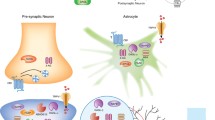
Abstract
The endocannabinoid system consists of cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors, endogenous ligands and their synthesising/metabolising enzymes. Cannabinoid receptors are present at key sites involved in the relay and modulation of nociceptive information. The analgesic effects of cannabinoids have been well documented. The usefulness of nonselective cannabinoid agonists can, however, be limited by psychoactive side effects associated with activation of CB1 receptors. Following the recent evidence for CB2 receptors existing in the nervous system and reports of their up-regulation in chronic pain states and neurodegenerative diseases, much research is now aimed at shedding light on the role of the CB2 receptor in human disease. Recent studies have demonstrated anti-nociceptive effects of selective CB2 receptor agonists in animal models of pain in the absence of CNS side effects. This review focuses on the analgesic potential of CB2 receptor agonists for inflammatory, post-operative and neuropathic pain states and discusses their possible sites and mechanisms of action.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SNL:
-
spinal nerve ligation
- CCI:
-
chronic constriction injury
- CB1 :
-
cannabinoid CB1 receptor
- CB2 :
-
cannabinoid CB2 receptor
- DRG:
-
dorsal root ganglion
- PEA:
-
palmitoyl ethanolamide
References
Gaoni Y, Mechoulam R (1964) Isolation, structure and partial synthesis of an active constituent of hashish. J Am Chem Soc 86:1646–1647
Matsuda LA, Lolait SJ, Brownstein MJ, Young AC, Bonner TI (1990) Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature 346:561–564
Munro S, Thomas KL, Abu-Shaar M (1993) Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nature 365:61–65
Gerard CM, Mollereau C, Vassart G, Parmentier M (1991) Molecular cloning of a human cannabinoid receptor which is also expressed in testis. Biochem J 279:129–134
Chakrabarti A, Onaivi ES, Chaudhuri G (1995) Cloning and sequencing of a cDNA encoding the mouse brain-type cannabinoid receptor protein. DNA Seq 5:385–388
Shire D, Calandra B, Rinaldi-Carmona M, Oustric D, Pessegue B, Bonnin-Cabanne O, Le Fur G, Caput D, Ferrara P (1996) Molecular cloning, expression and function of the murine CB2 peripheral cannabinoid receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta 1307:132–136
Griffin G, Tao Q, Abood ME (2000) Cloning and pharmacological characterization of the rat CB(2) cannabinoid receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 292:886–894
Howlett AC, Barth F, Bonner TI, Cabral G, Casellas P, Devane WA, Felder CC, Herkenham M, Mackie K, Martin BR, Mechoulam R, Pertwee RG (2002) International Union of Pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol Rev 54:161–202
Walker JM, Huang SM (2002) Cannabinoid analgesia. Pharmacol Ther 95:127–135
Pertwee RG (2001) Cannabinoid receptors and pain. Prog Neurobiol 63:569–611
Rice AS, Farquhar-Smith WP, Nagy I (2002) Endocannabinoids and pain: spinal and peripheral analgesia in inflammation and neuropathy. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 66:243–256
Hohmann AG (2002) Spinal and peripheral mechanisms of cannabinoid antinociception: behavioral, neurophysiological and neuroanatomical perspectives. Chem Phys Lipids 121:173–190
Walker JM, Krey JF, Chu CJ, Huang SM (2002) Endocannabinoids and related fatty acid derivatives in pain modulation. Chem Phys Lipids 121:159–172
Mackie K (2006) Cannabinoid receptors as therapeutic targets. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 46:101–122
Malan TP Jr, Ibrahim MM, Lai J, Vanderah TW, Makriyannis A, Porreca F (2003) CB2 cannabinoid receptor agonists: pain relief without psychoactive effects? Curr Opin Pharmacol 3:62–67
Chapman V, Finn DP (2003) Analgesic effects of cannabinoids: sites and mechanisms of action. Rev Analg 7:25–39
