Abstract
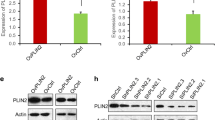
Low-density lipoprotein receptor class A domain containing 2 (LDLRAD2) acts as a protein-coding gene in a large number of human diseases. However, the potential roles and underlying mechanism in pancreatic cancer remains unclear. Therefore, this study was conducted to address this question. Herein, we found that the expression of LDLRAD2 was elevated in pancreatic cancer tissues and cell lines. LDLRAD2 knockdown inhibited pancreatic cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro. Besides, silencing LDLRAD2 impaired tumor growth and metastasis in vivo and up-regulated the E-Cadherin level, whereas down-regulated the expression of N-Cadherin and Vimentin levels, which indicating that LDLRAD2 knockdown suppresses EMT. Additionally, LDLRAD2 knockdown decreased the Warburg effect and glycolytic enzymes expression. Pathway scan assay and western blotting assay indicated that LDLRAD2 knockdown significantly down-regulated the expression of phosphorylation of Akt and phosphorylation of mTOR, which suggested that knockdown of LDLRAD2 inhibits Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Taken together, these findings suggested that LDLRAD2 may be an oncogene in pancreatic cancer via modulating Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maitra A. Pancreatic cancer hidden in plain sight. Nature. 2020;581(7806):34–5.
Kozlowski MR, Kozlowski RE. A novel, small peptide with activity against human pancreatic cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2020;10(5):1356–65.
Ye J, et al. PRDM3 attenuates pancreatitis and pancreatic tumorigenesis by regulating inflammatory response. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(3):187.
Menini S, et al. Diabetes promotes invasive pancreatic cancer by increasing systemic and tumour carbonyl stress in Kras(G12D/+) mice. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):152.
Wei Y, et al. LDLRAD2 overexpression predicts poor prognosis and promotes metastasis by activating Wnt/beta-catenin/EMT signaling cascade in gastric cancer. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(20):8951–68.
Kuwada K, et al. The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition induced by tumor-associated macrophages confers chemoresistance in peritoneally disseminated pancreatic cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37(1):307.
Wang C, Yin W, Liu H. MicroRNA-10a promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness maintenance of pancreatic cancer stem cells via upregulating the Hippo signaling pathway through WWC2 inhibition. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(11):4505–21.
Li M, et al. miR-193a-5p promotes pancreatic cancer cell metastasis through SRSF6-mediated alternative splicing of OGDHL and ECM1. Am J Cancer Res. 2020;10(1):38–59.
Xu M, et al. miR-22 suppresses epithelial–mesenchymal transition in bladder cancer by inhibiting Snail and MAPK1/Slug/vimentin feedback loop. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(2):209.
Yoshida J, et al. Metformin inhibits TGFbeta1-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition and liver metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2020;44(1):371–81.
Shen L, et al. Metabolic reprogramming in triple-negative breast cancer through Myc suppression of TXNIP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(17):5425–30.
Cairns RA, Harris IS, Mak TW. Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11(2):85–95.
Cantor JR, Sabatini DM. Cancer cell metabolism: one hallmark, many faces. Cancer Discov. 2012;2(10):881–98.
Qiao S, et al. REDD1 loss reprograms lipid metabolism to drive progression of RAS mutant tumors. Genes Dev. 2020;34(11–12):751–66.
Warburg O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science. 1956;123(3191):309–14.
Ji S, et al. FBW7 (F-box and WD Repeat Domain-Containing 7) negatively regulates glucose metabolism by targeting the c-Myc/TXNIP (Thioredoxin-Binding Protein) axis in pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22(15):3950–60.
Carmona-Fontaine C, et al. Emergence of spatial structure in the tumor microenvironment due to the Warburg effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(48):19402–7.
Ye H, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages promote progression and the Warburg effect via CCL18/NF-kB/VCAM-1 pathway in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(5):453.
Zhang M, et al. SOCS5 inhibition induces autophagy to impair metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(8):612.
Su CC. Tanshinone IIA can inhibit MiaPaCa2 human pancreatic cancer cells by dual blockade of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways. Oncol Rep. 2018;40(5):3102–11.
Xu X, et al. Indole-2-carboxamide derivative LG25 inhibits triple-negative breast cancer growth by suppressing Akt/mTOR/NF-kappaB signalling pathway. Drug Des Dev Ther. 2019;13:3539–50.
Li J, et al. OTUB2 stabilizes U2AF2 to promote the Warburg effect and tumorigenesis via the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Theranostics. 2019;9(1):179–95.
Yan X, et al. Knockdown of KRT17 decreases osteosarcoma cell proliferation and the Warburg effect via the AKT/mTOR/HIF1alpha pathway. Oncol Rep. 2020;44(1):103–14.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by Youth Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (#20202BAB216027), Jiangxi Provincial Education Fund Project (#701223001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Huang, W., Han, Q. et al. LDLRAD2 promotes pancreatic cancer progression through Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Med Oncol 38, 2 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-020-01451-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-020-01451-0