Abstract
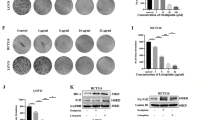
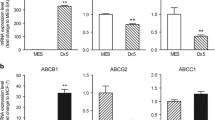
Oxaliplatin is a member of platinum-based chemotherapy drugs frequently used in colorectal cancer (CRC). However, resistance to oxaliplatin causes tumor progression and metastasis. Akt1 and Gpx4 are essential regulator genes of apoptosis and ferroptosis pathways. Inhibition of these genes might eradicate oxaliplatin resistance in resistant CRC cells. We compared two cell death strategies to reverse drug resistance in Caco-2 and HT-29 oxaliplatin-resistant cell lines. We used the AKT1-specific siRNA to induce apoptosis. Also, GPX4-specific siRNA and FIN56 were utilized to generate ferroptosis. The effect of these treatments was assessed by reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation, cell viability, and protein expression level assays. Besides, the expression of GPX4, CoQ10, and NRF2 was assessed in both cell lines after treatments. Correctly measuring the expression of these responsible genes and proteins confirms the occurrence of different types of cell death. In addition, the ability of Akt1/ GPX4 siRNA in resensitizing HT-29 and Caco-2 oxaliplatin resistance cells was evaluated. Our finding showed that the upregulation of GPX4/siRNA caused a reduction in GPX4 and CoQ10 expressions in both cell lines. However, the expression level of NRF2 showed the same level in our cell lines, so we observed a downregulation of NRF2 in resistant CRC cell lines. Cell viability assay indicated that induction of ferroptosis by GPX4/siRNA or FIN56 and apoptosis by Akt1/siRNA in resistant cell lines could reverse the oxaliplatin resistance. We concluded that downregulation of Akt1 or Gpx4 could increase the efficacy of oxaliplatin to overcome the resistance compared to FIN56.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Rawla P, Sunkara T, Barsouk A. Epidemiology of colorectal cancer: incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Gastroenterology Review. 2019;14(2):89–103.
Quiroz-Reyes AG, Islas JF, Delgado-Gonzalez P, Franco-Villarreal H, Garza-Treviño EN. Therapeutic approaches for metastases from colorectal cancer and pancreatic ductal carcinoma. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(1):103.
Zhang W, Zhu Y, Yu H, Liu X, Jiao B, Lu X. Libertellenone H, a natural pimarane diterpenoid, inhibits thioredoxin system and induces ROS-mediated apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. Molecules. 2021;26(2):315.
Abraham JP, Magee D, Cremolini C, Antoniotti C, Halbert DD, Xiu J, Stafford P, Berry DA, Oberley MJ, Shields AF, Marshall JL, Salem ME, Falcone A, Grothey A, Hall MJ, Venook AP, Lenz H-J, Helmstetter A, Korn WM, Spetzler DB. Clinical validation of a machine-learning–derived signature predictive of outcomes from first-line oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in advanced colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(4):1174–83.
Andreidesz K, Koszegi B, Kovacs D, Vantus VB, Gallyas F, Kovacs K. Effect of oxaliplatin, olaparib and LY294002 in combination on triple-negative breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):2056.
Hannani D, Ma Y, Yamazaki T, Déchanet-Merville J, Kroemer G, Zitvogel L. Harnessing γδ T cells in anticancer immunotherapy. Trends Immunol. 2012;33(5):199–206.
Wang X, Li M, Ren K, Xia C, Li J, Yu Q, Qiu Y, Lu Z, Long Y, Zhang Z, He Q. On-demand autophagy cascade amplification nanoparticles precisely enhanced oxaliplatin-induced cancer immunotherapy. Adv Mater. 2020;32(32):2002160.
Bruno PM, Liu Y, Park GY, Murai J, Koch CE, Eisen TJ, Pritchard JR, Pommier Y, Lippard SJ, Hemann MT. A subset of platinum-containing chemotherapeutic agents kills cells by inducing ribosome biogenesis stress. Nat Med. 2017;23(4):461–71.
Wang Z. Drug resistance and novel therapies in cancers in 2019. Cancers. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040924.