Finn DP, Chapman V (2004) Cannabinoids as analgesic agents: evidence from in vivo studies. Curr Neuropharmacol 2:75–89
Tsou K, Brown S, Sanudo-Pena MC, Mackie K, Walker JM (1998) Immunohistochemical distribution of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 83:393–411
Egertova M, Elphick MR (2000) Localisation of cannabinoid receptors in the rat brain using antibodies to the intracellular C-terminal tail of CB. J Comp Neurol 422:159–171
Herkenham M, Lynn AB, Johnson MR, Melvin LS, de Costa BR, Rice KC (1991) Characterization and localization of cannabinoid receptors in rat brain: a quantitative in vitro autoradiographic study. J Neurosci 11:563–583
Ross RA, Coutts AA, McFarlane SM, Anavi-Goffer S, Irving AJ, Pertwee RG, MacEwan DJ, Scott RH (2001) Actions of cannabinoid receptor ligands on rat cultured sensory neurones: implications for antinociception. Neuropharmacology 40:221–232
Hohmann AG, Herkenham M (1999) Cannabinoid receptors undergo axonal flow in sensory nerves. Neuroscience 92:1171–1175
Galiegue S, Mary S, Marchand J, Dussossoy D, Carriere D, Carayon P, Bouaboula M, Shire D, Le Fur G, Casellas P (1995) Expression of central and peripheral cannabinoid receptors in human immune tissues and leukocyte subpopulations. Eur J Biochem 232:54–61
Nunez E, Benito C, Pazos MR, Barbachano A, Fajardo O, Gonzalez S, Tolon RM, Romero J (2004) Cannabinoid CB2 receptors are expressed by perivascular microglial cells in the human brain: an immunohistochemical study. Synapse 53:208–213
Carlisle SJ, Marciano-Cabral F, Staab A, Ludwick C, Cabral GA (2002) Differential expression of the CB2 cannabinoid receptor by rodent macrophages and macrophage-like cells in relation to cell activation. Int Immunopharmacol 2:69–82
Carrier EJ, Kearn CS, Barkmeier AJ, Breese NM, Yang W, Nithipatikom K, Pfister SL, Campbell WB, Hillard CJ (2004) Cultured rat microglial cells synthesize the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonylglycerol, which increases proliferation via a CB2 receptor-dependent mechanism. Mol Pharmacol 65:999–1007
Facchinetti F, Del Giudice E, Furegato S, Passarotto M, Leon A (2003) Cannabinoids ablate release of TNFalpha in rat microglial cells stimulated with lypopolysaccharide. Glia 41:161–168
Klegeris A, Bissonnette CJ, McGeer PL (2003) Reduction of human monocytic cell neurotoxicity and cytokine secretion by ligands of the cannabinoid-type CB2 receptor. Br J Pharmacol 139:775–786
Walter L, Franklin A, Witting A, Wade C, Xie Y, Kunos G, Mackie K, Stella N (2003) Nonpsychotropic cannabinoid receptors regulate microglial cell migration. J Neurosci 23:1398–1405
Ashton JC, Friberg D, Darlington CL, Smith PF (2006) Expression of the cannabinoid CB2 receptor in the rat cerebellum: an immunohistochemical study. Neurosci Lett 396:113–116
Van Sickle MD, Duncan M, Kingsley PJ, Mouihate A, Urbani P, Mackie K, Stella N, Makriyannis A, Piomelli D, Davison JS, Marnett LJ, Di Marzo V, Pittman QJ, Patel KD, Sharkey KA (2005) Identification and functional characterization of brainstem cannabinoid CB2 receptors. Science 310:329–332
Gong JP, Onaivi ES, Ishiguro H, Liu QR, Tagliaferro PA, Brusco A, Uhl GR (2006) Cannabinoid CB2 receptors: immunohistochemical localization in rat brain. Brain Res 1071:10–23
Ibrahim MM, Porreca F, Lai J, Albrecht PJ, Rice FL, Khodorova A, Davar G, Makriyannis A, Vanderah TW, Mata HP, Malan TP Jr (2005) CB2 cannabinoid receptor activation produces antinociception by stimulating peripheral release of endogenous opioids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:3093–3098
Stander S, Schmelz M, Metze D, Luger T, Rukwied R (2005) Distribution of cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and 2 (CB2) on sensory nerve fibers and adnexal structures in human skin. J Dermatol Sci 38:177–188
