington PJ, Rieger A, Ghorayeb C, Calabresi PA, Waubant E et al (2010) Abnormal B-cell cytokine responses a trigger of T-cell-mediated disease in MS? Ann Neurol 67(4):452–461
Hirotani M, Niino M, Fukazawa T, Kikuchi S, Yabe I, Hamada S, Tajima Y, Sasaki H (2010) Decreased IL-10 production mediated by Toll-like receptor 9 in B cells in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 221(1–2):95–100
Ayyoub M, Deknuydt F, Raimbaud I, Dousset C, Leveque L, Bioley G, Valmori D (2009) Human memory FOXP3+ Tregs secrete IL-17 ex vivo and constitutively express the T(H)17 lineage-specific transcription factor RORgamma t. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(21):8635–8640
Bach JF (2005) Infections and autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun 25(Suppl):74–80
Beriou G, Costantino CM, Ashley CW, Yang L, Kuchroo VK, Baecher-Allan C, Hafler DA (2009) IL-17-producing human peripheral regulatory T cells retain suppressive function. Blood 113(18):4240–4249
Liu H, Komai-Koma M, Xu D, Liew FY (2006) Toll-like receptor 2 signaling modulates the functions of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(18):7048–7053
Miyara M, Yoshioka Y, Kitoh A, Shima T, Wing K, Niwa A, Parizot C, Taflin C et al (2009) Functional delineation and differentiation dynamics of human CD4+ T cells expressing the FoxP3 transcription factor. Immunity 30(6):899–911
Nyirenda MH, Sanvito L, Darlington PJ, O’Brien K, Zhang GX, Constantinescu CS, Bar-Or A, Gran B (2011) TLR2 stimulation drives human naive and effector regulatory T cells into a Th17-like phenotype with reduced suppressive function. J Immunol 187(5):2278–2290
Sutmuller RP, den Brok MH, Kramer M, Bennink EJ, Toonen LW, Kullberg BJ, Joosten LA, Akira S et al (2006) Toll-like receptor 2 controls expansion and function of regulatory T cells. J Clin Invest 116(2):485–494
Sutmuller RP, Morgan ME, Netea MG, Grauer O, Adema GJ (2006) Toll-like receptors on regulatory T cells: expanding immune regulation. Trends Immunol 27(8):387–393
Mercier BC, Cottalorda A, Coupet CA, Marvel J, Bonnefoy-Berard N (2009) TLR2 engagement on CD8 T cells enables generation of functional memory cells in response to a suboptimal TCR signal. J Immunol 182(4):1860–1867
Jack CS, Arbour N, Manusow J, Montgrain V, Blain M, McCrea E, Shapiro A, Antel JP (2005) TLR signaling tailors innate immune responses in human microglia and astrocytes. J Immunol 175(7):4320–4330
Li Y, Chu N, Hu A, Gran B, Rostami A, Zhang GX (2007) Increased IL-23p19 expression in multiple sclerosis lesions and its induction in microglia. Brain 130(Pt 2):490–501
de Jong BA, Huizinga TW, Bollen EL, Uitdehaag BM, Bosma GP, van Buchem MA, Remarque EJ, Burgmans AC et al (2002) Production of IL-1beta and IL-1Ra as risk factors for susceptibility and progression of relapse-onset multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 126(1–2):172–179
Huang WX, Huang P, Hillert J (2004) Increased expression of caspase-1 and interleukin-18 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 10(5):482–487
Schrijver HM, Crusius JB, Uitdehaag BM, Garcia Gonzalez MA, Kostense PJ, Polman CH, Pena AS (1999) Association of interleukin-1beta and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist genes with disease severity in MS. Neurology 52(3):595–599
Zhang X, Jin J, Tang Y, Speer D, Sujkowska D, Markovic-Plese S (2009) IFN-beta1a inhibits the secretion of Th17-polarizing cytokines in human dendritic cells via TLR7 up-regulation. J Immunol 182(6):3928–3936
Fernald GH, Knott S, Pachner A, Caillier SJ, Narayan K, Oksenberg JR, Mousavi P, Baranzini SE (2007) Genome-wide network analysis reveals the global properties of IFN-beta immediate transcriptional effects in humans. J Immunol 178(8):5076–5085
Bustamante MF, Fissolo N, Rio J, Espejo C, Costa C, Mansilla MJ, Lizasoain I, Moro MA et al (2011) Implication of the Toll-like receptor 4 pathway in the response to interferon-beta in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 70(4):634–645
Aung LL, Fitzgerald-Bocarsly P, Dhib-Jalbut S, Balashov K (2010) Plasmacytoid dendritic cells in multiple sclerosis: chemokine and chemokine receptor modulation by interferon-beta. J Neuroimmunol 226(1–2):158–164