Bukowski K, Kciuk M, Kontek R. Mechanisms of multidrug resistance in cancer chemotherapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(9):3233.
Kim YE, Kim E-K, Song M-J, Kim T-Y, Jang HH, Kang D. SILAC-based quantitative proteomic analysis of oxaliplatin-resistant pancreatic cancer cells. Cancers. 2021;13(4):724.
Wang Y, Lu J-H, Wang F, Wang Y-N, He M-M, Wu Q-N, Lu Y-X, Yu H-E, Chen Z-H, Zhao Q, Liu J, Chen Y-X, Wang D-S, Sheng H, Liu Z-X, Zeng Z-L, Xu R-H, Ju H-Q. Inhibition of fatty acid catabolism augments the efficacy of oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancers. Cancer Lett. 2020;473:74–89.
Han J, Sun W, Liu R, Zhou Z, Zhang H, Chen X, Ba Y. Plasma exosomal miRNA expression profile as oxaliplatin-based chemoresistant biomarkers in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.01495.
Huang H, Aladelokun O, Ideta T, Giardina C, Ellis LM, Rosenberg DW. Inhibition of PGE2/EP4 receptor signaling enhances oxaliplatin efficacy in resistant colon cancer cells through modulation of oxidative stress. Sci Rep. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-40848-4.
Pereira DM, Gomes SE, Borralho PM, Rodrigues CMP. MEK5/ERK5 activation regulates colon cancer stem-like cell properties. Cell Death Discovery. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-019-0150-1.
Combes E, Andrade AF, Tosi D, Michaud HA, Coquel F, Garambois V, Desigaud D, Jarlier M, Coquelle A, Pasero P, Bonnefoy N, Moreaux J, Martineau P, Rio MD, Beijersbergen RL, Vezzio-Vie N, Gongora C. Inhibition of ataxia-telangiectasia mutated and RAD3-related (ATR) overcomes oxaliplatin resistance and promotes antitumor immunity in colorectal cancer. Can Res. 2019;79(11):2933–46.
Li L, Jian S, Yupeng Z, Liu S, Yanan P, Zhou Z, Pan H, Xiaobing W, Chen L, Zhao Q. MEG3 is a prognostic factor for CRC and promotes chemosensitivity by enhancing oxaliplatin-induced cell apoptosis. Oncol Rep. 2017;38(3):1383–92.
Lin L, Li X, Pan C, Lin W, Shao R, Liu Y, Zhang J, Luo Y, Qian K, Shi M, Bin J, Liao Y, Liao W. ATXN2L upregulated by epidermal growth factor promotes gastric cancer cell invasiveness and oxaliplatin resistance. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(3):1–13.
Liu R, Chen Y, Liu G, Li C, Song Y, Cao Z, Li W, Hu J, Lu C, Liu Y. PI3K/AKT pathway as a key link modulates the multidrug resistance of cancers. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(9):1–12.
Nakayama H, Ikebe T, Beppu M, Shirasuna K. High expression levels of nuclear factor κB IκB kinase α and Akt kinase in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Cancer. 2001;92(12):3037–44.
Chen SJ, Kuo CC, Pan HY, Tsou TC, Yeh SC, Chang JY. Desferal regulates hCtr1 and transferrin receptor expression through Sp1 and exhibits synergistic cytotoxicity with platinum drugs in oxaliplatin-resistant human cervical cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget. 2016;7(31):49310–21.
Chen Y, Deng G, Fu Y, Han Y, Guo C, Yin L, Cai C, Shen H, Wu S, Zeng S. <p>FOXC2 Promotes Oxaliplatin Resistance by Inducing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via MAPK/ERK Signaling in Colorectal Cancer</p>. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:1625–35.
Roh JL, Kim EH, Jang HJ, Park JY, Shin D. Induction of ferroptotic cell death for overcoming cisplatin resistance of head and neck cancer. Lett. 2016;381(1):96–103.