Walczak JS, Pichette V, Leblond F, Desbiens K, Beaulieu P (2005) Behavioral, pharmacological and molecular characterization of the saphenous nerve partial ligation: a new model of neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 132:1093–1102
Walczak JS, Pichette V, Leblond F, Desbiens K, Beaulieu P (2006) Characterization of chronic constriction of the saphenous nerve, a model of neuropathic pain in mice showing rapid molecular and electrophysiological changes. J Neurosci Res 83:1310–1322
Beltramo M, Bernardini N, Bertorelli R, Campanella M, Nicolussi E, Fredduzzi S, Reggiani A (2006) CB2 receptor-mediated antihyperalgesia: possible direct involvement of neural mechanisms. Eur J Neurosci 23:1530–1538
Wotherspoon G, Fox A, McIntyre P, Colley S, Bevan S, Winter J (2005) Peripheral nerve injury induces cannabinoid receptor 2 protein expression in rat sensory neurons. Neuroscience 135:235–245
Ross RA, Gibson TM, Brockie HC, Leslie M, Pashmi G, Craib SJ, Di Marzo V, Pertwee RG (2001) Structure-activity relationship for the endogenous cannabinoid, anandamide, and certain of its analogues at vanilloid receptors in transfected cells and vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol 132:631–640
Price TJ, Helesic G, Parghi D, Hargreaves KM, Flores CM (2003) The neuronal distribution of cannabinoid receptor type 1 in the trigeminal ganglion of the rat. Neuroscience 120:155–162
Hanus L, Breuer A, Tchilibon S, Shiloah S, Goldenberg D, Horowitz M, Pertwee RG, Ross RA, Mechoulam R, Fride E (1999) HU-308: a specific agonist for CB(2), a peripheral cannabinoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:14228–14233
Malan TP Jr, Ibrahim MM, Deng H, Liu Q, Mata HP, Vanderah T, Porreca F, Makriyannis A (2001) CB2 cannabinoid receptor-mediated peripheral antinociception. Pain 93:239–245
Facci L, Dal Toso R, Romanello S, Buriani A, Skaper SD, Leon A (1995) Mast cells express a peripheral cannabinoid receptor with differential sensitivity to anandamide and palmitoylethanolamide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:3376–3380
Mazzari S, Canella R, Petrelli L, Marcolongo G, Leon A (1996) N-(2-hydroxyethyl)hexadecanamide is orally active in reducing edema formation and inflammatory hyperalgesia by down-modulating mast cell activation. Eur J Pharmacol 300:227–236
Calignano A, La Rana G, Giuffrida A, Piomelli D (1998) Control of pain initiation by endogenous cannabinoids. Nature 394:277–281
Jaggar SI, Hasnie FS, Sellaturay S, Rice AS (1998) The anti-hyperalgesic actions of the cannabinoid anandamide and the putative CB2 receptor agonist palmitoylethanolamide in visceral and somatic inflammatory pain. Pain 76:189–199
Farquhar-Smith WP, Jaggar SI, Rice AS (2002) Attenuation of nerve growth factor-induced visceral hyperalgesia via cannabinoid CB(1) and CB(2)-like receptors. Pain 97:11–21
Farquhar-Smith WP, Rice AS (2001) Administration of endocannabinoids prevents a referred hyperalgesia associated with inflammation of the urinary bladder. Anesthesiology 94:507–513 (discussion 6A)
Ibrahim MM, Rude ML, Stagg NJ, Mata HP, Lai J, Vanderah TW, Porreca F, Buckley NE, Makriyannis A, Malan TP Jr (2006) CB2 cannabinoid receptor mediation of antinociception. Pain 122:36–42
Valenzano KJ, Tafesse L, Lee G, Harrison JE, Boulet JM, Gottshall SL, Mark L, Pearson MS, Miller W, Shan S, Rabadi L, Rotshteyn Y, Chaffer SM, Turchin PI, Elsemore DA, Toth M, Koetzner L, Whiteside GT (2005) Pharmacological and pharmacokinetic characterization of the cannabinoid receptor 2 agonist, GW405833, utilizing rodent models of acute and chronic pain, anxiety, ataxia and catalepsy. Neuropharmacology 48:658–672
Huffman JW, Liddle J, Yu S, Aung MM, Abood ME, Wiley JL, Martin BR (1999) 3-(1′,1′-Dimethylbutyl)-1-deoxy-delta8-THC and related compounds: synthesis of selective ligands for the CB2 receptor. Bioorg Med Chem 7:2905–2914
