Abstract
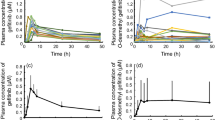
The objective of this study was to explore the relationship between gefitinib exposure and clinical outcome in gefitinib-treated patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Thirty patients participated in this pharmacokinetic study and received 250-mg oral doses of gefitinib once daily. Blood samples were collected before dosing and on days 7, 14, 21, and 28. The plasma concentrations of gefitinib were evaluated using a validated high-performance liquid chromatographic method with tandem mass spectrometric detection. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to determine predictive factors for response and survival of patients. EGFR mutations were analyzed retrospectively. Median survival time (MST) was 9.97 months (95%CI 2.79–17.14 months). The geometric mean trough gefitinib plasma concentration (C ssmin ) was 266 ng/ml (range 94–538 ng/ml). In the multivariate analysis, only skin rash was associated with gefitinib-induced disease control (P = 0.017); Adenocarcinoma, skin rash, and ‘high’ C ssmin (C ssmin ≥ 200 ng/ml) were independently associated with overall survival (P = 0.004, 0.028,0.007, respectively). MST of EGFR wild-type patients with ‘high’ C ssmin was longer than that with ‘low’ C ssmin (P = 0.002). Our study results show that pharmacokinetic variability may also account for the different outcomes following treatment with gefitinib for patients with wild-type EGFR. Further studies are needed to confirm these results.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–39.
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–500.
Cappuzzo F, Hirsch FR, Rossi E, Bartolini S, Ceresoli GL, Bemis L, Haney J, Witta S, Danenberg K, Domenichini I, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor gene and protein and gefitinib sensitivity in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97:643–55.
Hirsch FR, Varella-Garcia M, McCoy J, West H, Xavier AC, Gumerlock P, Bunn PA Jr, Franklin WA, Crowley J, Gandara DR. Increased epidermal growth factor receptor gene copy number detected by fluorescence in situ hybridization associates with increased sensitivity to gefitinib in patients with bronchioloalveolar carcinoma subtypes: a Southwest Oncology Group Study. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:6838–45.
Swaisland HC, Smith RP, Laight A, Kerr DJ, Ranson M, Wilder-Smith CH, Duvauchelle T. Single-dose clinical pharmacokinetic studies of gefitinib. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2005;44:1165–77.
Jones HK, Stafford LE, Swaisland HC, Payne R. A sensitive assay for ZD1839 (Iressa) in human plasma by liquid-liquid extraction and high performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometric detection: validation and use in Phase I clinical trials. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2002;29:221–8.
Han SW, Kim TY, Hwang PG, Jeong S, Kim J, Choi IS, Oh DY, Kim JH, Kim DW, Chung DH, et al. Predictive and prognostic impact of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2493–501.
Bai H, Mao L, Wang HS, Zhao J, Yang L, An TT, Wang X, Duan CJ, Wu NM, Guo ZQ, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in plasma DNA samples predict tumor response in Chinese patients with stages IIIB to IV non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:2653–9.
Albanell J, Rojo F, Averbuch S, Feyereislova A, Mascaro JM, Herbst R, LoRusso P, Rischin D, Sauleda S, Gee J, et al. Pharmacodynamic studies of the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor ZD1839 in skin from cancer patients: histopathologic and molecular consequences of receptor inhibition. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:110–24.
Baselga J, Rischin D, Ranson M, Calvert H, Raymond E, Kieback DG, Kaye SB, Gianni L, Harris A, Bjork T, et al. Phase I safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic trial of ZD1839, a selective oral epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with five selected solid tumor types. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:4292–302.
Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, Tamura T, Nakagawa K, Douillard JY, Nishiwaki Y, Vansteenkiste J, Kudoh S, Rischin D, et al. Multi-institutional randomized phase II trial of gefitinib for previously treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (The IDEAL 1 Trial) [corrected]. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:2237–46.
Giaccone G, Herbst RS, Manegold C, Scagliotti G, Rosell R, Miller V, Natale RB, Schiller JH, Von Pawel J, Pluzanska A, et al. Gefitinib in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase III trial–INTACT 1. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:777–84.
Herbst RS, Giaccone G, Schiller JH, Natale RB, Miller V, Manegold C, Scagliotti G, Rosell R, Oliff I, Reeves JA, et al. Gefitinib in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase III trial–INTACT 2. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:785–94.
Swaisland HC, Cantarini MV, Fuhr R, Holt A. Exploring the relationship between expression of cytochrome P450 enzymes and gefitinib pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2006;45:633–44.
Li J, Karlsson MO, Brahmer J, Spitz A, Zhao M, Hidalgo M, Baker SD. CYP3A phenotyping approach to predict systemic exposure to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:1714–23.
Ranson M, Wardell S. Gefitinib, a novel, orally administered agent for the treatment of cancer. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2004;29:95–103.
Li J, Zhao M, He P, Hidalgo M, Baker SD. Differential metabolism of gefitinib and erlotinib by human cytochrome P450 enzymes. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:3731–7.
Lu JES, Lum BL, Hamilton M, Rakhit A, Gaudreault J. A population pharmacokinetic (PK) model for erlotinib (E), a small molecule inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) [abstract 2032]. JClin Oncol. 2005;23:143s.
Lu JF, Eppler SM, Wolf J, Hamilton M, Rakhit A, Bruno R, Lum BL. Clinical pharmacokinetics of erlotinib in patients with solid tumors and exposure-safety relationship in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006;80:136–45.
Hamilton M, Wolf JL, Rusk J, Beard SE, Clark GM, Witt K, Cagnoni PJ. Effects of smoking on the pharmacokinetics of erlotinib. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:2166–71.
Hamilton M, Wolf JL, Zborowski D. Tarceva2 (erlotinib) exposure/effects (EE) analysis from a phase III study in advanced NSCLC: effect of smoking on the PK of erlotinib [abstract 6165]. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2005;46:1451.
Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, Doherty J, Politi K, Sarkaria I, Singh B, Heelan R, Rusch V, Fulton L, et al. EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from “never smokers” and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:13306–11.
Shigematsu H, Lin L, Takahashi T, Nomura M, Suzuki M, Wistuba II, Fong KM, Lee H, Toyooka S, Shimizu N, et al. Clinical and biological features associated with epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations in lung cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97:339–46.
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. Dave Clarke and Mr. Paul Martin from Research & Development Department of AstraZeneca Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., at Alderly Park, Great Britain, for their technical assistance in Gefitinib PK analysis. We also thank all patients and their families for their participation in this study. Our study was funded by Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China(07001532).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Y.-Y. Zhao and S. Li contributed equally to this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, YY., Li, S., Zhang, Y. et al. The relationship between drug exposure and clinical outcomes of non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib. Med Oncol 28, 697–702 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9541-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9541-0