Luo E-F, Li H-X, Qin Y-H, Qiao Y, Yan G-L, Yao Y-Y, Li L-Q, Hou J-T, Tang C-C, Wang D. Role of ferroptosis in the process of diabetes-induced endothelial dysfunction. World J Diabetes. 2021;12(2):124.
Friedmann Angeli JP, Krysko DV, Conrad M. Ferroptosis at the crossroads of cancer-acquired drug resistance and immune evasion. Nat Rev Cancer. 2019;19(7):405–14.
Yang WS, Sriramaratnam R, Welsch ME, Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, Cheah JH, Clemons PA, Shamji AF, Clish CB, Brown LM, Girotti AW, Cornish VW, Schreiber SL, Stockwell BR. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. 2014;156(1–2):317–31.
Lei P, Bai T, Sun Y. Mechanisms of ferroptosis and relations with regulated cell death: a review. Front Physiol. 2019;10:139.
Gheytanchi E, Naseri M, Karimi-Busheri F, Atyabi F, Mirsharif ES, Bozorgmehr M, Ghods R, Madjd Z. Morphological and molecular characteristics of spheroid formation in HT-29 and Caco-2 colorectal cancer cell lines. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-021-01898-9.
Trajkovic V, Mukherjee S, Dash S, Lohitesh K, Chowdhury R. The dynamic role of autophagy and MAPK signaling in determining cell fate under cisplatin stress in osteosarcoma cells. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(6):e0179203.
Dabkeviciene D, Jonusiene V, Zitkute V, Zalyte E, Grigaitis P, Kirveliene V, Sasnauskiene A. The role of interleukin-8 (CXCL8) and CXCR2 in acquired chemoresistance of human colorectal carcinoma cells HCT116. Med Oncol. 2015;32(12):258.
Kukcinaviciute E, Jonusiene V, Sasnauskiene A, Dabkeviciene D, Eidenaite E, Laurinavicius A. Significance of Notch and Wnt signaling for chemoresistance of colorectal cancer cells HCT116. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(7):5913–20.
Steckiewicz KP, Barcinska E, Malankowska A, Zauszkiewicz-Pawlak A, Nowaczyk G, Zaleska-Medynska A, Inkielewicz-Stepniak I. Impact of gold nanoparticles shape on their cytotoxicity against human osteoblast and osteosarcoma in in vitro model. Evaluation of the safety of use and anti-cancer potential. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(2):22.
Rahbar Saadat Y, Yari Khosroushahi A, Movassaghpour AA, Talebi M, PourghassemGargari B. Modulatory role of exopolysaccharides of Kluyveromyces marxianus and Pichia kudriavzevii as probiotic yeasts from dairy products in human colon cancer cells. J Func Foods. 2020;64:103675.
VakiliSaatloo M, Aghbali AA, Koohsoltani M, Yari Khosroushahi A. Akt1 and Jak1 siRNA based silencing effects on the proliferation and apoptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Gene. 2019;714:143997.
Avelar-Freitas BA, Almeida VG, Pinto MCX, Mourão FAG, Massensini AR, Martins-Filho OA, Rocha-Vieira E, Brito-Melo GEA. Trypan blue exclusion assay by flow cytometry. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2014;47(4):307–15.
Rawla P, Sunkara T, Barsouk A. Epidemiology of colorectal cancer: Incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Przeglad gastroenterologiczny. 2019;14(2):89.
Kawai S, Takeshima N, Hayasaka Y, Notsu A, Yamazaki M, Kawabata T, Yamazaki K, Mori K, Yasui H. Comparison of irinotecan and oxaliplatin as the first-line therapies for metastatic colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 2021;21(1):1–11.
Wang Y, Zhang D, Li Y, Fang F. MiR-138 Suppresses the PDK1 expression to decrease the oxaliplatin resistance of colorectal cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:3607.
Song R, Tian K, Wang W, Wang L. P53 suppresses cell proliferation, metastasis, and angiogenesis of osteosarcoma through inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Int J Surg. 2015;20:80–7.
Somanath PR, Razorenova OV, Chen J, Byzova TV. Akt1 in endothelial cell and angiogenesis. Cell Cycle. 2006;5(5):512–8.