Elmes SJ, Jhaveri MD, Smart D, Kendall DA, Chapman V (2004) Cannabinoid CB2 receptor activation inhibits mechanically evoked responses of wide dynamic range dorsal horn neurons in naive rats and in rat models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Eur J Neurosci 20:2311–2320
Rinaldi-Carmona M, Barth F, Millan J, Derocq JM, Casellas P, Congy C, Oustric D, Sarran M, Bouaboula M, Calandra B, Portier M, Shire D, Breliere JC, Le Fur GL (1998) SR 144528, the first potent and selective antagonist of the CB2 cannabinoid receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 284:644–650
Rinaldi-Carmona M, Barth F, Heaulme M, Alonso R, Shire D, Congy C, Soubrie P, Breliere JC, Le Fur G (1995) Biochemical and pharmacological characterisation of SR141716A, the first potent and selective brain cannabinoid receptor antagonist. Life Sci 56:1941–1947
Nackley AG, Makriyannis A, Hohmann AG (2003) Selective activation of cannabinoid CB(2) receptors suppresses spinal fos protein expression and pain behavior in a rat model of inflammation. Neuroscience 119:747–757
Whiteside GT, Gottshall SL, Boulet JM, Chaffer SM, Harrison JE, Pearson MS, Turchin PI, Mark L, Garrison AE, Valenzano KJ (2005) A role for cannabinoid receptors, but not endogenous opioids, in the antinociceptive activity of the CB2-selective agonist, GW405833. Eur J Pharmacol 528:65–72
Clayton N, Marshall FH, Bountra C, O’Shaughnessy CT (2002) CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors are implicated in inflammatory pain. Pain 96:253–260
Sanson M, Bueno L, Fioramonti J (2006) Involvement of cannabinoid receptors in inflammatory hypersensitivity to colonic distension in rats. Neurogastroenterol Motil 18:949–956
Jonsson KO, Persson E, Fowler CJ (2006) The cannabinoid CB2 receptor selective agonist JWH133 reduces mast cell oedema in response to compound 48/80 in vivo but not the release of beta-hexosaminidase from skin slices in vitro. Life Sci 78:598–606
Quartilho A, Mata HP, Ibrahim MM, Vanderah TW, Porreca F, Makriyannis A, Malan TP Jr (2003) Inhibition of inflammatory hyperalgesia by activation of peripheral CB2 cannabinoid receptors. Anesthesiology 99:955–960
Sokal DM, Elmes SJ, Kendall DA, Chapman V (2003) Intraplantar injection of anandamide inhibits mechanically-evoked responses of spinal neurones via activation of CB2 receptors in anaesthetised rats. Neuropharmacology 45:404–411
Guindon J, Desroches J, Beaulieu P (2007) The antinociceptive effects of intraplantar injections of 2-arachidonoyl glycerol are mediated by cannabinoid CB2 receptors. Br J Pharmacol 150:693–701
Jhaveri MD, Richardson D, Chapman V (2007) Endocannabinoid metabolism and uptake: novel targets for neuropathic and inflammatory pain. British Journal of Pharmacology, DOI 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707433
Brennan TJ, Vandermeulen EP, Gebhart GF (1996) Characterization of a rat model of incisional pain. Pain 64:493–501
LaBuda CJ, Koblish M, Little PJ (2005) Cannabinoid CB2 receptor agonist activity in the hindpaw incision model of postoperative pain. Eur J Pharmacol 527:172–174
Ramirez BG, Blazquez C, Gomez del Pulgar T, Guzman M, de Ceballos ML (2005) Prevention of Alzheimer’s disease pathology by cannabinoids: neuroprotection mediated by blockade of microglial activation. J Neurosci 25:1904–1913
Benito C, Nunez E, Tolon RM, Carrier EJ, Rabano A, Hillard CJ, Romero J (2003) Cannabinoid CB2 receptors and fatty acid amide hydrolase are selectively overexpressed in neuritic plaque-associated glia in Alzheimer’s disease brains. J Neurosci 23:11136–11141
Yiangou Y, Facer P, Durrenberger P, Chessell IP, Naylor A, Bountra C, Banati RR, Anand P (2006) COX-2, CB2 and P2X7-immunoreactivities are increased in activated microglial cells/macrophages of multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spinal cord. BMC Neurol 6:12
Maresz K, Carrier EJ, Ponomarev ED, Hillard CJ, Dittel BN (2005) Modulation of the cannabinoid CB2 receptor in microglial cells in response to inflammatory stimuli. J Neurochem 95:437–445