Balashov KE, Aung LL, Vaknin-Dembinsky A, Dhib-Jalbut S, Weiner HL (2010) Interferon-beta inhibits toll-like receptor 9 processing in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 68(6):899–906
Coccia EM, Severa M, Giacomini E, Monneron D, Remoli ME, Julkunen I, Cella M, Lande R et al (2004) Viral infection and Toll-like receptor agonists induce a differential expression of type I and lambda interferons in human plasmacytoid and monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol 34(3):796–805
Hundeshagen A, Hecker M, Paap BK, Angerstein C, Kandulski O, Fatum C, Hartmann C, Koczan D et al (2012) Elevated type I interferon-like activity in a subset of multiple sclerosis patients: molecular basis and clinical relevance. J Neuroinflammation 9:140
Liu YJ (2005) IPC: professional type 1 interferon-producing cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cell precursors. Annu Rev Immunol 23:275–306
Inoue M, Shinohara ML (2013) The role of interferon-beta in the treatment of multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis - in the perspective of inflammasomes. Immunology 139(1):11–18
Enevold C, Oturai AB, Sorensen PS, Ryder LP, Koch-Henriksen N, Bendtzen K (2010) Polymorphisms of innate pattern recognition receptors, response to interferon-beta and development of neutralizing antibodies in multiple sclerosis patients. Mult Scler 16(8):942–949
Hayashi T, Gray CS, Chan M, Tawatao RI, Ronacher L, McGargill MA, Datta SK, Carson DA et al (2009) Prevention of autoimmune disease by induction of tolerance to Toll-like receptor 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(8):2764–2769
O’Brien K, Fitzgerald D, Rostami A, Gran B (2010) The TLR7 agonist, imiquimod, increases IFN-beta production and reduces the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 221(1–2):107–111
Al-Katib A, Arnold AA, Aboukameel A, Sosin A, Smith P, Mohamed AN, Beck FW, Mohammad RM (2010) I-kappa-kinase-2 (IKK-2) inhibition potentiates vincristine cytotoxicity in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Mol Cancer 9:228
Connolly DJ, O’Neill LA (2012) New developments in Toll-like receptor targeted therapeutics. Curr Opin Pharmacol 12(4):510–518
O’Neill LA, Bryant CE, Doyle SL (2009) Therapeutic targeting of Toll-like receptors for infectious and inflammatory diseases and cancer. Pharmacol Rev 61(2):177–197
Sun L, Wu J, Du F, Chen X, Chen ZJ (2013) Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science 339(6121):786–791
Smith CM, Wilson NS, Waithman J, Villadangos JA, Carbone FR, Heath WR, Belz GT (2004) Cognate CD4(+) T cell licensing of dendritic cells in CD8(+) T cell immunity. Nat Immunol 5(11):1143–1148
Cameron JS, Alexopoulou L, Sloane JA, DiBernardo AB, Ma Y, Kosaras B, Flavell R, Strittmatter SM et al (2007) Toll-like receptor 3 is a potent negative regulator of axonal growth in mammals. J Neurosci 27(47):13033–13041
Kim D, Kim MA, Cho IH, Kim MS, Lee S, Jo EK, Choi SY, Park K et al (2007) A critical role of toll-like receptor 2 in nerve injury-induced spinal cord glial cell activation and pain hypersensitivity. J Biol Chem 282(20):14975–14983
Lafon M, Megret F, Lafage M, Prehaud C (2006) The innate immune facet of brain: human neurons express TLR-3 and sense viral dsRNA. J Mol Neurosci 29(3):185–194
Tang SC, Arumugam TV, Xu X, Cheng A, Mughal MR, Jo DG, Lathia JD, Siler DA et al (2007) Pivotal role for neuronal Toll-like receptors in ischemic brain injury and functional deficits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(34):13798–13803
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the FEDER-FIS, Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria of the Spanish Health, Social Services and Equality Ministry (FIS project #PI12/02759), the Ramon Areces Foundation, grant XVII Concurso Nacional de Ayudas a la Investigación and FIS grant Ref. PI14/00616; R.P.D. is supported by the “Ramon y Cajal” program (MINECO, Spain). We are grateful to Marina Lorne for her assistance with figure design.
Conflict of interest
The authors state no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández-Paredes, L., de Diego, R.P., de Andrés, C. et al. Close Encounters of the First Kind: Innate Sensors and Multiple Sclerosis. Mol Neurobiol 54, 101–114 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9665-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9665-5