Koseoglu S, Lu Z, Kumar C, Kirschmeier P, Zou J. AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3-dependent cell survival is cell line-specific and knockdown of all three isoforms selectively induces apoptosis in 20 human tumor cell lines. Cancer Biol Ther. 2007;6(5):755–62.
Garofalo M, Quintavalle C, Zanca C, De Rienzo A, Romano G, Acunzo M, Puca L, Incoronato M, Croce CM, Condorelli G. Akt regulates drug-induced cell death through Bcl-w downregulation. PLoS ONE. 2008;3(12):e4070.
Han Z, Hong L, Wu K, Han S, Shen H, Liu C, Han Y, Liu Z, Han Y, Fan D. Reversal of multidrug resistance of gastric cancer cells by downregulation of Akt1 with Akt1 siRNA. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2006;25(4):601.
Dai Y, Jin S, Li X, Wang D. The involvement of Bcl-2 family proteins in AKT-regulated cell survival in cisplatin resistant epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(1):1354.
Letai A. Cell death and cancer therapy: don’t forget to kill the cancer cell. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1204.
Zou Z, Chang H, Li H, Wang S. Induction of reactive oxygen species: an emerging approach for cancer therapy. Apoptosis. 2017;22(11):1321–35.
L. Nonnenmacher, S. Hasslacher, J. Zimmermann, G. Karpel-Massler, K. La Ferla-Brühl, S.E. Barry, T. Burster, M.D. Siegelin, O. Brühl, M.E. Halatsch, K.M. Debatin, M.A. Westhoff, Cell Death Induction in Cancer Therapy− Past, Present, and Future, Critical Reviews™ in Oncogenesis 21(3–4) (2016).
Yu H, Yang C, Jian L, Guo S, Chen R, Li K, Qu F, Tao K, Fu Y, Luo F, Liu S. Sulfasalazine-induced ferroptosis in breast cancer cells is reduced by the inhibitory effect of estrogen receptor on the transferrin receptor. Oncol Rep. 2019;42(2):826–38.
Conrad M, Friedmann Angeli JP. Glutathione peroxidase 4 (Gpx4) and ferroptosis: what’s so special about it? Mol Cell Oncol. 2015;2(3):e995047.
Eaton JK, Furst L, Ruberto RA, Moosmayer D, Hilpmann A, Ryan MJ, Zimmermann K, Cai LL, Niehues M, Badock V, Kramm A, Chen S, Hillig RC, Clemons PA, Gradl S, Montagnon C, Lazarski KE, Christian S, Bajrami B, Neuhaus R, Eheim AL, Viswanathan VS, Schreiber SL. Selective covalent targeting of GPX4 using masked nitrile-oxide electrophiles. Nat Chem Biol. 2020;16(5):497–506.
Forcina GC, Dixon SJ. GPX4 at the crossroads of lipid homeostasis and ferroptosis. Proteomics. 2019;19(18):1800311.
Shimada K, Skouta R, Kaplan A, Yang WS, Hayano M, Dixon SJ, Brown LM, Valenzuela CA, Wolpaw AJ, Stockwell BR. Global survey of cell death mechanisms reveals metabolic regulation of ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol. 2016;12(7):497–503.
Funding
This project is part of a Ph.D. thesis (grant No. 59305) and Pharm.D. thesis (grant No.64435), funded by Drug Applied Research Center, Faculty of Pharmacy, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MG performed experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the paper. HRH supervised the research, analyzed the data, and prepared the manuscript; AAA performed experiments and analyzed the data. YF provided a resistance cell line and prepared a manuscript. MT served flow cytometry and analyzed its data. AYK designed the investigation and then led and supervised the project.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no significant competing financial, professional, or personal interests that might have influenced the performance or presentation of the work described in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
There is no involvement of humans or animals in this study.
Consent for publication
All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Golbashirzadeh, M., Heidari, H.R., Aghamolayi, A.A. et al. In vitro siRNA-mediated GPX4 and AKT1 silencing in oxaliplatin resistance cancer cells induces ferroptosis and apoptosis. Med Oncol 40, 279 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-02130-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-02130-6