Zhang J, Hoffert C, Vu HK, Groblewski T, Ahmad S, O’Donnell D (2003) Induction of CB2 receptor expression in the rat spinal cord of neuropathic but not inflammatory chronic pain models. Eur J Neurosci 17:2750–2754
Scott DA, Wright CE, Angus JA (2004) Evidence that CB-1 and CB-2 cannabinoid receptors mediate antinociception in neuropathic pain in the rat. Pain 109:124–131
Ibrahim MM, Deng H, Zvonok A, Cockayne DA, Kwan J, Mata HP, Vanderah TW, Lai J, Porreca F, Makriyannis A, Malan TP Jr (2003) Activation of CB2 cannabinoid receptors by AM1241 inhibits experimental neuropathic pain: Pain inhibition by receptors not present in the CNS. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:10529–10533
Liu C, Walker JM (2006) Effects of a cannabinoid agonist on spinal nociceptive neurons in a rodent model of neuropathic pain. J Neurophysiol 96:2984–2994
Sagar DR, Kelly S, Millns PJ, O’Shaughnessey CT, Kendall DA, Chapman V (2005) Inhibitory effects of CB1 and CB2 receptor agonists on responses of DRG neurons and dorsal horn neurons in neuropathic rats. Eur J Neurosci 22:371–379
Patel HJ, Birrell MA, Crispino N, Hele DJ, Venkatesan P, Barnes PJ, Yacoub MH, Belvisi MG (2003) Inhibition of guinea-pig and human sensory nerve activity and the cough reflex in guinea-pigs by cannabinoid (CB2) receptor activation. Br J Pharmacol 140:261–268
Griffin G, Fernando SR, Ross RA, McKay NG, Ashford ML, Shire D, Huffman JW, Yu S, Lainton JA, Pertwee RG (1997) Evidence for the presence of CB2-like cannabinoid receptors on peripheral nerve terminals. Eur J Pharmacol 339:53–61
Wieseler-Frank J, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2005) Central proinflammatory cytokines and pain enhancement. Neurosignals 14:166–174
Tanga FY, Raghavendra V, DeLeo JA (2004) Quantitative real-time RT-PCR assessment of spinal microglial and astrocytic activation markers in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Neurochem Int 45:397–407
McMahon SB, Cafferty WB, Marchand F (2005) Immune and glial cell factors as pain mediators and modulators. Exp Neurol 192:444–462
Inoue A, Ikoma K, Morioka N, Kumagai K, Hashimoto T, Hide I, Nakata Y (1999) Interleukin-1beta induces substance P release from primary afferent neurons through the cyclooxygenase-2 system. J Neurochem 73:2206–2213
Stella N (2004) Cannabinoid signaling in glial cells. Glia 48:267–277
Zhang DX, Owens CM, Willis WD (1991) Two forms of inhibition of spinothalamic tract neurons produced by stimulation of the periaqueductal gray and the cerebral cortex. J Neurophysiol 65:1567–1579
Puffenbarger RA, Boothe AC, Cabral GA (2000) Cannabinoids inhibit LPS-inducible cytokine mRNA expression in rat microglial cells. Glia 29:58–69
Ortega-Gutierrez S, Molina-Holgado E, Guaza C (2005) Effect of anandamide uptake inhibition in the production of nitric oxide and in the release of cytokines in astrocyte cultures. Glia 52:163–168
Elmes SJ, Winyard LA, Medhurst SJ, Clayton NM, Wilson AW, Kendall DA, Chapman V (2005) Activation of CB1 and CB2 receptors attenuates the induction and maintenance of inflammatory pain in the rat. Pain 118:327–335
Acknowledgement
We would like to thank Wellcome Trust, Medical Research Council, Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council and GlaxoSmithKline for financial support towards the original research presented in this review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jhaveri and Sagar joint first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jhaveri, M.D., Sagar, D.R., Elmes, S.J.R. et al. Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor-Mediated Anti-nociception in Models of Acute and Chronic Pain. Mol Neurobiol 36, 26–35 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-007-8007-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-007-8007-7